当前位置:网站首页>Li Kou daily question 1 (2)
Li Kou daily question 1 (2)
2022-07-06 08:50:00 【Baby paper d】
Persimmons should always be picked up and pinched soft , The daily question must also be written from the simplest . Probably just because it started , Just don't want to give up . Simple though , Stick to it, too , Is it just an effort to show yourself ? Perhaps my so-called insistence is also quite ridiculous .
It's just , How happy how to come .
One 、5.28 Remove the outermost bracket
The main idea of the topic : A set of strings , It consists of several characters , It contains several sets of parentheses , The requirement of this question is to delete the outermost parentheses of each group in the string , Output the remaining string .
analysis : It matches the parentheses almost , You need to use a stack to save parentheses , You also need another string to hold the output .
class Solution:
def removeOuterParentheses(self, s: str) -> str:
stack = []
res = ''
for i in s:
# First judge whether there is a right bracket , If you have any , Then output its left bracket
if i == ')':
stack.pop()
# If the stack is not empty , It means that it is not the outermost character , Is added to the result string
if stack:
res += i
# If left parenthesis , Add to the stack
if i == '(':
stack.append(i)
return res
Two 、5.25 The unique substring in the surround string
The main idea of the topic : Given a set of strings p, Judgment string p in a-z-a-z The number of non empty substrings in the circular string , namely p The substring of is in the circular string . Involving dynamic programming , Nor is it simply seeking the longest substring , Because we just find the number of non empty substrings .
I still don't understand dynamic planning , We can't draw inferences from one instance , Just remember that this problem is solved like this , My understanding ability is not good , Have a chance , Have a chance to have a good look , It is important to understand the process of Dynamic Planning . And sliding windows .
class Solution:
def findSubstringInWraproundString(self, p: str) -> int:
dp = defaultdict(int)
# k Used to record the number of consecutive characters
k = 0
for i, ch in enumerate(p):
# The difference between characters is 1 or -25
if i > 0 and (ord(ch) - ord(p[i - 1])) % 26 == 1:
k += 1
else:
k = 1
# dp Is used to record the longest substring ending with the current character
dp[ch] = max(dp[ch], k)
# That's going to be dp All values in add up , It's just a string p Number of all substrings in
return sum(dp.values())3、 ... and 、5.24 Single valued binary trees
The main idea of the topic : Determine whether all values of the binary tree are the same , If the same , return True, otherwise False.
analysis : Breadth first search BFS, Depth-first search DFS Fine , Just traverse the binary tree once .
Breadth first search : You need to complete the search with the help of queues .
There is no need to determine which layer to traverse :
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isUnivalTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
q = deque()
q.append(root)
val = root.val
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
if not cur:
continue
if val != cur.val:
return False;
# Traverse the nodes of the current layer
q.append(cur.left)
q.append(cur.right)
return TrueDepth-first search : There are three kinds of , The first sequence traversal 、 In the sequence traversal 、 After the sequence traversal , Let's take preorder traversal as an example
class Solution:
def isUnivalTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
return self.dfs(root, root.val)
def dfs(self, root, val):
if not root:
return True
if val != root.val:
return False
return self.dfs(root.left, val) and self.dfs(root.right, val)Four 、 In the length of 2N To find out the repetition N Secondary elements
The main idea of the topic : Given an array , The length is 2N, Among them is N+1 Elements , And just one element repeats N Time , Ask for repetition N The next element .
analysis : There's a repetition of an element N Time , And there are N+1 Elements , The length is 2N, Then other elements only appear once . Traverse one side of the array to count and find . Or use hash table ( It is a set of key value structures ), Count .
class Solution:
def repeatedNTimes(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
# # Traversal count
# n = len(nums)/2
# flag = [0 for i in range(0, max(nums)+1)]
# for j in nums:
# flag[j] += 1
# if flag[j] == n:
# return j
# Hash
found = set()
for i in nums:
if i in found:
return i
found.add(i)边栏推荐
- Deep analysis of C language data storage in memory
- Crash problem of Chrome browser
- Detailed explanation of dynamic planning
- Super efficient! The secret of swagger Yapi
- Image,cv2读取图片的numpy数组的转换和尺寸resize变化
- JS native implementation shuttle box
- Unsupported operation exception
- LeetCode:剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和
- After reading the programmer's story, I can't help covering my chest...
