当前位置:网站首页>Enterprise log analysis system elk
Enterprise log analysis system elk
2022-07-07 15:58:00 【Oranges are delicious】
List of articles
- One 、ELK Brief introduction of log analysis system
- Two 、 Why use ELK
- 3、 ... and 、 The basic characteristics of complete log system
- Four 、ELK How it works
- 5、 ... and 、 Deploy ELK Log analysis system
One 、ELK Brief introduction of log analysis system
ELK The platform is a complete set of centralized log processing solutions , take ElasticSearch、Logstash and Kiabana Three open source tools are used together , Complete more powerful user query of logs 、 Sort 、 Statistical needs .
1、ElasticSearch
- ElasticSearch: Is based on Lucene( The architecture of a full-text search engine ) Developed distributed storage retrieval engine , Used to store all kinds of logs .
- Elasticsearch Yes, it is Java Developed , It can be done by RESTful Web Interface , So that users can communicate with Elasticsearch signal communication .
- Elasticsearch It's a real-time 、 Distributed and scalable search engine , Allow full text 、 Structured search , It is usually used to index and search large amounts of log data , It can also be used to search for many different types of documents .
2、Kiabana
Kibana Usually with Elasticsearch Deploy together ,Kibana yes Elasticsearch A powerful data visualization Dashboard,Kibana Provide graphical web Interface to browse Elasticsearch Log data , Can be used to summarize 、 Analyze and search important data .
3、Logstash
Logstash As a data collection engine . It supports dynamic data collection from various data sources , And filter the data 、 analysis 、 Enrich 、 Unified format and other operations , Then store it in the location specified by the user , Usually sent to Elasticsearch.
Logstash from Ruby Language writing , Running on the Java virtual machine (JVM) On , It is a powerful data processing tool , Data transmission can be realized 、 Format processing 、 Format output .Logstash It has powerful plug-in function , Commonly used for log processing .
4、 Other components Filebeat
Filebeat: Lightweight open source log file data collector . It is usually installed on the client that needs to collect data Filebeat, And specify the directory and log format ,Filebeat Can quickly collect data , And send it to logstash To analyze , Or send it directly to Elasticsearch Storage , Performance compared to JVM Upper logstash Obvious advantages , It's a replacement . Often applied to EFLK Architecture .
5、filebeat combination logstash Benefits
adopt Logstash With disk based adaptive buffering system , The system will absorb the incoming throughput , To lessen Elasticsearch Pressure to keep writing data
From other data sources ( Like databases ,S3 Object store or message delivery queue ) Extract from
Sending data to multiple destinations , for example S3,HDFS(Hadoop distributed file system ) Or write to a file
Use conditional data flow logic to form more complex processing pipelines
6、 cache / Message queue
cache / Message queue (redis 、kafka、RabbitMQ etc. ): You can peak traffic for highly concurrent log data , Such buffering can protect data from loss to a certain extent , You can also apply decoupling to the entire architecture .
7、Fluentd
Fluentd Is a popular open source data collector . because logstash The disadvantage of being too heavy ,Logstash Low performance 、 More resource consumption and other problems , And then there's this Fluentd Appearance . Comparison logstash,Fluentd An alternative to , Often applied to EFK Architecture . stay Kubernetes It is also commonly used in clusters EFK As a scheme for log data collection . stay Kubernetes In the cluster, it is generally through DaemonSet To run the Fluentd, So that it's in every Kubernetes You can run one on a work node Pod. It gets the container log file 、 Filter and transform log data , And then pass the data to Elasticsearch colony , Index and store it in the cluster .
Two 、 Why use ELK
Logs mainly include system logs 、 Application logs and security logs . The system operation and maintenance personnel and developers can understand the software and hardware information of the server through the log 、 Check the errors in the configuration process and the causes of the errors . Regular log analysis can help you understand the load of the server , Performance security , So as to take measures to correct mistakes in time .
