当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of express framework
Detailed explanation of express framework
2022-07-06 11:36:00 【Advanced diary】
Express
Use express You can quickly create web Web server or API Interface server
1. establish express Of web The server
// Import express
const express = require("express")
// establish web The server
const app = express()
// start-up web The server
app.listen(8088,()=>{
console.log('http://127.0.0.1:8088');
})
2. monitor get/post request
// monitor GET Request and return the response content , The first parameter is the requested url
app.get('/get',(req,res)=>{
//req.query Get request is the parameter sent
console.log(req.query)//http://127.0.0.1:8088/get?name=zs&age=18
//{ name: 'zs', age: '18' }
// call express Provided res.send() Method , Set the returned JSON object
res.send({name:"zs",age:20,gender:" male "})
})
// monitor POST Request and return the response content , The first parameter is the requested url
app.post('/post',(req,res)=>{
// call express Provided res.send() Method , Set the returned JSON object
res.send({name:"zs",age:20,gender:" male "})
})
towards http://127.0.0.1:8088/post The return value of the send request is
{ "name": "zs",
"age": 20,
"gender": " male "}
3. To obtain parameters
// Static parameters
app.get('/get',(req,res)=>{
//req.query Get request is the parameter sent
//http://127.0.0.1:8088/get?name=zs&age=18
res.send(req.query)
//{ name: 'zs', age: '18' }
})
// Dynamic parameters
app.get('/getId/:id',(req,res)=>{
//req.query Get request is the parameter sent
//http://127.0.0.1:8088/getId/12
res.send(req.params)
})
// return
{
"id": "12"
}
// Multiple dynamic parameters
app.get('/getId/:id/:name',(req,res)=>{
//req.query Get request is the parameter sent
//http://127.0.0.1:8088/getId/12/zs
res.send(req.params)
})
// return
{
"id": "12"
"name":"zs"
}
4. middleware
//app.use() The function is to register the global middleware ,app.use('path',function()) The first parameter is the path. If it is / Omission
express There are three kinds of middleware
1. Built in middleware static
2. Custom middleware
3. Third-party middleware (body-parser) ( Interceptor )
app.use(express.static('public'))
app.use(express.static('dome'))
// You can directly access
http://127.0.0.1:8088/index.html
http://127.0.0.1:8088/index.css
http://127.0.0.1:8088/index.js
// Will prioritize public In the document index file , If you can't find it, find dome Medium index file
app.use('/public',express.static('public'))
// To access http://127.0.0.1:8088/public/index.html
// Customize the middleware with global effect Multiple middleware can be defined , The middleware will be called in sequence
app.use(function (req, res, next) {/* Indicates that it matches any route */
