当前位置:网站首页>Analyze "C language" [advanced] paid knowledge [II]
Analyze "C language" [advanced] paid knowledge [II]
2022-07-07 01:49:00 【Choice~】
List of articles
Calculate the length
sizeof:
Calculated variables , Array , The size of the type , Unit is byte ( The operator )
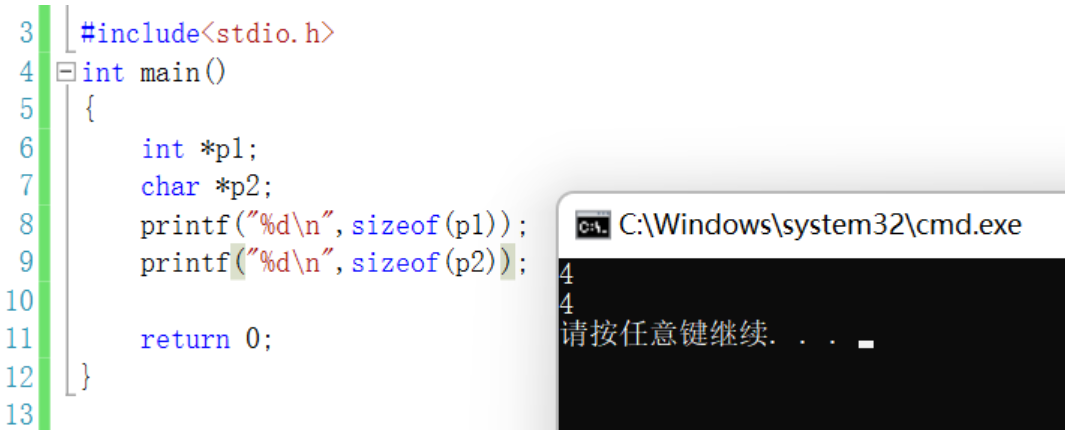
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
//sizeof( Array name )- The array name represents the name of the entire array - It calculates the size of the entire array
//& Array name - The array name represents the entire array , It takes out the address of the entire array
// besides , All array names are the address of the first element of the array
// Shape array
int a[]={
1,2,3,4};
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a));//16
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+0));//4/8 a+0 Is the address of the first element ,sizeof(a+0) It calculates the size of the address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*a));//4 *a Is the first element of the array ,sizoef(*a) It calculates the size of the first element
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+1));//4/8 a+1 Is the address of the second element ,sizeof(a+1) The size of the calculated address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[1]));//4 It calculates the size of the second element
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a));// 4/8 [email protected] Although the address of the array , But it's also the address ,sizeof(&a) It calculates the size of an address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*&a));//16 - Calculate the size of the array
//&a -- int(*p)[4]=&a;
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a+1));//4/8 - &a+1-- The address of the space behind the array
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]+1));//4/8
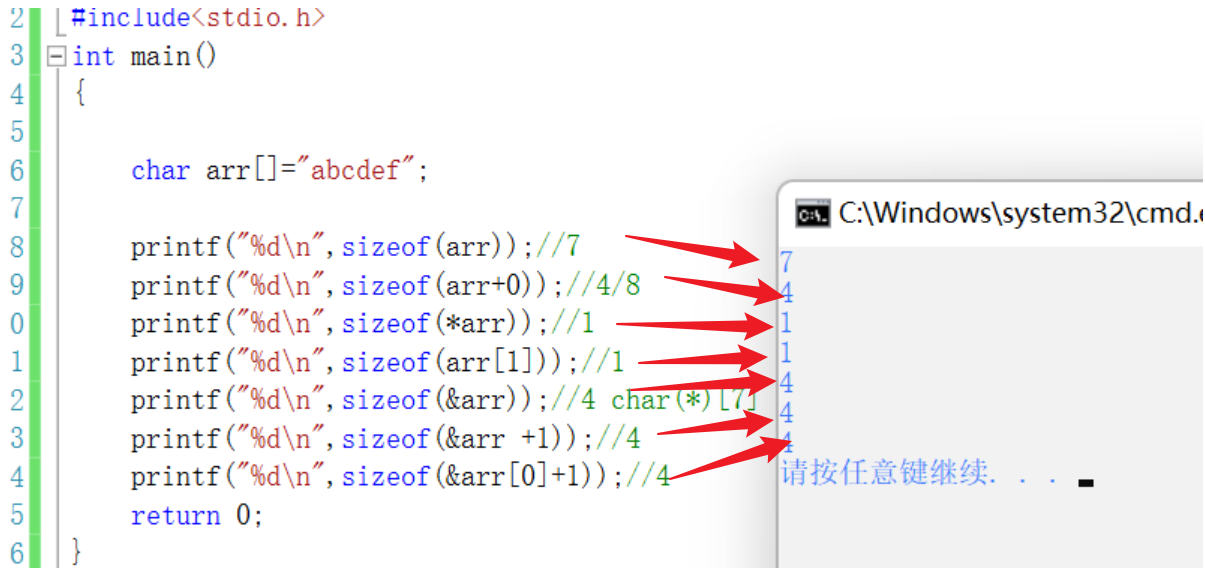
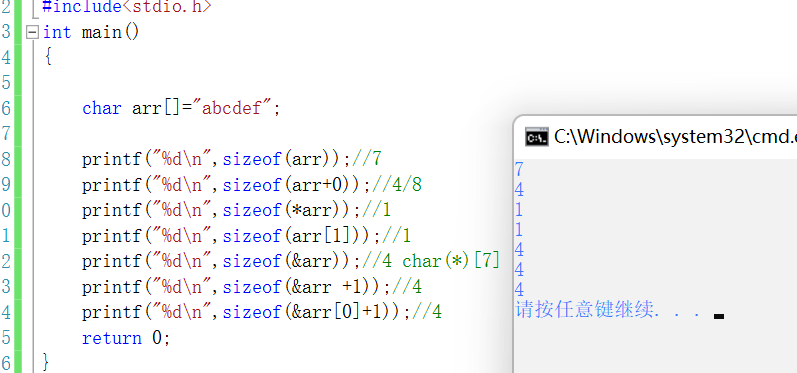
// A character array
char arr[]={
'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr));//6
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr+0));//4/8 - Pointer size - The address indicated by the pointer is 4 A byte address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*arr));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr[1]));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr +1));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr[0]+1));//4/8
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
//sizeof( Array name )- The array name represents the name of the entire array - It calculates the size of the entire array
//& Array name - The array name represents the entire array , It takes out the address of the entire array
// besides , All array names are the address of the first element of the array
// Shape array
int a[]={
1,2,3,4};
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a));//16