Often we use the log of a single machine grep、awk And other tools can basically achieve simple analysis , But when logs are distributed across different devices . If you manage hundreds of servers , You're still using the traditional method of logging in each machine in turn to look up the logs . Does this feel tedious and inefficient . We need to use centralized log management , for example : Open source syslog, Summarize the log collection on all servers . After centralized management of logs , Log statistics and retrieval has become a more cumbersome thing , Generally we use grep、awk and wc etc. Linux Command can realize retrieval and statistics , But for more demanding queries 、 Sorting and statistics requirements and large number of machines are still using this method, which is hard to avoid .
Generally, a large system is a distributed deployment architecture , Different service modules are deployed on different servers , When problems arise , Most situations need to be based on the key information exposed by the problem , Go to specific servers and service modules , Building a centralized log system , It can improve the efficiency of location problem .
3、 ... and 、 The basic characteristics of complete log system
collect : Be able to collect log data from multiple sources
transmission : It can stably parse, filter and transmit log data to the storage system
Storage : Store log data
analysis : Support UI analysis
Warning : Able to provide error reports , Monitoring mechanism
Four 、ELK How it works
(1) Deploy on all servers that need to collect logs Logstash; Or you can centralize the log management on the log server , Deploy on the log server Logstash.
(2)Logstash Collect the logs , Format the log and output it to Elasticsearch In a crowd .
(3)Elasticsearch Index and store the formatted data .
(4)Kibana from ES Query data in the cluster to generate charts , And display the front-end data .
summary :logstash As a log collector , Collect data from a data source , And filter the data , format processing , And then leave it to Elasticsearch Storage ,kibana Visualize the log .
5、 ... and 、 Deploy ELK Log analysis system
Experiment preparation
node1 node (2c/4g):20.0.0.5
node2 node (2c/4g):20.0.0.6
apache node :20.0.0.12
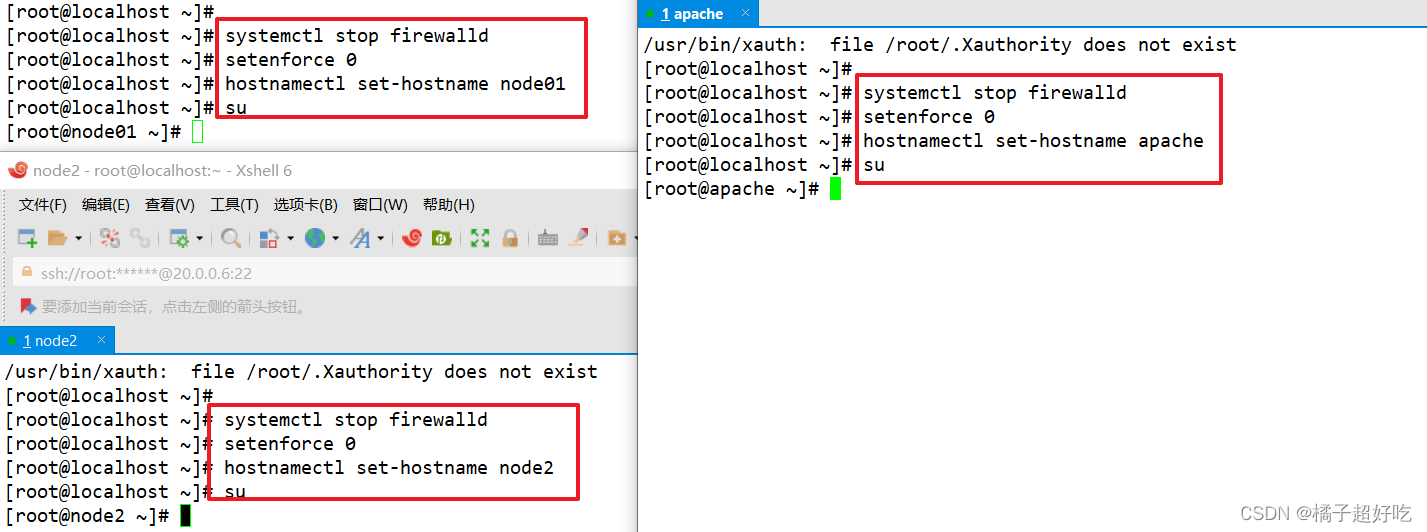
## All servers
systemctl stop firewalld
setenforce 0
## Modify hostname
hostnamectl set-hostname node1
su
hostnamectl set-hostname node2
su
hostnamectl set-hostname apache
su
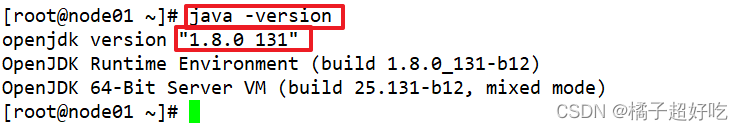
## Set up Java Environmental Science
java -version ## The default is installed , If not installed ,yum -y install java
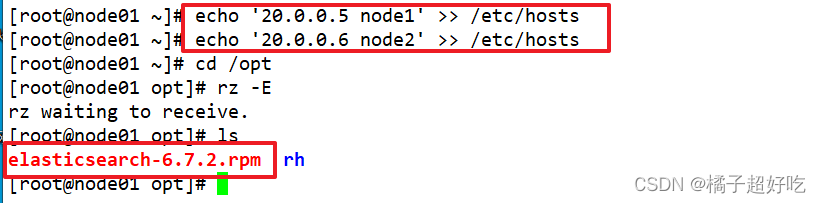
1、 To configure elasticsearch Environmental Science (node1、node2)
With node1 For example ,node2 Configuration and 1 almost , The name in the configuration file is different
echo '20.0.0.5 node1' >> /etc/hosts
echo '20.0.0.6 node2' >> /etc/hosts
cd /opt
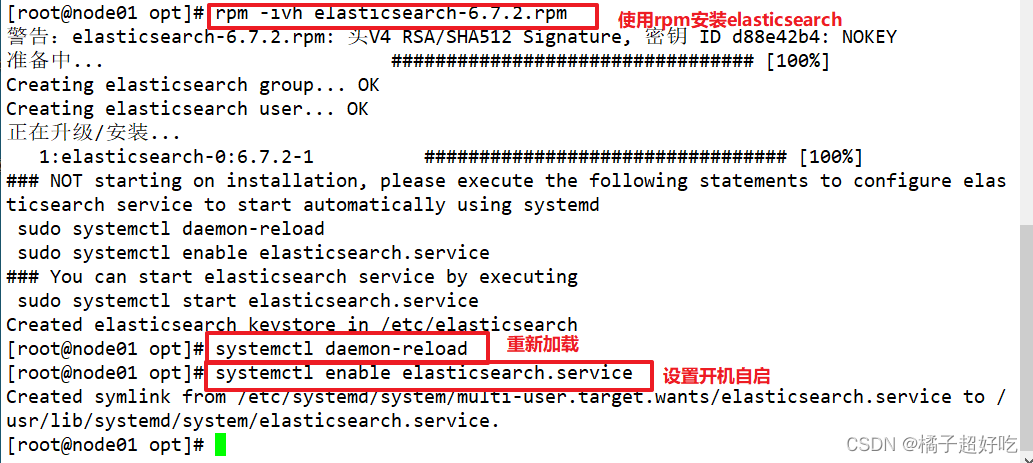
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-6.7.2.rpm
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
cp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.bak
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
--17-- uncomment , Specify the cluster name
cluster.name: my-elk-cluster
