当前位置:网站首页>[C language] advanced pointer --- do you really understand pointer?
[C language] advanced pointer --- do you really understand pointer?
2022-07-07 21:18:00 【Pigskin brother】
🧸🧸🧸 Hello everyone , I'm pig skin brother 🧸🧸🧸
Here is the following knowledge content 🥳🥳🥳
Preface
What we are learning today is Advanced pointer .
One 、 Classification of knowledge points
Today's advanced pointer includes character pointer , Array pointer , Pointer array , Array parameter passing and pointer parameter passing , A function pointer , Function pointer array , A pointer to an array of function pointers , Callback functions, etc .
Two 、 The ginseng
1. One dimensional array parameters
// Formal parameters can be written in the form of arrays and pointers
// Real arrays will not be created here , So there is no need to write any size here
// Because only the address of the first element of the array is passed
void test1(int arr[10]);
void test1(int arr[]);
void test1(int *arr);
void test2(int**arr);
void test2(int*arr[]);
int main()
{
int arr1[10]={
0};
int*arr2[20]={
0};
test1(arr1);
test2(arr2);
return 0;
}
2. Pass parameters of two-dimensional array
The first element of a two-dimensional array actually represents the address of the first row
1. Formal parameters are written in the form of arrays
test(int arr[3][5]); Because it's the address in the first line , So here 3 It doesn't make sense , Just columns ( Columns cannot be omitted )
2. Formal parameters are written as pointers
void test(int (*p)[5]);
This is an array pointer ,*p Means it is a pointer ,[5] Represents that this array has five elements ,int The type representing each element is int
It must not be written as void test(int(*p)[3][5]); This represents the entire two-dimensional array , And the address of the first line is only needed for parameter transmission
3、 ... and 、 Various pointers and arrays
1. Special examples of array names
The array name usually represents the address of the first element , But there are two exceptions
1.sizeof( Array name ):sizeof The size of the whole array is calculated with a single array name .
2.& Array name :& Followed by a separate array name, the address of the entire array is taken
2. A function pointer
A function pointer –> Pointer to function
The form of function pointer :
Like functions
int Add(int x,int y)
Then the function pointer is
int (*pf)(int,int);
int Add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
int test(char*str)
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[10];
int(*p)[10]=&arr;
printf("%p\n",&Add);
printf("%p\n",Add);// It can be explained that Add and &Add The address of is the same
// The writing is different , But the meaning is the same , All we get is the address of the function
int(*pf)(int,int)=Add;
// Equate to
//int(*pf)(int,int)=&Add;
int ret=(*pf)(2,3);
//int ret=(********pf)(2,3);
//int ret=Add(2,3);
// there pf That's the function pointer
int(*pf2)(char*)=test;//&test
printf("%d\n",(*pf)(2,3));
printf("%d\n",ret);
return 0;
}
Explanation of function pointer examples
int main()
{
//1.
(*(void(*)())0)();
//void(*)() Is the type of a function pointer
//(void(*)())0 That is the 0 Cast the type to such a function pointer
// signify 0 There is such a function at the address , Which function has the address 0( Here knowledge assumes access 0 This address )
// The application is not accessible 0 At this address
// and int (*pf)(int,int)=Add; analogy , That is to say pf A function is placed at
// Then dereference this address *(void(*)())0 Find this function , Call again *(void(*)())0()
//2.