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+0));//4/8 a+0 Is the address of the first element ,sizeof(a+0) It calculates the size of the address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*a));//4 *a Is the first element of the array ,sizoef(*a) It calculates the size of the first element
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+1));//4/8 a+1 Is the address of the second element ,sizeof(a+1) The size of the calculated address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[1]));//4 It calculates the size of the second element
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a));// 4/8 [email protected] Although the address of the array , But it's also the address ,sizeof(&a) It calculates the size of an address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*&a));//16 - Calculate the size of the array
//&a -- int(*p)[4]=&a;
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a+1));//4/8 - &a+1-- The address of the space behind the array
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]+1));//4/8
// A character array
char arr[]={
'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr));//6
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr+0));//4/8 - Pointer size - The address indicated by the pointer is 4 A byte address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*arr));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr[1]));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr +1));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr[0]+1));//4/8
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int a[3][4] = {
0 };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a));//48 = 3*4*sizeof(int)
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0][0]));//4 - a[0][0] - Is the first element in the first line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0]));//16
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0] + 1));//4 explain :a[0] As an array name, it is not placed separately in sizeof Inside ,
// I didn't take the address , therefore a[0] It's the first address on the first line
//a[0]+1, Is the address of the second element in the first line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a[0] + 1)));//4 - explain :*(a[0] + 1) Is the second element in the first line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1));//4 - explain :a Is the array name of a two-dimensional array , No address
// It's not alone sizeof Inside , therefore a It represents the address of the first element of the two-dimensional array , namely : The address on the first line
//a + 1 Is the address of the second row of the two-dimensional array
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a + 1)));//16 explain :a+1 Is the address on the second line , therefore *(a+1) It means the second line
// So the calculation is the second 2 The size of the line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1));//4 explain :a[0] Is the array name in the first row ,
