当前位置:网站首页>Smart grid overview
Smart grid overview
2022-07-08 01:08:00 【Intelligent control and optimization decision Laboratory of Cen】
Smart grid
Definition of smart grid
Smart grid is the intellectualization of power grid , Also known as “ Power grid 2.0”, It is based on the physical power grid , Advanced sensing and measurement technology 、 Information and communication technology 、 Computer technology and control technology are highly integrated with the original power grid infrastructure to form a new power grid , It is monitored , Protect and automatically optimize the operation of internal components , Realize grid flexibility 、 clean 、 Security 、 economic 、 Friendly goals , To achieve the optimal management of the entire power system operation .
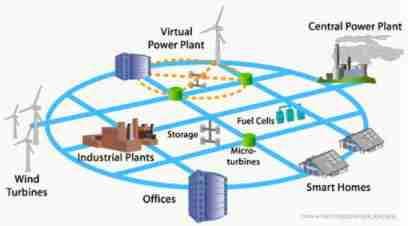
Smart grid “ intelligence ” Mainly reflected in four aspects :
- Observable
Use measurements , Sensing technology for power generation , Electricity transmission , Power transformation , distribution , Observe the state of key components in the process of power consumption , Realize the visualization of the whole process
- Controllable
Use the observed state information , Control the working state of key components of the power grid
- Adaptive and self-healing
Realize the automatic optimization of power grid , Reduce human intervention
- Real time analysis
From data to information , Form a two-way flow of digital information , Build a bridge between the power grid and user terminals
In the current era , The proposal of smart grid has its specific purpose , There are mainly the following aspects :
- From the perspective of environment
The situation of global warming is becoming increasingly serious , Environmental protection issues have attracted worldwide attention . Smart grid on the one hand through Introduce distributed power supply and energy storage equipment , Many different types of energy ( Especially wind energy , Renewable energy such as solar energy ) Incorporated into the power grid , Promote energy conservation, emission reduction and sustainable development , On the other hand, by Two way interaction between power grid and end users strengthens demand side management , Reduce energy waste
- Social perspective
With the development of communication and information technology , Digital technology is popularized in life . Digital society puts forward higher requirements for power supply reliability and power quality of power grid . On the one hand, smart grid can Compatible with a variety of energy , Ensure power quality through reasonable scheduling optimization , On the other hand, use two-way information flow , Form monitoring 、 control 、 maintain 、 Management and other information systems , Improve the reliability of power supply
- From the perspective of the power grid itself
First , With the development of society , The scale of electricity consumption is expanded , The security problem of large-scale operation of power grid is becoming increasingly serious . secondly , With the improvement of environmental awareness , Power companies began to seek ways different from traditional ways to meet the balance of supply and demand . Smart grid, on the one hand, through a large number of smart devices , Monitor the working status of internal key components in real time , Forecast failure , Improve the overall visualization of the system , Realize the safe and stable operation of the large system , On the other hand, through advanced marketization and demand side management , stay Try to meet the premise of supply and demand balance , Reduce the waste of fixed capital and energy
The functional characteristics of smart grid
- self-healing
The smart grid controls the operation state of the power grid in real time , Discover in time 、 Quickly diagnose and eliminate hidden trouble ; stay Try to minimize human intervention Next , Quickly isolate faults 、 Self recovery , Avoid large-scale power failure
- Safe and reliable
Whether the power system is under external attack , Or end-user behavior changes , Smart grid can Find problems through instant information exchange and take measures quickly , Reduce the resulting damage to the power system
- compatible
The traditional power grid is mainly for centralized power generation , And smart grid also supports The access of distributed generation and the large-scale application of renewable energy , Meet electricity and natural environment 、 The requirements of harmonious social and economic development
- Interaction coordination
The power grid interacts with user equipment and behavior in operation , To meet the needs of customers with the best power quality and power supply reliability . System operation and wholesale 、 Seamless connection of retail electricity market , meanwhile Through market transactions, we can better encourage the main body of the power market to participate in the power grid security management , So as to improve the safe operation level of the power system