void (*signal(int, void(*)(int)))(int);
//void(*)(int) yes signal Second parameter of , Is a function pointer
//signal The return type of a function is a function pointer
}
3. Function pointer array
int Add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
int Sub(int x,int y)
{
return x-y;
}
int Mul(int x,int y)
{
return x*y;
}
int Div(int x,int y)
{
return x/y;
}
int main()
{
// Pointer array
// Character pointer array
char*arr[5];
// Array of integer pointers
int*arr2[4];
int(*pf1)(int,int)=Add;
int(*pf2)(int,int)=Sub;
int(*pf3)(int,int)=Mul;
int(*pf4)(int,int)=Div;
// Function pointer array
int (*pf[4])(int,int)={
Add,Sub,Mul,Div};
printf("%d",pf[0](1,2));
return 0;
// First, pf[4] Represents an array , The size is 4
// The type of each element is int (*)(int,int);
}
4. The function pointer array implements the arithmetic unit
int Add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
int Sub(int x,int y)
{
return x-y;
}
int Mul(int x,int y)
{
return x*y;
}
int Div(int x,int y)
{
return x/y;
}
void menu()
{
printf("********************\n");
printf("*** 1.Add ***\n");
printf("*** 2.Sub ***\n");
printf("*** 3.Mul ***\n");
printf("*** 4.Div ***\n");
printf("*** 0.Exit ***\n");
}
// Implement calculator
int main()
{
int input;
int x,y;
int ret;
int (*pf[5])(int,int) = (0,Add,Sub,Mul,Div);
// This initialization is because the array is from 0 At the beginning
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select :>");
scanf("%d\n",&input);
if(input==0)
{
printf(" Exit calculator .....\n");
break;
}
else if(input>=1&&input<=4)
{
printf(" Please enter two operands :>");
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
ret=pf[input](x,y);
printf("ret=%d\n",ret);
}
else
{
printf(" Wrong choice \n");
}
}while(input);
return 0;
}
3、 ... and 、 Callback function and qsort function
1. Callback function
Concept :
A callback function is a function called through a function pointer . If you pass the pointer of a function, that is, the address, as a parameter to another function , When this pointer is used to call the function it points to , Let's just say this is a callback function
The callback function is not called directly by the function's implementer , It's called by another party when a particular event or condition occurs , Used to respond to time or conditions .
A The address of the function is passed to B function , stay B Functions are called callback functions
void test()
{
printf("zhupi\n");
}
void print_zhupi(void(*pf)())
{
if( A condition )// If a certain condition or time occurs , The response
pf();
}
int main()
{
print_zhupi(test);
return 0;
}
Use the callback function to complete the calculator
int Add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
int Sub(int x,int y)
{
return x-y;
}
int Mul(int x,int y)
{
return x*y;
}
int Div(int x,int y)
