当前位置:网站首页>2. Nonlinear regression
2. Nonlinear regression
2022-07-08 01:01:00 【booze-J】
The code running platform is jupyter-notebook, Code blocks in the article , According to jupyter-notebook Written in the order of division in , Run article code , Glue directly into jupyter-notebook that will do .
1. Import third-party library
import keras
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Sequential Sequential model
from keras.models import Sequential
# Dense Fully connected layer
from keras.layers import Dense,Activation
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD
2. Randomly generate data sets
# Use numpy Generate 200 A random point
# stay -0.5~0.5 Generate 200 A little bit
x_data = np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,200)
noise = np.random.normal(0,0.02,x_data.shape)
# y = x^2 + noise
y_data = np.square(x_data) + noise
# Show random points
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data)
plt.show()
Running results :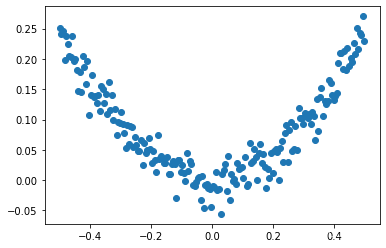
3. Nonlinear regression
# Build a sequential model
model = Sequential()
# Press shift+tab Parameters can be displayed
# 1-10-1 Input a neural layer ,10 Hidden layers , Output a neural layer
model.add(Dense(units=10,input_dim=1))
# Add activation function The activation function is linear by default , But we are nonlinear regression , Therefore, the activation function should be modified
# Add activation function Mode one : Add... Directly activation Parameters
# model.add(Dense(units=10,input_dim=1,activation="relu"))
# Add activation function Mode two : Add... Directly Activation Activation layer
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
model.add(Dense(units=1,input_dim=10))
# model.add(Dense(units=1,input_dim=10,activation="relu"))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
# Define optimization algorithms Improving the learning rate can reduce the number of iterations
sgd = SGD(lr=0.3)
# sgd:Stochastic gradient descent , Random gradient descent method default sgd The learning rate table is smaller Therefore, the number of iterations required is relatively large It takes more time
# mse:Mean Squared Error , Mean square error
model.compile(optimizer=sgd,loss='mse')
# Training 3001 Lots
for step in range(3001):
# One batch at a time
cost = model.train_on_batch(x_data,y_data)
# Every time 500 individual batch Print once cost
if step%500==0:
print("cost:",cost)
# Print weights and batch values
W,b = model.layers[0].get_weights()
print("W:",W)
print("b:",b)
# x_data Input the predicted value in the network
y_pred = model.predict(x_data)
# Show random points
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data)
# Show forecast results
plt.plot(x_data,y_pred,"r-",lw=3)
plt.show()
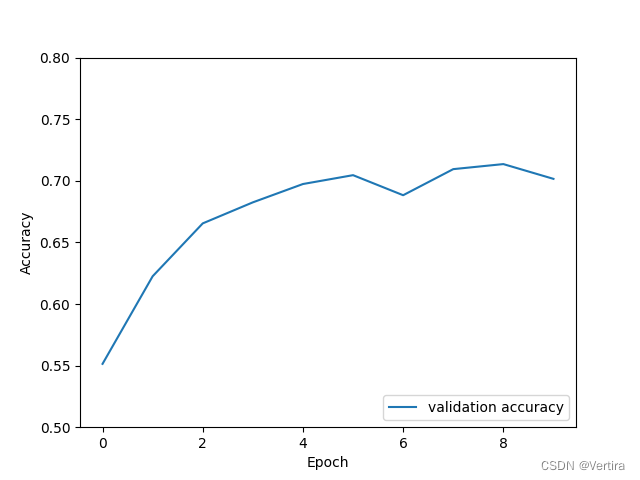
Running results :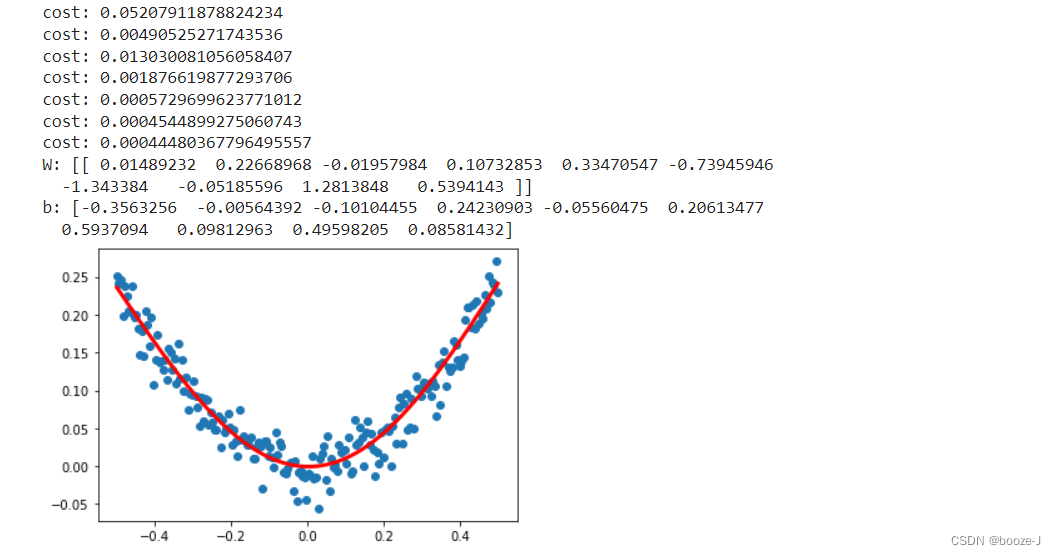
Be careful
- 1. For nonlinear regression, we should pay attention to modifying the activation function , Because the activation function is linear by default .
- 2. default sgd The learning rate table is smaller Therefore, the number of iterations required is relatively large It takes more time , So you can customize sgd Learning rate to learn .
- 3. On the whole, the code is very similar to the code of linear regression , Just modify the data set , A network model , Activation function , And optimizer .
边栏推荐
- 3.MNIST数据集分类
- Password recovery vulnerability of foreign public testing
- Prediction of the victory or defeat of the League of heroes -- simple KFC Colonel
- Huawei switch s5735s-l24t4s-qa2 cannot be remotely accessed by telnet
- A network composed of three convolution layers completes the image classification task of cifar10 data set
- Implementation of adjacency table of SQLite database storage directory structure 2-construction of directory tree
- CVE-2022-28346:Django SQL注入漏洞
- Thinkphp内核工单系统源码商业开源版 多用户+多客服+短信+邮件通知
- [Yugong series] go teaching course 006 in July 2022 - automatic derivation of types and input and output
- 10.CNN应用于手写数字识别
猜你喜欢