//&a[0] What you take out is the address in the first line ,&a[0]+1 It's the address on the second line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(&a[0] + 1)));//&a[0]+1 It's the address on the second line
//*(&a[0]+1) The second line , So the address of the second line of the calculation
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a));//16 explain :a Array name as a two-dimensional array , No, &, Not alone in sizeof Inside
//a Is the address of the first element , That is, the address on the first line , therefore *a It's the first line , It calculates the size of the first line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[3]));//16 explain :a[3] It's actually the array name on the fourth line ( If any )
// So it doesn't really exist , You can also calculate the size by type
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[-1]));
return 0;
}
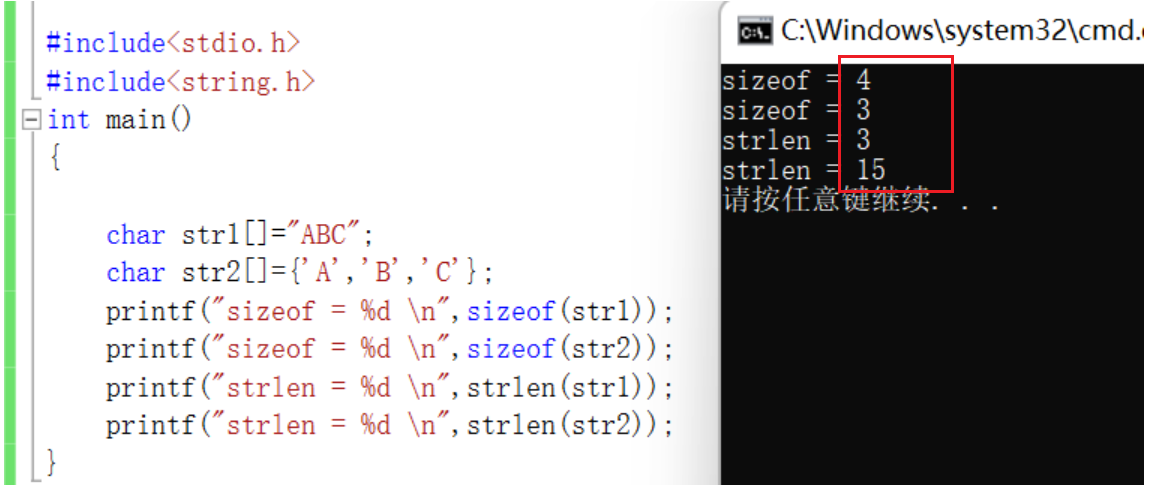
strlen
strlen: Is to find the length of the string , Only for string length ( Library function - Use the reference header file )
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char arr[]={
'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
printf("%d\n",strlen(arr));// Random value - encounter ‘\0’ end
printf("%d\n",strlen(arr+0));// Random value
//printf("%d\n",strlen(*arr));//err
//printf("%d\n",strlen(arr[1]));//err
printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr));// Random value
printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr+1));// Random value - 6
printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr[0]+1));// Random value - 1
return 0;
}
because strlen Just find the length of the string , Random values are generated for characters
The pointer
The size of the pointer variable
32 Bit computer system The integer pointer accounts for 4 Bytes , The actual parameter is passed to the character parameter 4 Bytes
void test1 (char ch)//char *ch
{printf("%d\n",sizeof(ch));//4 Bytes , Because the first address of the character is passed in , That's the pointer char *ch , The length of the pointer is 4, therefore char The passed parameter of character type is the passed pointer byte}
char arr[10]={0};
printf(“%d\n”,sizeof(char));//10
test1(ch);// The first element of the character array
- As long as 32 Bit operating environment , No matter what type , All are 4 Bytes
- stay 64 Bit environment
Declaration pointer
int* a,b,c;
In fact, only variables are declared a It's the pointer type
If you want to declare three pointers :
int *a ,*b, *c;

Structure
. : Structural variable . member
-> : Structure pointer -> member

#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct Book
{
char book_name[20];
int price;
};
int main()
{
struct Book b={
"c Language programming ",55};
struct Book* p = &b;
// Change price
(*p).price=19;// Equate to p->price
printf("%d\n",b.price);
// Change book title
// Use library function strings to copy functions
//b1.name="c++";//error
strcpy(p->book_name,"C++");// because book_name Is a character array name , The array itself is an address , and price It's a variable.