{
return x/y;
}
void calc(int (*pf)(int,int))
{
int x,y;
int ret=0;
printf(" Please enter two operands :>");
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
ret=pf(x,y);
printf("%d\n",ret);
}
void menu()
{
printf("********************\n");
printf("*** 1.Add ***\n");
printf("*** 2.Sub ***\n");
printf("*** 3.Mul ***\n");
printf("*** 4.Div ***\n");
printf("*** 0.Exit ***\n");
}
// Implement calculator
int main()
{
int input;
int x,y;
int ret;
int (*pf[5])(int,int) = (0,Add,Sub,Mul,Div);
// This initialization is because the array is from 0 At the beginning
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select :>");
scanf("%d\n",&input);
switch(input)
{
case 1:
calc(Add);
break;
case 2:
calc(Sub);
break;
case 3:
calc(Mul);
break;
case 1:
calc(Div);
break;
case 0:
exit(-1);
}
return 0;
}
2.qsort function
qsort Function is a library function , It is a sorting function based on quick sorting algorithm
qsort The header file to be quoted is #include <stdlib.h>
qsort This function can sort any type of data
Functions written by ourselves may not be able to
For example, our bubble sort
void bubble_sort(int arr[],int len)
{
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<len-1-i;j++)
{
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1])
{
int temp=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[]={
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
int len=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
bubble_sort(arr,len);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
// It can be seen that , Not universal
qsort: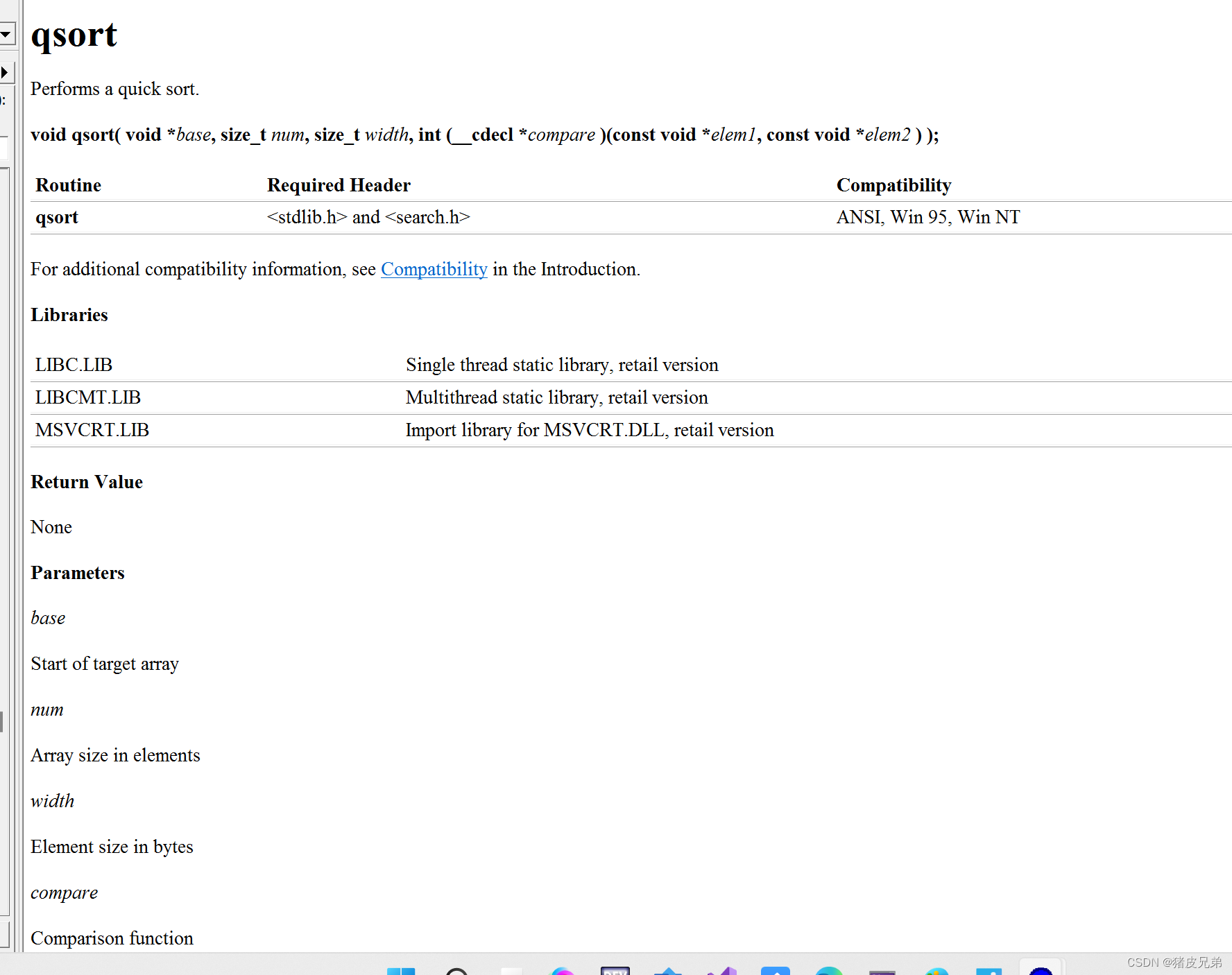
qsort The sorting function defined in the needs to return >0 <0 =0 The number of , After getting the result qsort You can sort according to the returned number
Right now qsort Parameters of
void qsort(void*base,
size_t num,
size_t width,
int(*cmmp)(const void*e1,const void*e2));
//base Is the actual location of the data to be sorted
//num Is the number of elements of the array
//width Is the size of each element
//elem1 elem2 Is the address of the two elements to be compared
// This comparison function requires qsort The user of the function customizes a comparison function
// Because the element types are different , Users according to the actual situation , Provide a comparison function
give an example =>
int cmp_int(const void*e1,const void*e2)
{
//void* Is a pointer without an exact type , Cannot dereference directly
// Because the type of pointer represents the permission to access several bytes when dereferencing , and void* It's not clear ;
//void* It's a garbage can , Any type can be put in , Then it's OK to force type conversion ;
//1.
if(*(int*)e1>*(int*)e2)
{
return 1;
}
else if(*(int*)e1<*(int*)e2)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
//2.
