当前位置:网站首页>Database under unity
Database under unity
2022-07-05 04:52:00 【yaohuiyaoo】
One .- stay linux platform :
1. Check for installation MYSQL: rmp -qa | grep mysql
2. Uninstall files : rmp -e file name - -nodeps
3. install MySQL Server side :rpm -ivh Installed packages (i Indicates the specified RMP software package ,v Represents the details of the installation .h Indicates that... Occurred during installation # Symbol to show the current installation process
4. start-up MySQL: service mysql start
5. Out of Service mysql: service mysql stop
6. Restart the service MySQL: service mysql restart
7. View service status : service mysql status
8. Set up mysql Login password :mysql_secure_installation
9. Log in mysql: mysql -uroot -p (u Followed by the user name p Followed by the password )
10. Display database : show databases;
service : Manual start
Two . In the small black box
1. start-up MySQL: net start mysql
2. stop it mysql : net stop mysql
3. Sign in mysql: mysql -h Server hostname -u user name -p
( Host name can be omitted for local login -p Followed by the password )
4. Reconfiguration MySQL: set character_set_client=gbk( modify MySQL The character encoding of the client )set character_set_results=gbk
3、 ... and . stay MySQL command line client
1. Ask for help : help
2. Create database : create databases Database name ;
3. Show all databases : show databases;
4. Show a database : show create database Database name ;
5. Modify character encoding : alter database Database name default character set Encoding mode ( The modified ) collate Encoding mode _bin
6. Delete database : drop database Database name ;
. Basic operation of data table
Look at all the tables : show tables;
1. Create data table : Step one . Create database :create database Database name
Step two . Create a database of tables : use Database name
Step three . To create a data table SQL: create table Table name ( Content );
2. Look at the data sheet :show create table Table name ;
3. View field information :describs Table name ;( or desc Table name )
Null : Indicates whether the column can store null values
Key: Indicates whether the column is indexed in
Defualt: Indicates whether the column has a default value
Extra: Represents the additional information obtained related to the given column
4. Modify the name of the table : alter table The old name of the table rename to The new name of the table ;
5. Modify field name :alter table Table name change Old paragraph name New paragraph name New data types ;
6. Change data type : alter table Table name modify Field name data type ;
7. Add fields : At the end of alter table Table name add new field name data type ;
8. start alter table Table name add Field name data type first
9. middle alter table Table name add Field name data type ( constraint condition ) after Old field name
10. Insert content :insert into Table name value() Note that the inserted content should be intentionally corresponding to
11. View what is written :select *from Table name ;
12. Delete field : alter table Table name drop Field name
13. Modify the arrangement position of field names :alter table Table name modify Field one data type first|after Field name 2
14. Delete data table :drop table Table name ;(drop table if exit Table name ; This command determines whether the table name exists before deleting )
5、 ... and . Table constraints
1. Primary key constraint : Single field constraint : Field name data type primary key[ The default value is ] perhaps primary key( Field name )
Multi field constraints :primary key ( Field name one , Field name 2 …)
2. Add primary key :alter table Table name add primary key ( Field name )
3. Delete primary key constraint :alter table Table name drop primary key ;
4. Self growth :auto_incerment;( expand auto_incerment= Numbers ( The value added to a number is constrained outside parentheses )
5. The first step of discontinuous increase :INSERT INTO tb_student3 VALUES(1,1,1); The second step INSERT INTO tb_student3 VALUES(null,1,1);
4. Non empty constraint : Field name data type not null;
5. Unique constraint : That is, the value of the field name in the table cannot be repeated
: Field name data type unique
7. Add unique constraints :alter table Table name add constraint Unique constraint name unique Field name
8. Delete unique constraint name :alter table Table name drop index Unique constraint name
2. Default constraint : Specify default values for field names in the data table
: Field name data type default The default value is ;
3. Add a foreign key : Grammar format :
ADD FOREIGN KEY [< Index name >] (< Name >,…)
stay ALTER TABLE Add this syntax component to the statement , Indicates adding foreign keys to the table while modifying the table
6、 ... and . Indexes
0. Display index :show index from Table name ;
1. Use the index information that displays the index :
Parameters explain
Table Indicates the name of the data table where the index is created , Here is tb_stu_info2 Data sheet .
Non_unique Indicates whether the index is unique . If not the only index , Then the value of this column is 1; If it's a unique index , Then the value of this column is 0.