--23-- uncomment , Specify the node name :node1 The node is node1,node2 The node is node2
node.name: node1
node.master: true # whether master node ,false Why not
node.data: true # Whether the data node ,false Why not
--35-- uncomment , Specify the data storage path
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
--39-- uncomment , Specify the log storage path
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
--45-- uncomment , avoid es Use swap Swap partition
bootstrap.memory_lock: false
--57-- uncomment , Set listening address ,0.0.0.0 For all addresses
network.host: 0.0.0.0
--61-- uncomment ,ES The default listening port of the service is 9200
http.port: 9200 # Appoint es The cluster provides an interface for external access
transport.tcp.port: 9300 # Appoint es Internal communication interface of the cluster
--71-- uncomment , Cluster discovery is realized by unicast , Specify the nodes to discover
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["node1:9300", "node2:9300"]
grep -v "^#" /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml

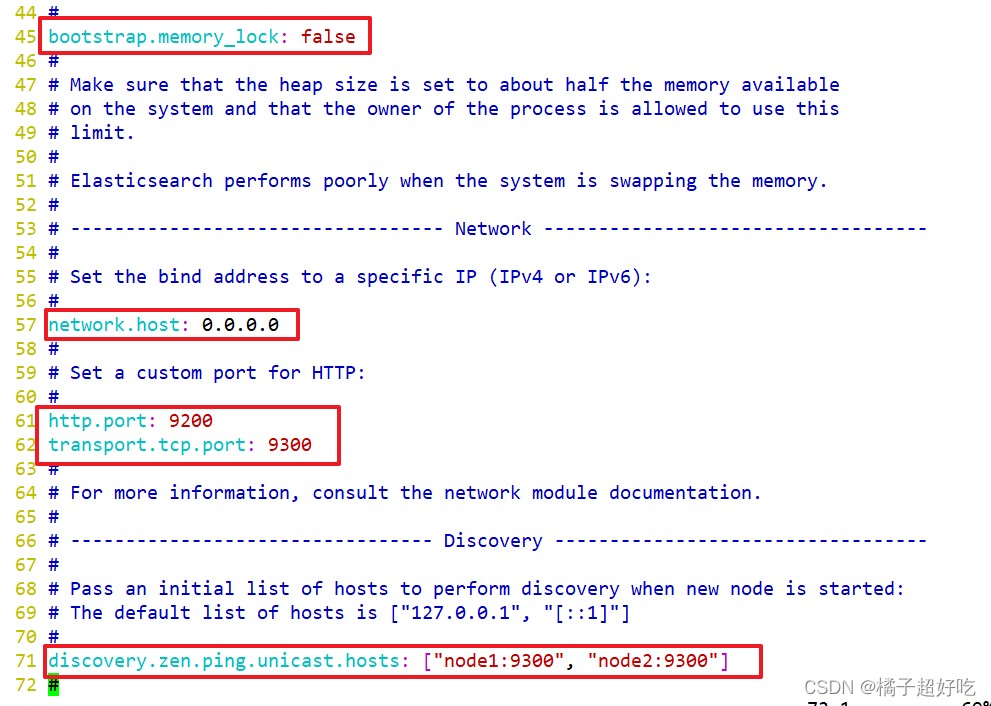
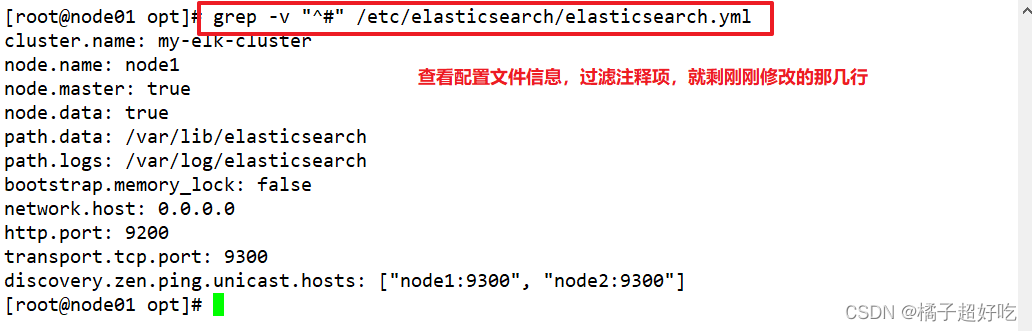
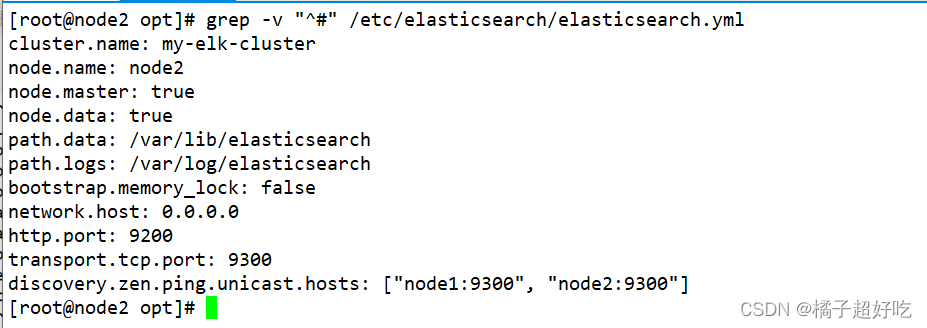
systemctl restart elasticsearch
netstat -antp |grep 9200
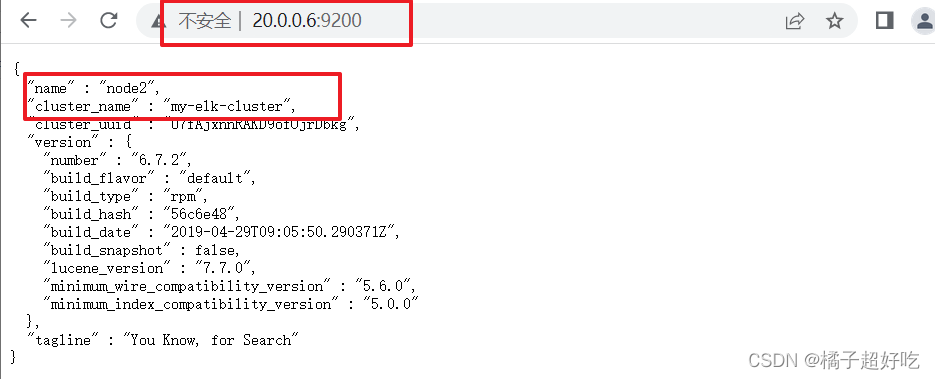
2、 View node information
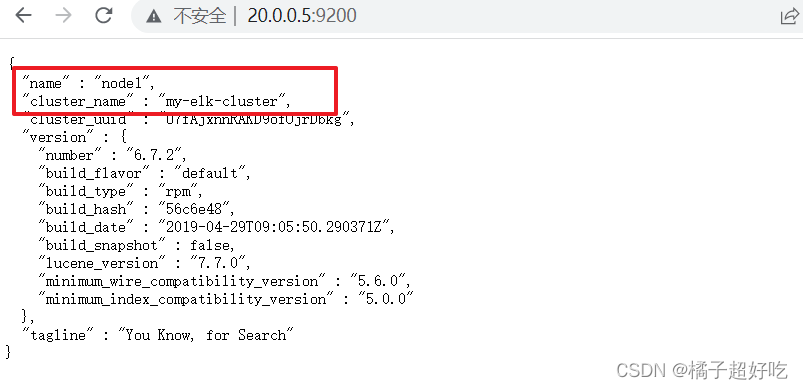
## browser
http://20.0.0.5:9200
http://20.0.0.6:9200
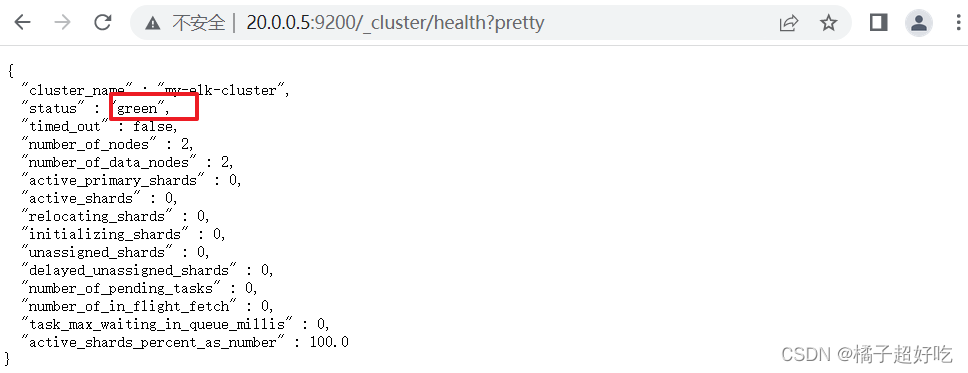
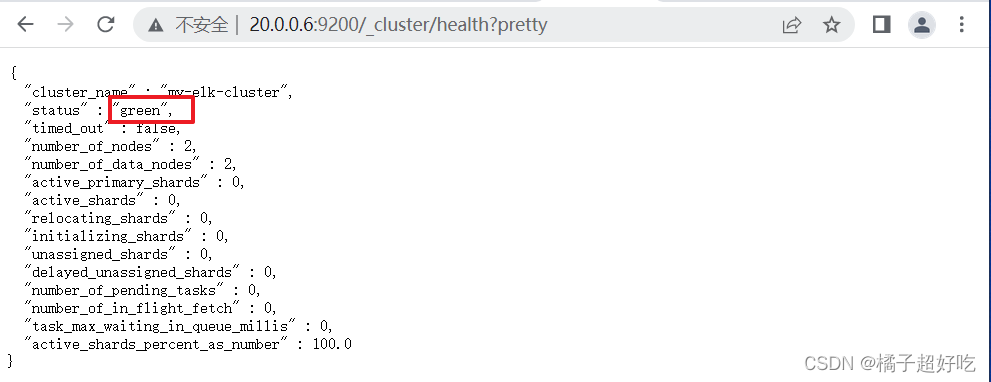
3、 View the cluster status
http://20.0.0.5:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