return (*(int*)e1-*(int*)e2;
}
void test()
{
int arr[]={
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
int len=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr,len,sizeof(arr[0]),cmp_int);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
Use qsort Sort structure
struct Stu
{
char mame[20];
int age;
double score;
};
int cmp_stu_by_name(const void*e1,const void*e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->mame, ((struct Stu*)e2)->mame);
}
void test()
{
struct Stu arr[3] = {
{
"zhangsan",20,55.5},{
"lisi",30,88.0},{
"wangwu",10,90.0} };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr,sz,sizeof(arr[0]),cmp_stu_by_name);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
3. General bubble sort
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2)// Compare what you decide
{
return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2;
}
void Swap(char*buf1,char*buf2,int width)
{
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char temp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = temp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
// Byte by byte exchange
}
void bubble_sort(void* base, size_t num, size_t width, int (*cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2))
{
for (int i = 0; i < num - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < num - 1 - i; j++)
{
// Compare , Because I know the width of each element , So cast the type to char*
if (cmp((char*)base+j*width,(char*)base+(j+1)*width)>0)
{
// In exchange for
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width,width);
}
}
}
}
void print_arr(int * base, int sz)
{
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ",*(base+i));
}
}
void test2()
{
int arr[] = {
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubble_sort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_int);
print_arr(arr,sz);
}
int main()
{
test2();
return;
}
Four 、 Various sizeof and strlen The calculation of !!!
1. One dimensional array
int main()
{
int a[] = {
1,2,3,4 };
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a));//16
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+0));//4/8, What is in parentheses is not a separate array name , So it represents the address of the first element , An address is a pointer
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*a));//4 Not a separate array name , therefore a Represents the address of the first element , Quoting , It's the first element
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+1));//4/8 It calculates the size of the address of the second element
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[1]));//4 It calculates the size of the second element
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a));//4/8 &a Take out Is the address of the array , The address of the array is also the address , It's the address ( The pointer ) Size is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*&a));//16 &a It takes out the address of the entire array , Then dereference to get the whole array , So we calculate the size of the whole array
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a+1));//4/8 &a What you get is the address of the whole array ,+1 Is to skip the entire array , But it's also the address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]));//4/8 Represents the address of the first element
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]+1));//4/8 Represents the address of the second element
return 0;
}
2. A character array
int main()
{
char arr[] = {
'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr));//6
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr+0));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*arr));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr[1]));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr+1));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr[0]+1));//4/8
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char arr[] = {
'a','b','c','d','e','f' };
//strlen Look for the end expression \0
printf("%d\n",strlen(arr));// Random value ,arr There is no \0, therefore strlen The function will continue to look back \0, Statistics \0 The number of characters that appear before
printf("%d\n",strlen(arr+0));// Random value
printf("%d\n",strlen(*arr));//error arr Is the address of the first element of the array ,*arr Is the first element of the array ,'a'-97,strlen hold 97 As an address , From this address
// Look back \0, There may be wild pointer problems , Error accessing memory , So the code itself is wrong , Did not get a valid address
// In the eyes of pointer variables , Everything is an address , Because the meaning of his natural existence is to store addresses
printf("%d\n",strlen(arr[1]));//error
printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr));// Random value , look for \0
printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr+1));// Random value
printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr[0]+1));// Random value
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr));//7
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr+0));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*arr));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr[1]));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr+1));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr[0]+1));//4/8