Key_name Represents the name of the index .
Seq_in_index Indicates the position of the column in the index , If the index is single column , Then the value of this column is 1; If the index is a composite index , Then the value of the column is the order of each column in the index definition .
Column_name Represents the column field that defines the index .
Collation Indicates the order in which columns are stored in the index . stay MySQL in , Display values in ascending order “A”( Ascending ), If displayed as NULL, It means no classification .
Cardinality An estimate of the number of unique values in an index . Cardinality counts based on statistics stored as integers , So even for a small watch , This value does not have to be accurate . The larger the base , When there is a union ,MySQL The greater the chance of using the index .
Sub_part Indicates the number of characters indexed in the column . If a column is only partially indexed , Then the value of this column is the number of characters indexed ; If the entire column is indexed , Then the value of this column is NULL.
Packed Indicates how keywords are compressed . If not compressed , The value is NULL.
Null Used to display whether the index column contains NULL. If column contains NULL, The value of this column is YES. If there is no , Then the value of this column is NO.
Index_type Displays the types and methods used by the index (BTREE、FULLTEXT、HASH、RTREE).
Comment Show comments .
Create a normal index :index ( Field name ) or CREATE < Index name > ON < Table name > (< Name > [< length >] [ ASC | DESC]) The grammar is as follows :
< Index name >: Specify the index name . A table can create multiple indexes , But the name of each index in the table is unique .
< Table name >: Specify the name of the table to create the index .
< Name >: Specifies the name of the column to create the index . In general, you can consider the query statement in JOIN Clause and WHERE The columns that often appear in clauses are used as index columns .
< length >: optional . Specifies to use the length Characters to create the index . Using a portion of a column to create an index helps reduce the size of the index file , Save space for index columns . In some cases , Only prefixes of columns can be indexed . There is a maximum limit on the length of an index column 255 Bytes (MyISAM and InnoDB The maximum upper limit of the table is 1000 Bytes ), If the length of the index column exceeds this limit , You can only index with the prefix of the column . in addition ,BLOB or TEXT Columns of type must also be indexed with prefixes .
ASC|DESC: optional .ASC Specifies that the index is arranged in ascending order ,DESC Specifies that the indexes are arranged in descending order , The default is ASC.
Indexes can also be used to create tables (CREATE TABLE) At the same time create . stay CREATE TABLE Add the following statement to the statement . Grammar format :
CONSTRAINT PRIMARY KEY [ Index type ] (< Name >,…)
stay CREATE TABLE Add this statement to the statement , Indicates that the primary key of the new table is created when the new table is created .
Grammar format :
KEY | INDEX [< Index name >] [< Index type >] (< Name >,…)
stay CREATE TABLE Add this statement to the statement , Indicates that the index of the new table is created at the same time as the new table is created .
Grammar format :
UNIQUE [ INDEX | KEY] [< Index name >] [< Index type >] (< Name >,…)
stay CREATE TABLE Add this statement to the statement , Indicates that the unique index of the new table is created when the new table is created .
Grammar format :
FOREIGN KEY < Index name > < Name >
stay CREATE TABLE Add this statement to the statement , Indicates that the foreign key of the new table is created at the same time
1. See if the index is being used :explain select* from Table name where Field name =1( Query the value of the field name , Just check )\G
2. Create unique index :unique index Index name ( Field name asc/desc)
3. Create full text index : fulltext index Index name ( Field name )( It must be declared non empty , The storage engine can only be myisam
4. Single index :index Index name ( Field name )
5. Multi column index :index Index name ( Field name one , Field name 2 )
6. Create spatial index : Field name GEOMETRY notnull,spatial index Index name ( Field name )
7. Create an index for an existing table :create [unique|fulltext|sptial] index Index name on Table name ( Field name [ length ][asc|desc]);
Create a normal index :create index Index name on Table name ( Field name );
Create unique index :create unique index Index name on Table name ( Field name );
Create a single column index :create index Index name on Table name ( Field name )
Create multi column indexes :create index Index name on Table name ( Field name one , Field name 2 );
Create full text index :create fulltext index Index name on Table name ( Field name );
Create spatial index :create spatial index Index name on Table name ( Field name );
8. Create an index for an existing table :
alter table Table name add [unique|fulltext|spatial] index Index name ( Field name [ Field name ( length )][asc|desc])
Create a normal index :alter table Table name add index Index name ( Field name );
Create unique index :alter table Table name add unique Index name ( Field name );
Create a single column index :alter table Table name add index Index name ( Field name );
Create multi column indexes :alter table Table name index Index name ( Field name one , Field name 2 );
Create full text index :alter table Table name add fulltext index Index name ( Field name );
Create spatial index :alter table Table name add spatial index Index name ( Field name );
9. Delete index :alter table Table name drop index Index name ;
10. Expand :
DROP PRIMARY KEY: Indicates to delete the primary key in the table . A table has only one primary key , The primary key is also an index .