printf("%s\n",(*p).book_name);
printf("%s\t %d\n",p->book_name,p->price);
printf("%s\t%d\n",(*p).book_name,(*p).price);//(*p).book_name,(*p).price Equate to p->book_name,p->price
printf("%s\n",b.book_name);
printf("%d\n",b.price);
return 0;
}
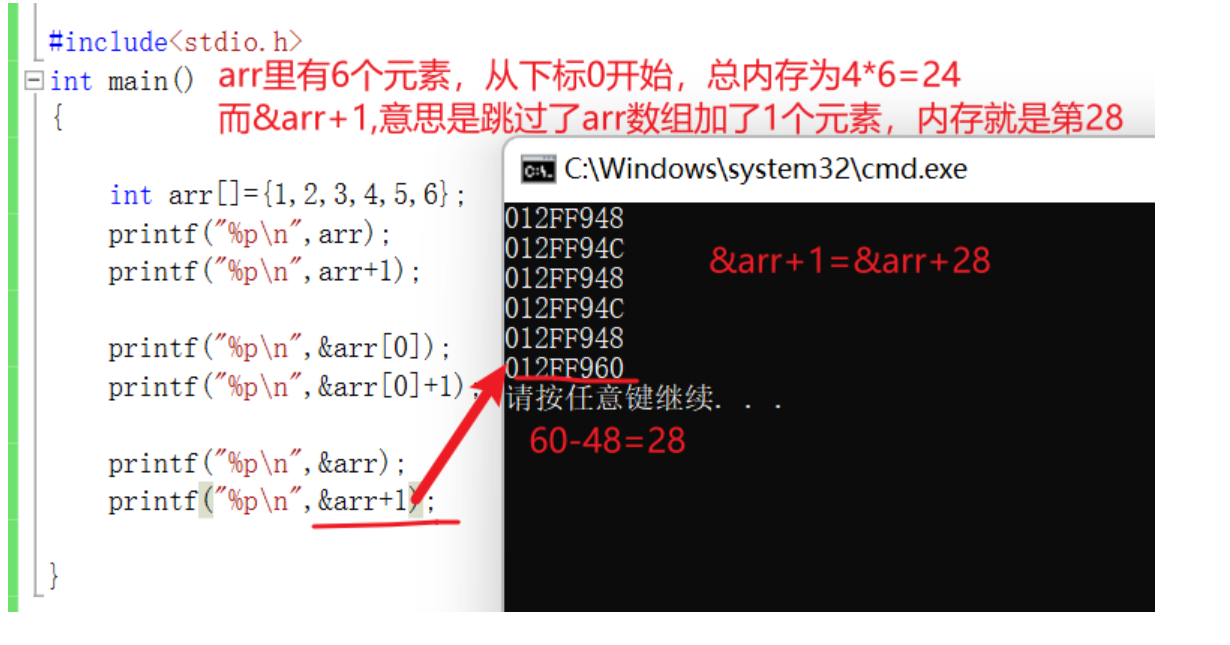
Array element address
1.sizeof( Array name ), Calculate the size of the entire array ,sizeof Put a separate array name inside , The array name represents the entire array
2.& Array name , The address of the extracted array .& Array name , The array name represents the entire array .
In addition to this 1,2 Except for two cases , All array names represent the address of the first element of the array
character string
String comparison
stract(str1,str1); //err, Because I will add that I will ’\0’ overwrite , No, it hasn't been ’\0’ Go back and forth
You can't compare two strings to make them equal , You should use the string
example :
char password[20]={
0};
sacnf("%s",password);
//if(pwssword == "123456")//err
if(strcmp(password,"123456")==0)
printf(" identical ");
Copy of string
Copy the string to the destination address , Debugging we found , encounter ’\0’ End copy
// Change book title
// Use library function strings to copy functions
//b1.name="c++";//error
strcpy(p->book_name,"C++");// because book_name Is a character array name , The array itself is an address
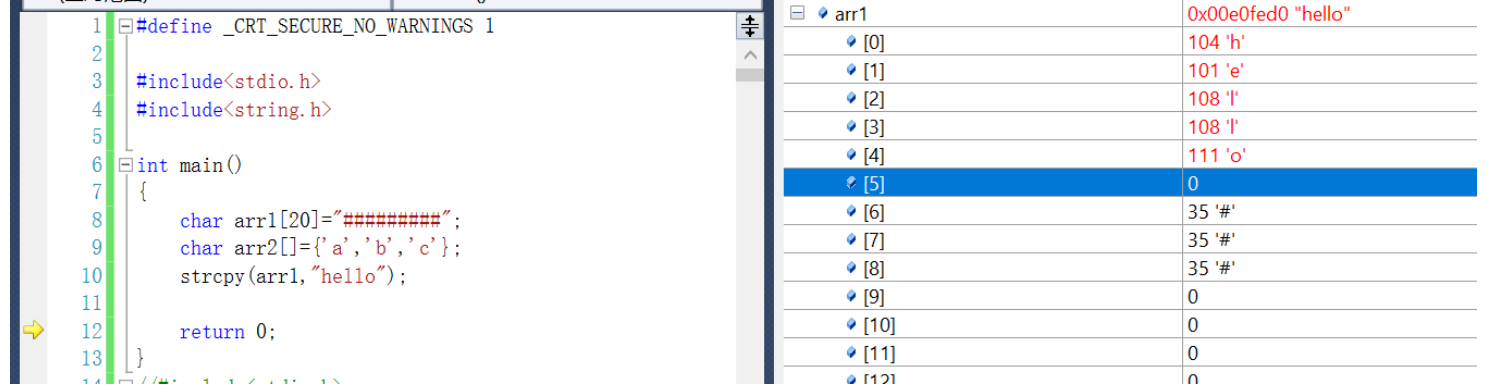
When the copy is not ’\0’ end , Program running error
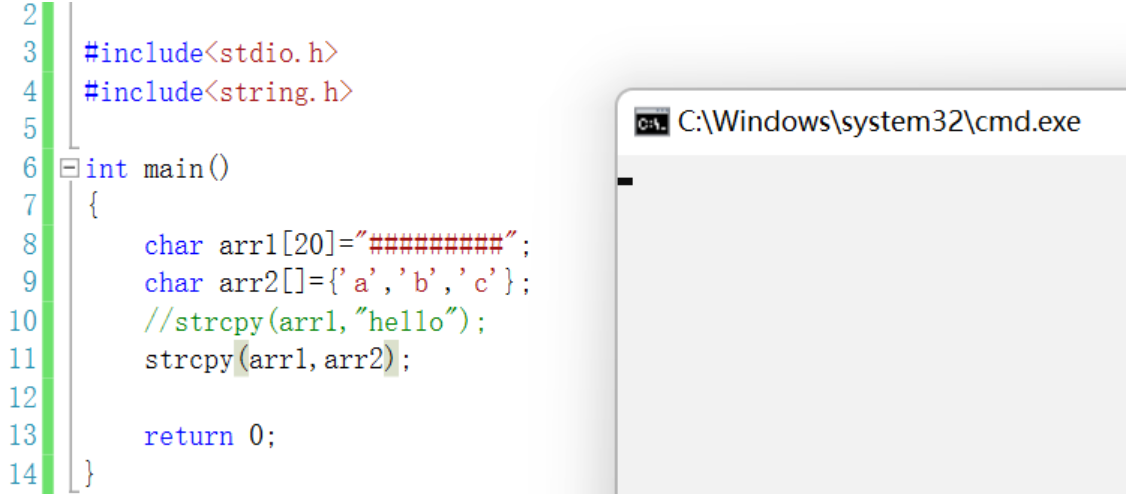
- The source string must be in ‘\0’ end .
- In the source string ‘\0’ Copy to target space .
- The target space has to be large enough , To ensure that the source string can be stored .
- The target space has to be variable .
- Learn to simulate .
Be careful : The source character must be a character array or a pointer to an array of dynamically allocated memory , Cannot use string constants !
Structure
Memory alignment
On the whole :
Memory alignment of structures is a way of trading space for time .
rise .
S1 and S2 The type of members as like as two peas , however S1 and S2 There are some differences in the amount of space taken up .
// for example :
struct S1
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
struct S2
{
char c1;
char c2;
int i;
};
Change the default alignment number
We met before #pragma This preprocessing instruction , Here we use again , We can change our default alignment number .
// for example :
struct S1
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
struct S2
{
char c1;
char c2;
int i;
};
#include <stdio.h>
#pragma pack(8)// Set the default alignment number to 8
struct S1
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
#pragma pack()// Unset the default number of alignments , Restore to default
#pragma pack(1)// Set the default alignment number to 1
struct S2
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
#pragma pack()// Unset the default number of alignments , Restore to default
int main()
{
// What is the result of the output ?