console.log(new Date())
next()/* Indicates that the middleware will continue to execute after the matching is completed .*/
})
// Local middleware
let func = function (req, res, next) {/* Indicates that it matches any route */
console.log(new Date())
next()/* Indicates that the middleware will continue to execute after the matching is completed .*/
}
// Multiple local middleware can be defined
app.get('/',func1,func2,(req,res)=>{
res.send('get router by :/')
})
// Use middleware to process request data
app.use(express.json())
app.use(express.urlencoded({extended:false})
// Use third-party middleware (body-parser) ( Interceptor )
1. npm install body-parser
// To middleware
const parser = require("body-parser")
// Register middleware
app.use(parser.urlencoded({extended:false})
//nodejs built-in querystring The module processes the query string and converts the query string into object format
const qs = require("querystring")
console.log(qs.parse(str))
5. nodemon
It can start the modified project less frequently ,nodemon It will automatically restart the project to facilitate development and testing
npm install -g nodemon
Use nodemon app.js To run the project , no need node app.js
6. route
1. Mount in the original way
const express = require("express")
const app = express();
// Mount route
app.get('/',(req,res)=>{
res.send('get router by :/')
})
app.post('/',(req,res)=>{
res.send('post router by :/')
})
app.listen(8088,()=>{
console.log("http://127.0.0.1:8088");
})
2. Use express route
// stay router.js Create a routing object in
const express = require("express")
const router = express.Router();
// Mount specific routes
router.get('/user/list',(rep,res)=>{
res.send("GER user list")
})
router.post("/user/add",(req,res)=>{
res.send("POST user add")
})
// Export routing objects out
module.exports = router
// stay index.js Reference route in
const express = require("express")
const app = express()
// Import routing module
const router = require("./router")
// Register routing module
app.use(router)
app.listen(8088,()=>{
console.log("http://127.0.0.1:8088");
})
//app.use('/api',router)// Add a uniform prefix to the route http://127.0.0.1:8088/api/user/add
7. To write get/post Interface
const express = require("express");
const app = express()
const router = express.Router()
app.use(express.urlencoded({extended:false}))
router.get('/get',(req,res)=>{
// Request data sent by the client
const query = req.query;
res.send({
status:0,//0 It means success ,1 It means failure
msg:"GET The request is successful ",// Description of the State
data:query// Data that needs to be responded to the client
})
})
router.post('/post',(req,res)=>{
// Request data sent by the client