DROP INDEX index_name: Indicates that the deletion name is index_name The index of .
DROP FOREIGN KEY fk_symbol: Indicates that the foreign key is deleted .
11.0 Delete index :drop index Index name on Table name ;
7、 ... and . Add data
1. Add data format :insert into Table name ( Field name one , Field name 2 ,…) value ( It's worth one , It's worth two …); perhaps :insert into Table name value ( It's worth one , It's worth two …);
2. Look at the inserted data :select from Table name ;
3. insert data :insert into Table name set Field name = It's worth one , Field name 2 = It's worth two …;
4. Add multiple pieces of data :insert into Table name [( Field name one , Field name 2 …)] value ( It's worth one , It's worth two , It's worth three …),( It's worth one , It's worth two , It's worth three ,…
8、 ... and . Update data
1. Record of updated data :update Table name set Field name one = It's worth one [ Field name 2 = It's worth one …][where Conditional expression (and) Conditional expression ]
Nine . Delete data
1. Delete data in table :delete from Table name [where Conditional statements ]
2. Delete all records delete from Table name perhaps truncate [ Table name ] Table name
Ten . Single table query
General order select sentence :select [distinct]| Field name one , Field name 2 …
From Table name
[where Conditional expression 1 ]
[group by Field name [having Conditional expression 2 ]]
[order by Field name |ASC|DESC]]
offset] Record number
1. Query the specified field :select Field name one , Field name 2 …from Table name
1. Look up everything in the table : select *from Table name
2. Eliminate duplicate data :select distinct Field name from Table name ;
3. Specify query criteria :select Field name …from Table name where Conditional expression ;
4. Specify query and data range :select Field name …from where Field name [not] in( Specific data 1 , Specific data 2 …)
5. To query for :select *(| Field name one , Field 2 …) from Table name where Field name [not] between It's worth one and It's worth two ;
6. Field null value query select *| Field name one , Field name 2 … from Table name where Field name is (not) null
7. Eliminate multiple duplicate data :select distinct Field name 1,…from Table name
8. Query the matching data :select *| Field name one … from Table name where Field name (not) like ‘ Matching string ’ ( Match string specifies the string used to match , Its value is an ordinary string , It can also include % perhaps _ The wildcard
9. With key and Multi criteria query of select *| Field name one … from Table name where Expression 1 and Expression two …
10. With the keyword or Multi criteria query of select | Field name one … from Table name where Expression 1 or Expression two …
Be careful :and Has a higher priority than or
11、 ... and . Aggregate functions
Count() Returns the number of rows in a column
Sum() Returns the sum of a column
Avg() Returns the average of a column
Max() Returns the maximum value of a column
Min() Returns the minimum value of a column
Twelve . Inquire about
1. Format :select count() from Table name where Conditional statements
2. Sort query results :select Field name one …from Table name order by Field name one (asc|desc)( Ascending | Descending ) Field name 2 …
3. Group query :select Field name one …from Table name group by Field name one …having Conditional statements
Use alone group by grouping :select *from Table name group by Field name ( The basis of grouping )
Group by Use with aggregate functions :select Aggregate functions , Field name from Table name group by Field name
Group by And having Use keywords together :select Aggregate functions , Field name from Table name group by Field name having Conditional statements
GROUP BY Keywords can be similar to GROUP_CONCAT() Functions together .GROUP_CONCAT() The function will display the field values of each group . Format :select Field name ,group_concat( Field name ) from Table name group by Field name
WITH POLLUP Keyword is used to add a record at the end of all records , This record is the sum of all the above records , That is, count the number of records .