http://20.0.0.6:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
4、 install elasticsearch-head plug-in unit
Elasticsearch stay 5.0 After version ,Elasticsearch-head The plug-in needs to be installed as a stand-alone service , Need to use npm Tools (NodeJS Package management tools ) install .
install Elasticsearch-head The dependent software needs to be installed in advance node and phantomjs.
node: It's based on Chrome V8 Engine JavaScript Running environment .
phantomjs: It's based on webkit Of JavaScriptAPI, It can be understood as an invisible browser , Anything based on webkit What browsers do , It can do .
4.1、 Compilation and installation node
## Two sets of node
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make
cd /opt
tar xzvf node-v8.2.1.tar.gz
cd node-v8.2.1/
./configure
make && make install

4.2、 install phantomjs
cd /opt
tar xvf phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
cd /opt/phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/bin
cp phantomjs /usr/local/bin
4.3、 install Elasticsearch-head Data visualization tool
cd /opt
tar zxvf elasticsearch-head.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/
npm install
4.4、 modify Elasticsearch Master profile
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
......
-- Add the following at the end --
http.cors.enabled: true # Enable cross domain access support , The default is false
http.cors.allow-origin: "*" # Specify the domain names and addresses allowed for cross domain access for all
systemctl restart elasticsearch
4.5、 start-up elasticsearch-head service
Must be after decompression elasticsearch-head Start the service in the directory , The process will read the gruntfile.js file , Otherwise, it may fail to start
cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/
npm run start &
> elasticsearch-[email protected]0.0.0 start /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head
> grunt server
Running "connect:server" (connect) task
Waiting forever...
Started connect web server on http://localhost:9100
#elasticsearch-head The listening port is 9100
netstat -natp |grep 9100
adopt Elasticsearch-head see Elasticsearch Information
Access... Through a browser http://20.0.0.5:9100/ Address and connect to the cluster . If you see a cluster health value of green green , It means the cluster is healthy .
(7) Insert Index
# Insert a test index by command , The index for index-demo, The type is test.
curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/index-demo/test/1?pretty&pretty' -H 'content-Type: application/json' -d '{
"user":"zhangsan","mesg":"hello world"}'
// The output is as follows :
{
"_index" : "index-demo",
"_type" : "test",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"created" : true
}
Browser access http://20.0.0.5:9100/ View index information , You can see that the index is fragmented by default 5 individual , And there's a copy .
Click on “ Data browsing ”, Will find node1 The index created on is index-demo, The type is test Information about .
5、ELK Logstash Deploy ( stay Apache Operation on node )
1.Logstash It is generally deployed on the server that needs to monitor its logs . In this case ,Logstash Deployed in Apache Server , Used to collect Apache Log information of the server and send it to Elasticsearch.