- Cost effective
Introduce advanced information and monitoring technology , Optimize resource allocation , Improve equipment transmission capacity and utilization ; stay Timely dispatch between different areas , Balance the power supply gap ; Requirements to support competition in the electricity market , Implement a dynamic floating electricity price system , Improve the utilization efficiency of individual assets . Realize the optimization of network operation as a whole , Reduce maintenance costs and investment
- High quality
adopt Reasonable allocation to ensure power quality , Provide a variety of quality / Price plan Realize differential pricing of power quality
- Integrate
The information system . Implementation include monitor 、 control 、 maintain 、 Comprehensive integration between management and other types of information systems , And realize business integration on this basis
| Smart grid | Traditional power grid | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy types | Multi energy compatibility | coal , oil , Mainly non renewable energy such as natural gas |
| Power generation mode | Centralized and distributed compatibility | Centralized power generation |
| Characteristics of electricity market | Integrate , mature | monopoly , closed |
| Power quality | guaranteed | No guarantee |
| Economic performance | Reduce environmental pollution , Optimize asset management , High economic benefits | Environmental pollution is serious , Low energy efficiency , Low economic benefits |
| Immunity ( self-healing ) | Real time prediction and analysis , Preventive control , Prevent power failure | Trip protection in case of disturbance |
| Resistance to attacks and disasters | Sensor warning , Continuous monitoring , Strong self-healing ability , Have certain resistance | Weak resistance |
| Communications | two-way | None or one-way |
The key technology of smart grid
The key technologies of smart grid mainly focus on four aspects : Advanced measurement system (Advanced Metering Infrastructure,AMI), Advanced power distribution operation (Advanced Distribution Operation,ADO), Advanced transmission operation (Advanced Transmission Operations,ATO) and Senior asset management (Advanced Asset Management,AAM).AMI The main function of is to authorize users , Connect the system with the load , Enable users to support the operation of the power grid ;ADO It can make the power grid realize self-healing function ;ATO Emphasize congestion management , And reduce the risk of large-scale outage ;AAM And AMI、ADO and ATO The integration of will greatly improve the operation of the power grid and the efficiency of asset utilization . Combine these four aspects , The main key technologies are :
- Advanced power electronic equipment
Power electronic equipment is AMI,ADO,ATO and AAM Key components in , stay Electricity generation 、 Electricity transmission 、 The whole process of power distribution and consumption plays an important role . Almost all power electronic devices used in modern power systems use fully controlled high-power power electronic devices and various new high-performance multi-level high-power converter topologies . The quality of power electronic equipment determines the quality of power grid
- Strong and flexible network topology
Firm 、 Flexible power grid structure is the foundation of smart grid in the future . Especially for ADO and ATO for , The network topology will determine the upper limit of its operation efficiency . From an environmental point of view , Power grid planning needs to consider the imbalance of energy distribution , While saving project investment, we should also take into account the ecological environment . From a social point of view , It is necessary to consider the productivity differences in different regions and analyze the power demand of local development , Allocate resources reasonably . From the perspective of power grid , With the expansion of the power grid , The formation of interconnected power grids , The security problem of power grid is becoming more and more prominent , The planning requirements for the main network architecture are correspondingly improved . Only a flexible power grid structure can cope with the ice disaster 、 War and other sudden disasters
- to open up 、 standard 、 Integrated communication system