const body = req.body;
// Configure the middle price of parsing form data
res.send({
status:0,//0 It means success ,1 It means failure
msg:"POST The request is successful ",// Description of the State
data:body// Data that needs to be responded to the client
})
})
app.use(router);
app.listen(8088,()=>{
console.log("get request ");
})
8.cors Cross domain solution
const express = require("express");
const cors = require("cors")
const app = express()
// Use third-party middleware to solve cross domain
app.use(cors())
// Customize cors Set up cross domain requests
var cors = function(req,res,next()){
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', 'http://localhost:8088');// Request address
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET,PUT,POST,DELETE');// Request mode
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Content-Type');// Request header
next()
}
app.use(cors)
边栏推荐
- [BSidesCF_2020]Had_a_bad_day
- 误删Path变量解决
- Learn winpwn (2) -- GS protection from scratch
- Library function -- (continuous update)
- AI benchmark V5 ranking
- Learning question 1:127.0.0.1 refused our visit
- 保姆级出题教程
- Base de données Advanced Learning Notes - - SQL statements
- Face recognition_ recognition
- AcWing 179. Factorial decomposition problem solution
猜你喜欢
![[yarn] CDP cluster yarn configuration capacity scheduler batch allocation](/img/85/0121478f8fc427d1200c5f060d5255.png)
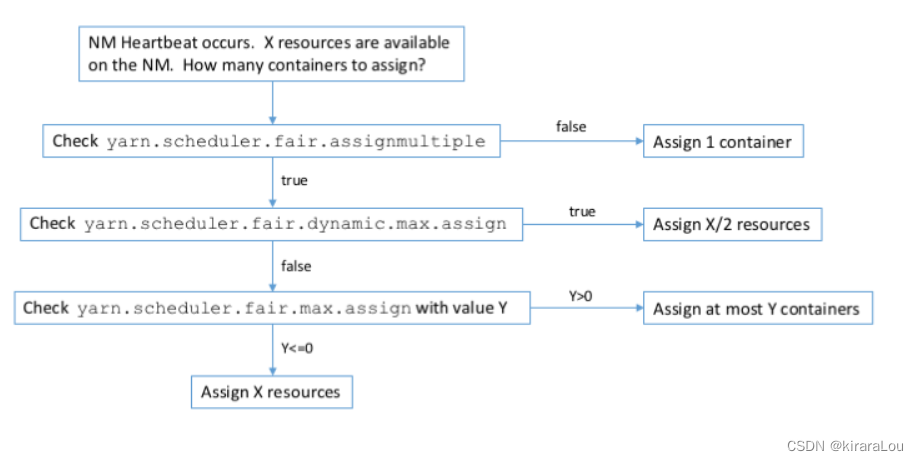
[yarn] CDP cluster yarn configuration capacity scheduler batch allocation
【CDH】CDH5.16 配置 yarn 任务集中分配设置不生效问题
Cookie setting three-day secret free login (run tutorial)
保姆级出题教程
![[蓝桥杯2017初赛]方格分割](/img/e9/e49556d0867840148a60ff4906f78e.png)
[蓝桥杯2017初赛]方格分割

{one week summary} take you into the ocean of JS knowledge

2019腾讯暑期实习生正式笔试
MySQL and C language connection (vs2019 version)
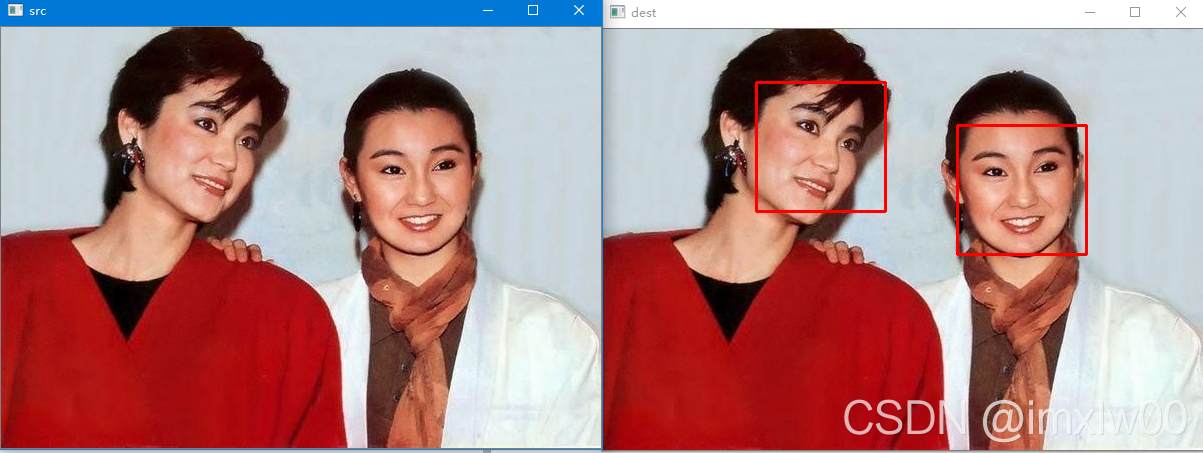
Face recognition_ recognition
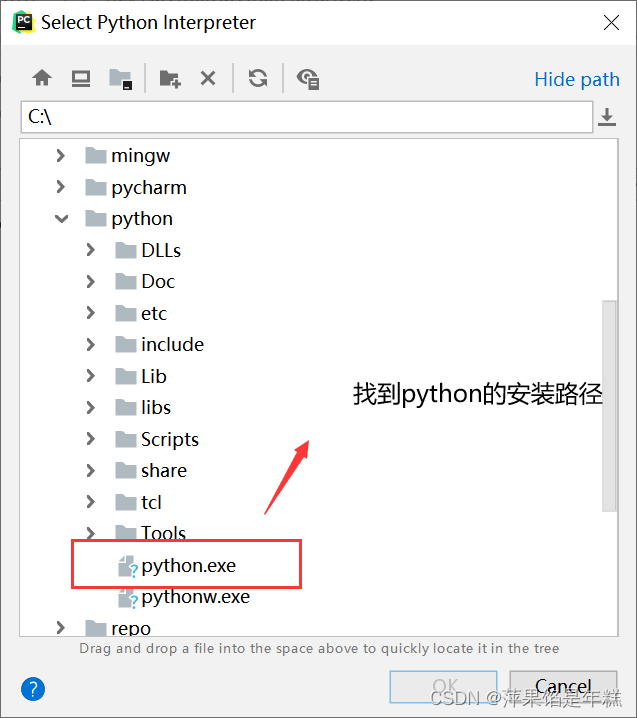
Unable to call numpy in pycharm, with an error modulenotfounderror: no module named 'numpy‘
随机推荐
Password free login of distributed nodes
[yarn] yarn container log cleaning
About string immutability
MATLAB学习和实战 随手记
学习问题1:127.0.0.1拒绝了我们的访问
4、安装部署Spark(Spark on Yarn模式)
Double to int precision loss
Pytorch基础
DICOM: Overview
Face recognition_ recognition
Vs2019 first MFC Application
L2-007 家庭房产 (25 分)
In the era of DFI dividends, can TGP become a new benchmark for future DFI?
02 staff information management after the actual project
Solution to the practice set of ladder race LV1 (all)
Unable to call numpy in pycharm, with an error modulenotfounderror: no module named 'numpy‘
L2-007 family real estate (25 points)
[BSidesCF_2020]Had_ a_ bad_ day
MongoDB
【kerberos】深入理解kerberos票据生命周期