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct S1));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct S2));
边栏推荐
- The difference between Tansig and logsig. Why does BP like to use Tansig
- 7.6 simulation summary
- String to date object
- LeetCode. 剑指offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数
- ROS学习(十九)机器人SLAM功能包——cartographer
- JVM 内存模型
- 百度飞将BMN时序动作定位框架 | 数据准备与训练指南 (上)
- Reptile practice (VI): novel of climbing pen interesting Pavilion
- Shell script quickly counts the number of lines of project code
- Machine learning: the difference between random gradient descent (SGD) and gradient descent (GD) and code implementation.
猜你喜欢

Baidu flying general BMN timing action positioning framework | data preparation and training guide (Part 1)

新工作感悟~辞旧迎新~

Clickhouse fields are grouped and aggregated, and SQL is queried according to the granularity of any time period

刨析《C语言》【进阶】付费知识【二】
Make Jar, Not War
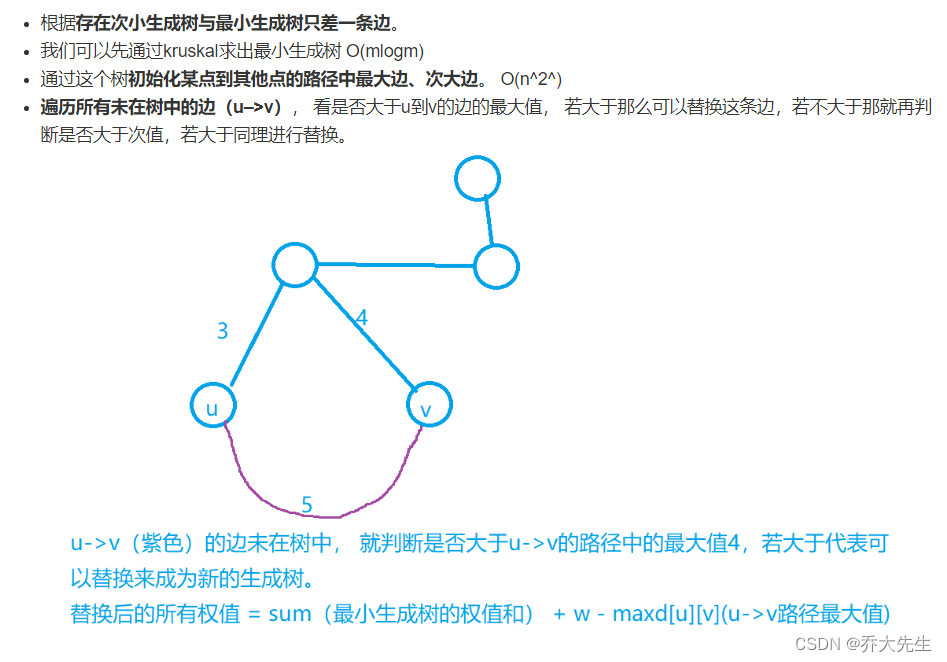
AcWing 1148. Secret milk transportation problem solution (minimum spanning tree)
C语言关于链表的代码看不懂?一篇文章让你拿捏二级指针并深入理解函数参数列表中传参的多种形式
JVM memory model
Appium foundation - appium inspector positioning tool (I)
ROS学习(22)TF变换
随机推荐
hdu 4661 Message Passing(木DP&amp;组合数学)
Mysqlbackup restores specific tables
ROS学习(24)plugin插件
一文带你走进【内存泄漏】
Use nodejs to determine which projects are packaged + released
WCF Foundation
ROS學習(23)action通信機制
Comparison of picture beds of free white whoring
AI automatically generates annotation documents from code
Transplant DAC chip mcp4725 to nuc980
ROS学习(26)动态参数配置
Can't you understand the code of linked list in C language? An article allows you to grasp the secondary pointer and deeply understand the various forms of parameter passing in the function parameter
公钥\私人 ssh避password登陆
[advanced C language] 8 written questions of pointer
AcWing 1142. Busy urban problem solving (minimum spanning tree)
LeetCode:1175. Prime permutation
ROS学习(21)机器人SLAM功能包——orbslam的安装与测试
Make Jar, Not War
JS reverse -- ob confusion and accelerated music that poked the [hornet's nest]
开发中对集合里面的数据根据属性进行合并数量时犯的错误