From starfish OS' continued deflationary consumption of SFO, the value of SFO in the long run

Cancel the down arrow of the default style of select and set the default word of select
网络模型的保存与读取
7.正则化应用
Kubernetes Static Pod (静态Pod)
A network composed of three convolution layers completes the image classification task of cifar10 data set

SDNU_ACM_ICPC_2022_Summer_Practice(1~2)

国内首次,3位清华姚班本科生斩获STOC最佳学生论文奖

13.模型的保存和載入
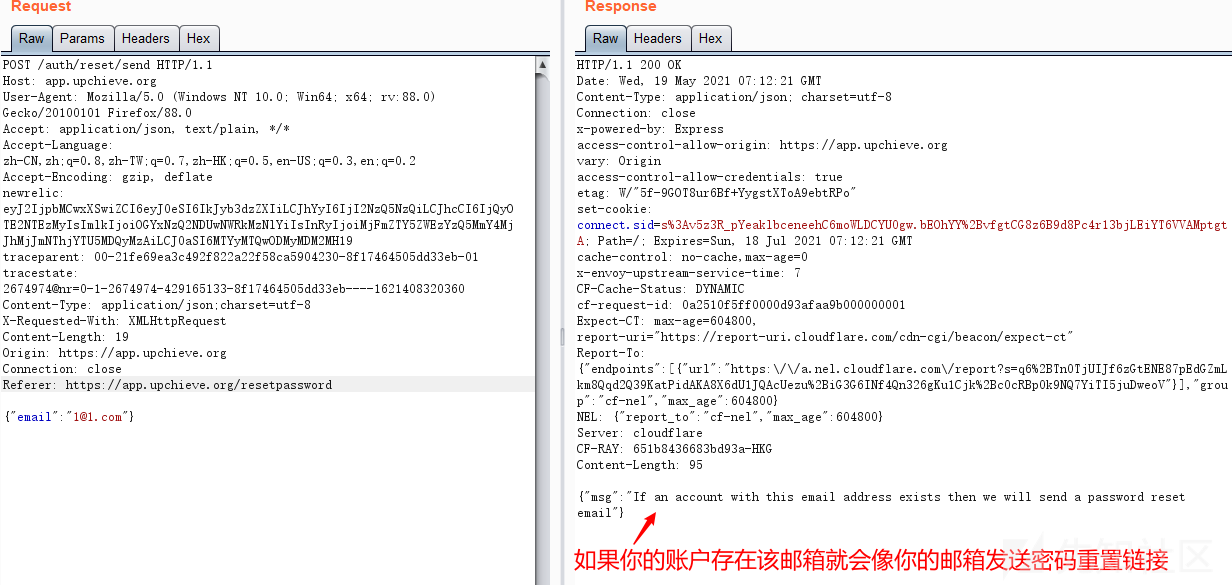
Password recovery vulnerability of foreign public testing
随机推荐
C # generics and performance comparison
Service mesh introduction, istio overview
Handwriting a simulated reentrantlock
Is it safe to speculate in stocks on mobile phones?
1.线性回归
Introduction to ML regression analysis of AI zhetianchuan
[deep learning] AI one click to change the sky
6.Dropout应用
Image data preprocessing
Service Mesh的基本模式
My best game based on wechat applet development
QT adds resource files, adds icons for qaction, establishes signal slot functions, and implements
Cascade-LSTM: A Tree-Structured Neural Classifier for Detecting Misinformation Cascades(KDD20)
ReentrantLock 公平锁源码 第0篇
Tapdata 的 2.0 版 ,开源的 Live Data Platform 现已发布
13.模型的保存和载入
Course of causality, taught by Jonas Peters, University of Copenhagen
AI遮天传 ML-回归分析入门
基于人脸识别实现课堂抬头率检测
1293_ Implementation analysis of xtask resumeall() interface in FreeRTOS