Format :select Field name from Table name group by Field name with pollup
4. Use limit Limit the number of query results :select Field name …from Table name limit( Number of items listed ) (offset,‘) Record number ,offset initial position
MySQL Functions of numerical type
The name of the function do use
ABS Find the absolute value
SQRT Find the quadratic root
MOD Mod
CEIL and CEILING The two functions have the same function , All return the minimum integer no less than the parameter , That is, round up
FLOOR Rounding down , The return value is converted to a BIGINT
RAND Generate a 0~1 Random number between , The input integer parameter is , Used to generate repeat sequences
ROUND Round the parameters passed
SIGN Returns the symbol of the parameter
POW and POWER The functions of the two functions are the same , Are the result values of the power of the passed parameters
SIN Find the sine
ASIN Find the inverse sine , And functions SIN They're inverse functions to each other
COS Find the cosine
ACOS Find the inverse cosine , And functions COS They're inverse functions to each other
TAN Find tangent
ATAN Find the arctangent , And functions TAN They're inverse functions to each other
COT Find the cotangent value
MySQL String function
The name of the function do use
LENGTH Evaluate string length function , Returns the byte length of the string
CONCAT Merge string functions , The return result is the string generated by the connection parameter , Parameters can make one or more
INSERT Replace string functions
LOWER Convert the letters in the string to lowercase
UPPER Convert the letters in the string to uppercase
LEFT Take the string from the left side of the word , Returns several characters to the left of the string
RIGHT Take the string from the right word , Returns several characters to the right of the string
TRIM Delete the spaces on the left and right of the string
REPLACE String replacement function , Return the new string after replacement
SUBSTRING Intercepting string , Returns a character change of a specified length starting at a specified location
REVERSE String inversion ( The reverse ) function , Returns the string in reverse order to the original string
MySQL Date and time functions
The name of the function do use
CURDATE and CURRENT_DATE The two functions work the same , Returns the date value of the current system
CURTIME and CURRENT_TIME The two functions work the same , Returns the time value of the current system
NOW and SYSDATE The two functions work the same , Returns the date and time values of the current system
UNIX_TIMESTAMP obtain UNIX Time stamp function , Return one to UNIX A timestamp based unsigned integer
FROM_UNIXTIME take UNIX Time stamp converted to time format , And UNIX_TIMESTAMP They're inverse functions to each other
MONTH Get the month in the specified date
MONTHNAME Get the English name of the month in the specified date
DAYNAME Get the English name of the day of the week corresponding to the specified date
DAYOFWEEK Gets the index location value of the week corresponding to the specified date
WEEK Get the specified date is the week of the year , Whether the return value range is 0〜52 or 1〜53
DAYOFYEAR The date of acquisition is the day of the year , The return value range is 1~366
DAYOFMONTH Get the specified date is the day of the month , The return value range is 1~31
YEAR Get year , The return value range is 1970〜2069
TIME_TO_SEC Convert the time parameter to seconds
SEC_TO_TIME Convert seconds to time , And TIME_TO_SEC They're inverse functions to each other
DATE_ADD and ADDDATE The two functions have the same function , All add the specified time interval to the date
DATE_SUB and SUBDATE The two functions have the same function , It's all subtracting the specified time interval from the date
ADDTIME Time addition operation , Add the specified time... To the original time
SUBTIME Time subtraction , Subtract the specified time from the original time
DATEDIFF Get the interval between two dates , Returns the parameter 1 Subtract the parameter 2 Value
DATE_FORMAT Format the specified date , Returns the value of the specified format according to the parameter
WEEKDAY Get the corresponding working day index of the specified date in a week
MySQL Aggregate functions
The name of the function effect
MAX Query the maximum value of the specified column
MIN Query the minimum value of the specified column
COUNT Count the number of rows in the query result
SUM Sum up , Returns the sum of the specified columns
AVG averaging , Returns the average of the specified column data
MySQL Process control functions
The name of the function effect
IF Judge , Process control
IFNULL Determine whether it is null
CASE Search statement
19. Alias the field :select Field name as Alias from Table name
20. Alias the table :select *from Table name as Alias
13、 ... and . Multi meter operation
1. Add foreign keys when creating a table : Add... To the foreign key table :foreign key Field name references Main table name Primary key name
2. Add foreign keys to existing tables :alter table Table name add constaint Foreign key name foreign key The field name that needs to be a foreign key references Main table name ( Main table field name )
{on delete{cascade|set null| no action|restrict}]
[on update{cascade| set null|no action|restrict}]
Cascade Delete all records with reference to the deleted value
Set Modify to include all records that have a reference relationship with the key value to delete , Use null Value substitution
Not action No operations
Restrict Reject the deletion or modification of foreign key relation Series in the main table
3. Delete foreign key constraint :alter table Table name Capacitance screen foreign key Foreign key name
边栏推荐
- Pdf to DWG in CAD
- MySQL audit log Archive
- Looking at Chinese science and technology from the Winter Olympics: what is the mystery of the high-speed camera that the whole people thank?
