当前位置:网站首页>341. Flatten nested list iterator
341. Flatten nested list iterator
2022-07-06 12:43:00 【Zhang Wenhao】
341. Flatten nested list iterators
Flatten Nested List Iterator
List of articles
Title Description :
Give you a nested list of integers nestedList . Each element is either an integer , Or a list ; The elements of the list may also be integers or other lists . Please implement an iterator to flatten it , So that it can traverse all integers in this list .
Implement the flat iterator class NestedIterator :
NestedIterator(List<NestedInteger> nestedList)Using nested lists nestedList
Initialize iterator .int next()Returns the next integer of the nested list .boolean hasNext()If there are still integers to be iterated , return true ; otherwise , return false .
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-nested-list-iterator/
You are given a nested list of integers nestedList. Each element is either an integer or a list whose elements may also be integers or other lists. Implement an iterator to flatten it.
Implement the NestedIterator class:
- NestedIterator(List nestedList) Initializes the
iterator with the nested listnestedList. - int next() Returns the next integer in the nested list.
- boolean hasNext() Returns true if there are still some integers in
the nested list and false otherwise.
Example :

Method
The mathematical formula
We can traverse the entire nested list first , Store all integers in an array , Then traverse the array to achieve next \texttt{next} next and hasNext \texttt{hasNext} hasNext Method .
Java
Depth-First Search (DFS)
/** * // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. * // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation * public interface NestedInteger { * * // @return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list. * public boolean isInteger(); * * // @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer * // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list * public Integer getInteger(); * * // @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list * // Return empty list if this NestedInteger holds a single integer * public List<NestedInteger> getList(); * } */
public class NestedIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
private List<Integer>list;
private int index=0;
private void dfs(List<NestedInteger> nestedList){
if(nestedList.size()==0){
return;
}
for(NestedInteger nestedInteger:nestedList){
if(nestedInteger.isInteger()){
list.add(nestedInteger.getInteger());
}else{
List<NestedInteger>nestedList1=nestedInteger.getList();
dfs(nestedList1);
}
}
}
public NestedIterator(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) {
list=new ArrayList<>();
dfs(nestedList);
}
@Override
public Integer next() {
return list.get(index++);
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index<list.size();
}
}
/** * Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * NestedIterator i = new NestedIterator(nestedList); * while (i.hasNext()) v[f()] = i.next(); */
Queue
/** * // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. * // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation * public interface NestedInteger { * * // @return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list. * public boolean isInteger(); * * // @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer * // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list * public Integer getInteger(); * * // @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list * // Return empty list if this NestedInteger holds a single integer * public List<NestedInteger> getList(); * } */
public class NestedIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
private Queue<Integer>q;
private void dfs(List<NestedInteger> nestedList){
if(nestedList.size()==0){
return;
}
for(NestedInteger nestedInteger:nestedList){
if(nestedInteger.isInteger()){
q.offer(nestedInteger.getInteger());
}else{
List<NestedInteger>nestedList1=nestedInteger.getList();
dfs(nestedList1);
}
}
}
public NestedIterator(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) {
q=new LinkedList<>();
dfs(nestedList);
}
@Override
public Integer next() {
return q.poll();
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return q.size()!=0;
}
}
/** * Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * NestedIterator i = new NestedIterator(nestedList); * while (i.hasNext()) v[f()] = i.next(); */
Stack
/** * // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. * // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation * public interface NestedInteger { * * // @return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list. * public boolean isInteger(); * * // @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer * // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list * public Integer getInteger(); * * // @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list * // Return empty list if this NestedInteger holds a single integer * public List<NestedInteger> getList(); * } */
public class NestedIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
private Stack<NestedInteger>st;
public NestedIterator(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) {
st=new Stack<>();
for(int i=nestedList.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
st.push(nestedList.get(i));
}
}
@Override
public Integer next() {
return st.pop().getInteger();
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
while(!st.isEmpty()){
NestedInteger cur=st.peek();
if(cur.isInteger()){
return true;
}
st.pop();
List<NestedInteger> list=cur.getList();
for(int i=list.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
st.push(list.get(i));
}
}
return false;
}
}
/** * Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * NestedIterator i = new NestedIterator(nestedList); * while (i.hasNext()) v[f()] = i.next(); */
C++
Depth-First Search (DFS)
/** * // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. * // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation * class NestedInteger { * public: * // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list. * bool isInteger() const; * * // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer * // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list * int getInteger() const; * * // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list * // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer * const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const; * }; */
class NestedIterator {
private:
vector<int>list;
int index=0;
void dfs(vector<NestedInteger> nestedList){
if(nestedList.size()==0){
return;
}
for(NestedInteger nestedInteger:nestedList){
if(nestedInteger.isInteger()){
list.push_back(nestedInteger.getInteger());
}else{
vector<NestedInteger>nestedList1=nestedInteger.getList();
dfs(nestedList1);
}
}
}
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
dfs(nestedList);
}
int next() {
return list[index++];
}
bool hasNext() {
return index<list.size();
}
};
/** * Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * NestedIterator i(nestedList); * while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next(); */
Queue
/** * // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. * // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation * class NestedInteger { * public: * // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list. * bool isInteger() const; * * // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer * // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list * int getInteger() const; * * // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list * // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer * const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const; * }; */
class NestedIterator {
private:
queue<int>q;
int index=0;
void dfs(vector<NestedInteger> nestedList){
if(nestedList.size()==0){
return;
}
for(NestedInteger nestedInteger:nestedList){
if(nestedInteger.isInteger()){
q.push(nestedInteger.getInteger());
}else{
vector<NestedInteger>nestedList1=nestedInteger.getList();
dfs(nestedList1);
}
}
}
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
dfs(nestedList);
}
int next() {
int front=q.front();
q.pop();
return front;
}
bool hasNext() {
return !q.empty();
}
};
/** * Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * NestedIterator i(nestedList); * while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next(); */
Stack
class NestedIterator {
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
for (int i = nestedList.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
st.push(nestedList[i]);
}
}
int next() {
NestedInteger cur = st.top(); st.pop();
return cur.getInteger();
}
bool hasNext() {
while (!st.empty()) {
NestedInteger cur = st.top();
if (cur.isInteger()) {
return true;
}
st.pop();
for (int i = cur.getList().size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
st.push(cur.getList()[i]);
}
}
return false;
}
private:
stack<NestedInteger> st;
};
author :fuxuemingzhu
link :https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-nested-list-iterator/solution/fu-xue-ming-zhu-xiang-jie-ti-yi-shu-li-d-n4qa/
source : Power button (LeetCode)
The copyright belongs to the author . Commercial reprint please contact the author for authorization , Non-commercial reprint please indicate the source .
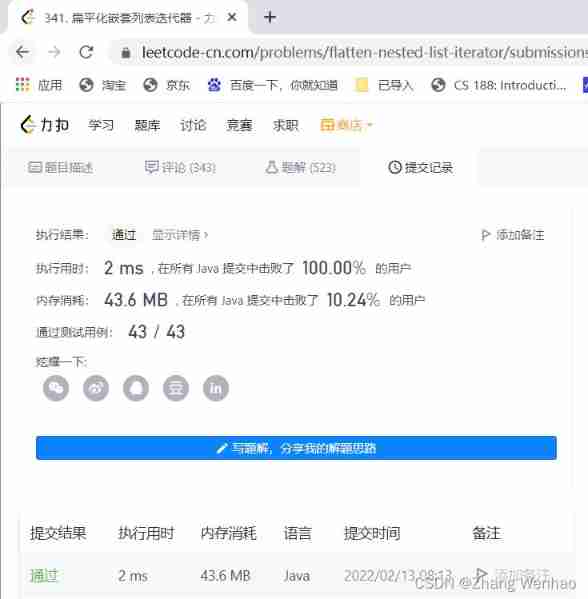
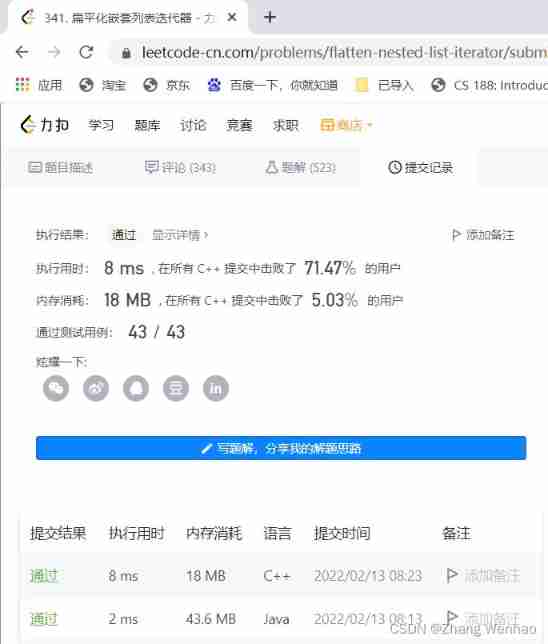
Through screenshots
边栏推荐
- 基于Redis的分布式锁 以及 超详细的改进思路
- Latex learning
- Redis cache update strategy, cache penetration, avalanche, breakdown problems
- @Autowired 和 @Resource 的区别
- 数据库课程设计:高校教务管理系统(含代码)
- ORA-02030: can only select from fixed tables/views
- ES6 grammar summary -- Part 2 (advanced part es6~es11)
- Introduction to the daily practice column of the Blue Bridge Cup
- Basic operations of databases and tables ----- modifying data tables
- 基于Redis的分布式ID生成器
猜你喜欢
Particle system for introduction to unity3d Foundation (attribute introduction + case production of flame particle system)
In 2020, the average salary of IT industry exceeded 170000, ranking first