Smart grid needs the ability to monitor and analyze the current state of the system in real time . It includes the prediction ability of identifying early symptoms of faults , It also includes the ability to respond to disturbances that have occurred . The communication system of smart grid plays a vital role . First , To strengthen the two-way interaction between power grid and users , Enhance demand side management , It is necessary to build an open communication system ; secondly , At present, communication technology is developing rapidly , Each company has its own standard , For the convenience of operation and management , Unified communication standards should be stipulated ; Last A highly integrated communication system will better interact with information , It is convenient for operation optimization
- Renewable energy and distributed energy access
Renewable energy and distributed energy will transmit electricity to the grid , Power distribution provides more options , Improve asset utilization , Energy conservation and emissions reduction , Promote sustainable development . But this also puts forward higher requirements for the current technology , from AMI angle , wind 、 Renewable energy such as solar energy is unevenly distributed in geographical location , And vulnerable to weather , The adjustable capacity of the generator is relatively weak , Wind power plant planning and operation research put forward higher requirements for the accuracy and calculation speed of wind farm dynamic model ; from ADO and ATO angle , Wind and solar energy are important components of distributed energy , all It has the characteristics of volatility and intermittency , Power transmission to the grid , The reliability of power distribution causes impact
- Intelligent scheduling technology
Intelligent dispatching is the inevitable trend of power grid development in the future , The ultimate goal of intelligent scheduling is Establish a new theory and technology of network protection and emergency control integration based on wide area synchronous information , Coordinate the protection and control of power system components 、 Regional stability control system and other comprehensive defense systems with multiple security lines . Intelligent scheduling The core is online real-time decision-making , The goal is disaster prevention . The key technologies of intelligent scheduling are :
- System fast simulation and simulation
- Intelligent early warning technology
- Optimized scheduling technology
- Prevention and control technology , Accident handling and accident recovery technology ( Such as intelligent identification and recovery of power grid faults )
- Intelligent data mining technology
- Visualization technology of scheduling decision
- Advanced measurement system and demand side management
The advanced metering system consists of smart meters installed at the user end 、 The measurement data management system located in the power company (MDMS) And the communication system connecting them . The intellectualization of the power grid requires the power supply institution to accurately know the power consumption law of users , So as to try to achieve a balance between supply and demand . Advanced measurement system needs to realize remote monitoring 、 Faster and accurate system response for time of use tariff and user side management
Challenges faced by smart grid
- Smart devices
Smart grid relies on a large number of embedded intelligent devices to monitor and control the system status in real time . These devices must have The ability to meet future application needs without replacement for a long time
- communication system
be based on Open system and highly integrated communication system It is the foundation of smart grid . It needs to ensure the ability of interactive operation , And it can be compatible with new communication media
- Data management and software application
Smart grid will enable power companies to obtain a large amount of data , How to manage and use these data is the key to realize benefits , Therefore must Find a method suitable for massive data management and develop advanced application software based on these data , To serve the optimal operation of the system
- Network security and information protection
to open up 、 Compatibility and interconnection are inevitably accompanied by risks of information security . Smart grid must Ensure network security to ensure the confidentiality of information 、 Integrity and availability
- Standards and protocols
The construction of smart grid involves multi system integration 、 Integration of many new technologies 、 Multi energy access , signal communication 、 interoperability 、 The formulation of standards and protocols for data collection and management is crucial . The lack of unified standards is not conducive to power generation 、 Electricity transmission 、 Information exchange between distribution and power consumers , Reduce the efficiency of the system
- Operation and planning model
The development of digital technology has great impact on power grid Power supply reliability and Power quality Put forward higher requirements , New real-time tools are needed to assist scheduling decision , This brings the following challenges :