- What are the common processes of software stress testing? Professional software test reports issued by companies to share
猜你喜欢

同一局域网的手机和电脑相互访问,IIS设置
Double pointeur en langage C - - modèle classique
JS inheritance method
win10系统中的截图,win+prtSc保存位置
Tcp/ip protocol
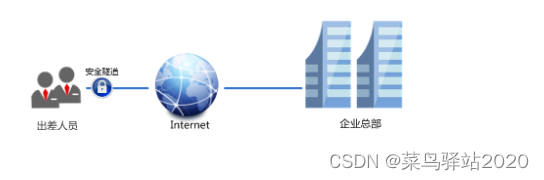
TP-LINK 企业路由器 PPTP 配置
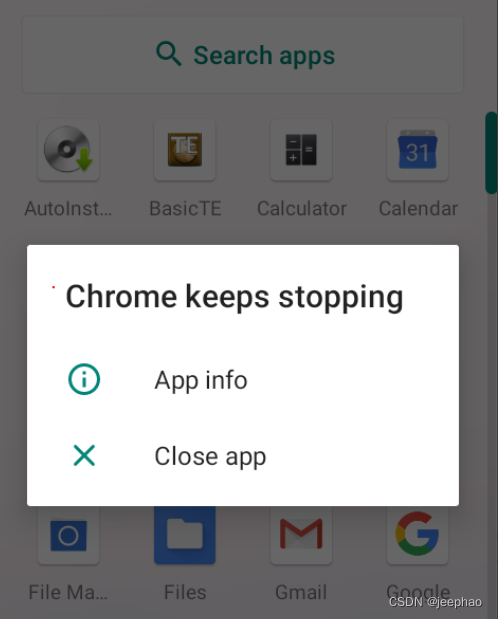
Crash problem of Chrome browser
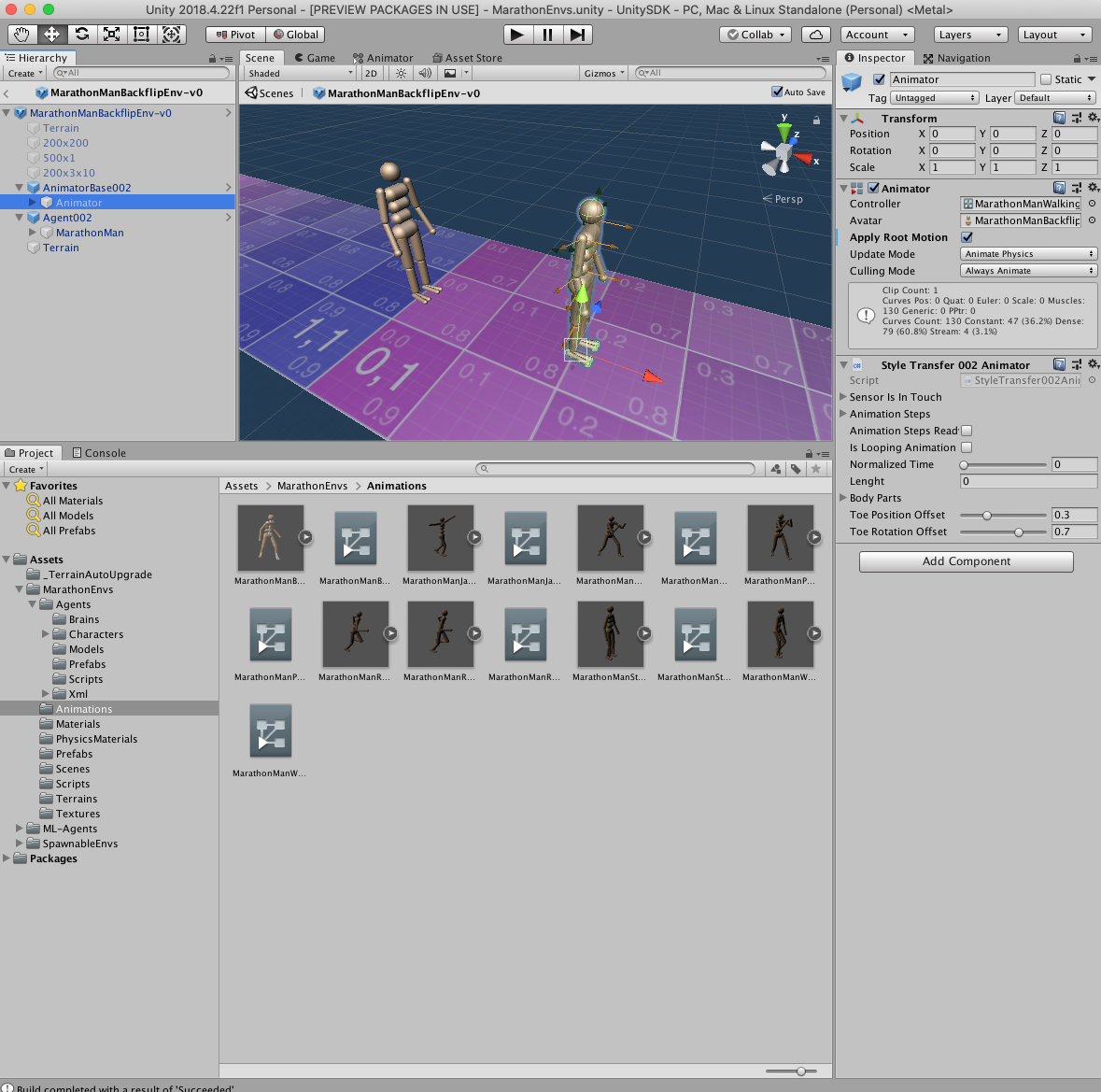
marathon-envs项目环境配置(强化学习模仿参考动作)
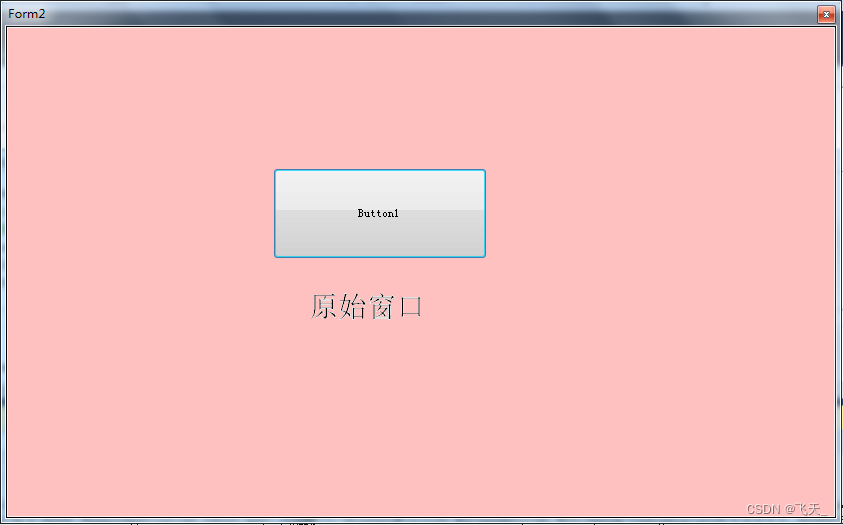
vb. Net changes with the window, scales the size of the control and maintains its relative position

Charging interface docking tutorial of enterprise and micro service provider platform
随机推荐
LeetCode:214. 最短回文串
egg. JS getting started navigation: installation, use and learning
Revit 二次开发 HOF 方式调用transaction
vb.net 随窗口改变,缩放控件大小以及保持相对位置
visdom可视化实现与检查介绍
JS pure function
How to conduct interface test? What are the precautions? Nanny level interpretation
电脑F1-F12用途
【Nvidia开发板】常见问题集 (不定时更新)
【ROS】usb_ Cam camera calibration
LeetCode:124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
Swagger setting field required is mandatory
gcc动态库fPIC和fpic编译选项差异介绍
Computer graduation design PHP Zhiduo online learning platform
@Jsonbackreference and @jsonmanagedreference (solve infinite recursion caused by bidirectional references in objects)
[embedded] cortex m4f DSP Library
Using pkgbuild:: find in R language_ Rtools check whether rtools is available and use sys The which function checks whether make exists, installs it if not, and binds R and rtools with the writelines
egg. JS directory structure
LeetCode:劍指 Offer 42. 連續子數組的最大和
【嵌入式】使用JLINK RTT打印log