Symbolic representation of functions in deep learning papers

Unity3D基础入门之粒子系统(属性介绍+火焰粒子系统案例制作)
NRF24L01故障排查
Pat 1097 duplication on a linked list (25 points)
JS變量類型以及常用類型轉換

数据库课程设计:高校教务管理系统(含代码)

Basic operations of databases and tables ----- classification of data

Basic operations of databases and tables ----- creating data tables
随机推荐
C programming exercise
Whistle+switchyomega configure web proxy
[leetcode15] sum of three numbers
基于Redis的分布式锁 以及 超详细的改进思路
InnoDB dirty page refresh mechanism checkpoint in MySQL
燕山大学校园网自动登录问题解决方案
Unity场景跳转及退出
ESP8266连接onenet(旧版MQTT方式)
[leetcode19] delete the penultimate node in the linked list
FairyGUI增益BUFF数值改变的显示
MySQL performance tuning - dirty page refresh
[offer9]用两个栈实现队列
(课设第一套)1-4 消息传递接口 (100 分)(模拟:线程)
Important methods of array and string
[golang] leetcode intermediate - fill in the next right node pointer of each node & the k-smallest element in the binary search tree
FairyGUI摇杆
ES6 grammar summary -- Part I (basic)
FairyGUI简单背包的制作
Design and implementation of general interface open platform - (39) simple and crude implementation of API services
Unity3d, Alibaba cloud server, platform configuration