- Lack of models and simulation tools to evaluate smart grid performance
- Lack of high fidelity prediction and analysis ability to improve scheduling decision . The large amount of distributed energy infiltrating into the power grid is uncertain , It brings difficulties to high fidelity prediction and analysis
- Lack of probabilistic simulation method of load forecasting under dynamic electricity price , This will hinder the simulation related to the demand elasticity of the electricity market 、 Analyze and evaluate
- Lack of smart grid evaluation indicators . Although the indicators for evaluating smart grid behavior have been studied , But it needs to be deepened and refined , Especially with renewable energy generation and load uncertainty 、 Indicators related to the impact of energy storage , These indicators should be measurable , And it can guide the operation and planning decision
- Energy storage
Steven Chu, the Nobel Prize winner in physics, once pointed out that energy storage is combined with solar energy , The impact in the field of distribution and power generation may be comparable to the disruptive impact caused by the Internet in that year . thus it can be seen , Energy storage has a huge driving force for the development of smart grid , There are two main points :
- From the perspective of power grid , It can be applied to frequently changing loads Load tracking 、 Reduce power distribution congestion 、 Translation load demand
- From the perspective of renewable energy , To improve energy efficiency , Reduce the impact of renewable energy uncertainty on grid stability , There is an urgent need Develop efficiently 、 long life 、 reliable 、 Affordable chemical batteries , Buffered by battery , When renewable energy is insufficient, discharge to make up , When there is excess renewable energy, charge and save
- Market design
The power market of smart grid is an integration , Open market , Reasonable regulations are needed to stimulate market investment , There are mainly :
- Implement time sharing / Real time electricity price , send “ electric energy ” The market value of a commodity is reasonably reflected
- Improve the policy of encouraging distributed energy to sell electricity back to the grid and use it as a backup power , Such as auxiliary FM market
- Establish a smart grid investment cost recovery policy . That is, formulate policies to ensure the rationality of investors' final settlement
Reference resources :
[1]: Chenshuyong , Song Shufang , Li Lanxin , Shen Jie . Overview of Smart Grid Technology [J]. Grid technology ,2009,33(08):1-7.
[2]: Zhang Wenliang , Liu Zhuangzhi , Wang Mingjun , Yang Xusheng . Research progress and development trend of smart grid [J]. Grid technology ,2009,33(13):1-11.
[3]: Yu Yixin , Luan Wenpeng . Review of smart grid [J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering ,2009,29(34):1-8.
[4]: Xiao Shijie . Thoughts on building China's smart grid technology [J]. Power system automation ,2009,33(09):1-4.
[5]: Yu Yixin , Luan Wenpeng . Smart grid [J]. Power grid and clean energy ,2009,25(01):7-11.
[6]: Fang, Xi, et al. “Smart grid—The new and improved power grid: A survey.” IEEE communications surveys & tutorials 14.4 (2011): 944-980.
边栏推荐
- [Yugong series] go teaching course 006 in July 2022 - automatic derivation of types and input and output
- 13.模型的保存和载入
- NVIDIA Jetson测试安装yolox过程记录
- 133. 克隆图
- 50Mhz产生时间
- 新库上线 | 中国记者信息数据
- Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)(A~D)
- 网络模型的保存与读取
- 大二级分类产品页权重低,不收录怎么办?
- Cross modal semantic association alignment retrieval - image text matching
猜你喜欢

国内首次,3位清华姚班本科生斩获STOC最佳学生论文奖

13. Enregistrement et chargement des modèles

How does starfish OS enable the value of SFO in the fourth phase of SFO destruction?
14.绘制网络模型结构
NVIDIA Jetson测试安装yolox过程记录
完整的模型训练套路
133. Clone map
【深度学习】AI一键换天
3. MNIST dataset classification

Cancel the down arrow of the default style of select and set the default word of select
随机推荐
2. Nonlinear regression
How to write mark down on vscode
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)
图像数据预处理
Is it safe to speculate in stocks on mobile phones?
13.模型的保存和载入
国外众测之密码找回漏洞
手写一个模拟的ReentrantLock
基础篇——整合第三方技术
10.CNN应用于手写数字识别
Complete model verification (test, demo) routine
Cascade-LSTM: A Tree-Structured Neural Classifier for Detecting Misinformation Cascades(KDD20)
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)
Where is the big data open source project, one-stop fully automated full life cycle operation and maintenance steward Chengying (background)?
12. RNN is applied to handwritten digit recognition
Image data preprocessing
1.线性回归
FOFA-攻防挑战记录
Lecture 1: the entry node of the link in the linked list
Cve-2022-28346: Django SQL injection vulnerability