- Research and forecast report on China's solution polymerized styrene butadiene rubber (SSBR) industry (2022 Edition)
- [groovy] closure (closure as function parameter | code example)
- [Chongqing Guangdong education] National Open University 2047t commercial bank operation and management reference test in autumn 2018
- JMeter -- distributed pressure measurement
- [Business Research Report] top ten trends of science and technology and it in 2022 - with download link
- 2022-2028 global and Chinese video coding and transcoding Market Research Report
- 2022-2028 global and Chinese virtual data storage Market Research Report
猜你喜欢
windows下Redis-cluster集群搭建
AutoCAD - window zoom

【acwing】240. food chain
A survey of automatic speech recognition (ASR) research

2022 thinking of Mathematical Modeling B problem of American college students / analysis of 2022 American competition B problem
The principle of attention mechanism and its application in seq2seq (bahadanau attention)
![[groovy] closure (Introduction to closure class closure | closure parametertypes and maximumnumberofparameters member usage)](/img/1b/1fa2ebc9a6c5d271c9b39f5e508fb0.jpg)
[groovy] closure (Introduction to closure class closure | closure parametertypes and maximumnumberofparameters member usage)
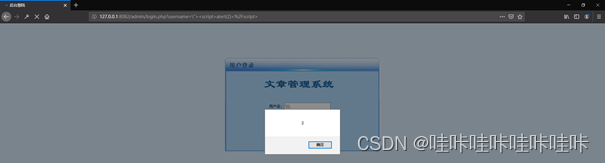
XSS injection
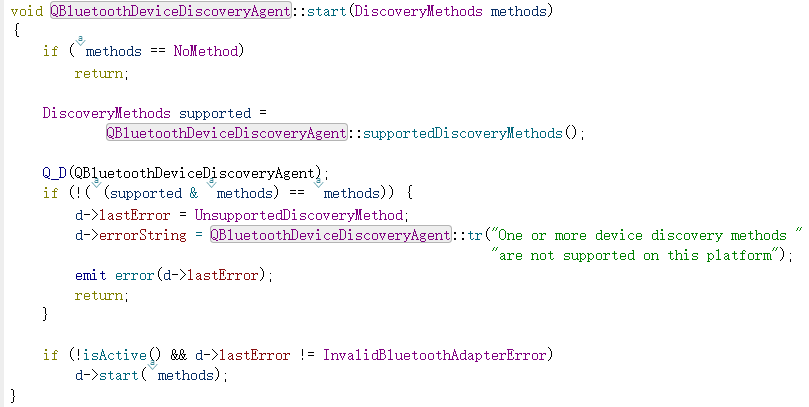
QT Bluetooth: a class for searching Bluetooth devices -- qbluetooth devicediscoveryagent

【Leetcode】1352. Product of the last K numbers
随机推荐
[goweb development] Introduction to authentication modes based on cookies, sessions and JWT tokens
3dsmax common commands
2022-2028 global and Chinese virtual data storage Market Research Report
次小生成树
MySQL in-depth learning - index creation and deletion, index design principles, index failure scenarios, query optimization, index push down ICP
Wan broadband access technology V EPON Technology
2021 electrician Cup - high speed rail traction power supply system operation data analysis and equivalent modeling ideas + code
Detailed introduction of OSPF header message
Mode in BST (binary tree & Notes on question brushing)
[groovy] closure closure (customize closure parameters | customize a single closure parameter | customize multiple closure parameters | specify the default value of closure parameters)
2022 U.S. college students' mathematical modeling e problem ideas / 2022 U.S. game e problem analysis
Function overloading
Minor spanning tree
[Chongqing Guangdong education] National Open University 2047t commercial bank operation and management reference test in autumn 2018
Variable category (automatic, static, register, external)
775 Div.1 B. integral array mathematics
54. 螺旋矩阵 & 59. 螺旋矩阵 II ●●
[groovy] closure (closure call | closure default parameter it | code example)
【acwing】837. Number of connected block points
QT Bluetooth: a class for searching Bluetooth devices -- qbluetooth devicediscoveryagent