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr));//6
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr + 0));//6
printf("%d\n", strlen(*arr));//error
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr[1]));//error
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr));//6
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr + 1));// Random value
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr[0] + 1));//5
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char* p = "abcdef";// Constant string
//p yes 'a' The address of
printf("%d\n",sizeof(p));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(p+1));//4/8 p+1 yes 'b' The address of
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*p));//18
printf("%d\n",sizeof(p[0]));//1
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&p));//4/8 &p Is the address of the pointer , Double pointer
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&p+1));//4/8
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&p[0]+1));//4/8
printf("%d\n",strlen(p));//6
printf("%d\n",strlen(p+1));//5
printf("%d\n",strlen(*p));//error
printf("%d\n",strlen(p[0]));//error
printf("%d\n",strlen(&p));// Random value
printf("%d\n",strlen(&p+1));// Random value
printf("%d\n",strlen(&p[0]+1));//5
return 0;
}
3. Two dimensional array
int main()
{
int a[3][4] = {
0 };
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a));//48 sizeof( Array name ) It calculates the size of the entire array
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[0][0]));//4
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[0]));//16 a[0] yes *(a+0) Is the address of the first element in the first line , That is, the array name in the first line , therefore sizeof(a[0]) In fact, it calculates the size of the first row
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[0]+1));//4/8 a[0] Is the array name in the first row ,a[0]+1 That is, the address of the second element in the first line
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*(a[0]+1)));//4 That is to say a[0][1]
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+1));//4/8 The array name of a two-dimensional array represents the address of the first line , therefore a+1 It represents the address in the second line
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*(a+1)));//16 a+1 Is the address on the second line , After dereference, the address of the first element in the second line , So we're calculating the size of the second line
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]+1));//4/8 It represents the address in the second line
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*(&a[0]+1)));//16 The parentheses indicate the address of the first element in the second line That is, the array name in the second line , It calculates the size of the second row of the array
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*a));//16 The address of the first row array is calculated
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[3]));//16 a[3] Is the address of the first element in the fourth line
return 0;
}
5、 ... and 、 5、 ... and The color spot Beautiful Of One some Scrap word
When you see here , I believe the above content has been memorized ️️️. If you find it helpful , Use your little hand to point . Is there a problem with one button three times ? No problem , What are these ? traditional code of conduct . It's not easy to create , Support a lot .
边栏推荐
- FatMouse&#39; Trade (Hangdian 1009)
- 嵌入式系统真正安全了吗?[ OneSpin如何为开发团队全面解决IC完整性问题 ]
- Don't fall behind! Simple and easy-to-use low code development to quickly build an intelligent management information system
- 反诈困境,国有大行如何破局?
- 使用枚举实现英文转盲文
- 【OpenCV 例程200篇】223. 特征提取之多边形拟合(cv.approxPolyDP)
- MinGW MinGW-w64 TDM-GCC等工具链之间的差别与联系「建议收藏」
- 微服务远程Debug,Nocalhost + Rainbond微服务开发第二弹
- Can Huatai Securities achieve Commission in case of any accident? Is it safe to open an account
- easyui 日期控件清空值
猜你喜欢
Apifox interface integrated management new artifact

神兵利器——敏感文件发现工具
Intelligent software analysis platform embold
SQL注入报错注入函数图文详解

Ubuntu安装mysql8遇到的问题以及详细安装过程

程序猿赚的那点钱算个P啊!

Measure the height of the building
MySQL storage expression error
![[paper reading] maps: Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Based Portfolio Management System](/img/76/b725788272ba2dcdf866b28cbcc897.jpg)
[paper reading] maps: Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Based Portfolio Management System

【C语言】指针进阶---指针你真的学懂了吗?
随机推荐
Awk processing JSON processing
恶魔奶爸 A1 语音听力初挑战
[UVALive 6663 Count the Regions] (dfs + 离散化)[通俗易懂]
Is private equity legal in China? Is it safe?
【OpenCV 例程200篇】223. 特征提取之多边形拟合(cv.approxPolyDP)
万字总结数据存储,三大知识点
阿里云有奖体验:如何通过ECS挂载NAS文件系统
恶魔奶爸 A3阶段 近常速语流初接触
Introduction to referer and referer policy
Micro service remote debug, nocalhost + rainbow micro service development second bullet
openGl超级宝典学习笔记 (1)第一个三角形「建议收藏」
单词反转实现「建议收藏」
I wrote a markdown command line gadget, hoping to improve the efficiency of sending documents by garden friends!
Le capital - investissement est - il légal en Chine? C'est sûr?
Spark judges that DF is empty
Unity3d 4.3.4f1 execution project
Unity3d 4.3.4f1执行项目
开户必须往账户里面赚钱吗,资金安全吗?
FTP steps for downloading files from Huawei CE switches
Usage of MySQL subquery keywords (exists)