2. install Apahce service (httpd)
yum -y install httpd
systemctl start httpd
3. install Java Environmental Science
yum -y install java
java -version
4. install logstash
# Upload package logstash-5.5.1.rpm To /opt Under the table of contents
cd /opt
rpm -ivh logstash-5.5.1.rpm
systemctl start logstash.service
systemctl enable logstash.service
ln -s /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash /usr/local/bin/
5. test Logstash
Logstash Command common options :
-f: With this option you can specify Logstash Configuration file for , Configure according to the configuration file Logstash Input and output streams of .
-e: Get... From the command line , Input 、 The output is followed by a string , This string can be treated as Logstash Configuration of ( If it's empty , It is used by default stdin As input ,stdout As the output ).
-t: Test the configuration file for correctness , And then quit .
Define input and output streams :
# The input is standard input , The output is standard output ( Similar pipe )
logstash -e 'input {
stdin{
} } output {
stdout{
} }'
......
www.baidu.com # Type in ( The standard input )
2022-7-5T03:58:47.799Z node1 www.baidu.com # Output results ( standard output )
www.sina.com.cn # Type in ( The standard input )
2022-7-5T03:59:02.908Z node1 www.sina.com.cn # Output results ( standard output )
// perform ctrl+c sign out
# Use rubydebug Output detailed format display ,codec For a codec
logstash -e 'input {
stdin{
} } output {
stdout{
codec=>rubydebug } }'
......
www.baidu.com # Type in ( The standard input )
{
"@timestamp" => 2022-7-5T02:15:39.136Z, # Output results ( The result of the treatment )
"@version" => "1",
"host" => "apache",
"message" => "www.baidu.com"
}
# Use Logstash Write the information Elasticsearch in
logstash -e 'input {
stdin{
} } output {
elasticsearch {
hosts=>["192.168.80.10:9200"] } }'
Input Output docking
......
www.baidu.com # Type in ( The standard input )
www.sina.com.cn # Type in ( The standard input )
www.google.com # Type in ( The standard input )
// The results are not displayed on the standard output , Instead, send to Elasticsearch in , Browser accessible http://20.0.0.5:9100/ View index information and data browsing .
6. Definition logstash The configuration file
Logstash The configuration file basically consists of three parts :input、output as well as filter( Optional , Choose to use as needed ).
input: Indicates collecting data from a data source , Common data sources such as Kafka、 Log files, etc
filter: Represents the data processing layer , Including formatting data 、 Data type conversion 、 Data filtering, etc , regular expression
output: It means that you will Logstash The collected data is processed by the filter and output to Elasticsearch.
# The format is as follows :
input {
...}
filter {
...}
output {
...}
# In each part , You can also specify multiple access methods . for example , To specify two log source files , The format is as follows :
input {
file {
path =>"/var/log/messages" type =>"syslog"}
file {
path =>"/var/log/httpd/access.log" type =>"apache"}
}
# modify Logstash The configuration file , Let it collect system logs /var/log/messages, And output it to elasticsearch in .
chmod +r /var/log/messages # Give Way Logstash You can read logs
vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf
input {
file{
path =>"/var/log/messages" # Specify the location of the logs to collect
type =>"system" # Custom log type identification
start_position =>"beginning" # Means to collect... From the beginning
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
# Output to elasticsearch
hosts => ["20.0.0.5:9200","20.0.0.6:9200"] # Appoint elasticsearch The address and port of the server
index =>"system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" # Specify output to elasticsearch Index format
}
}
systemctl restart logstash
Browser access http://20.0.0.5:9100/ View index information
6、ELK Kiabana Deploy ( stay Node1 Operation on node )
6.1、 install Kiabana
# Upload package kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm To /opt Catalog
cd /opt
rpm -ivh kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm
6.2、 Set up Kibana Primary profile for
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
--2-- uncomment ,Kiabana The default listening port of the service is 5601
server.port: 5601
--7-- uncomment , Set up Kiabana The monitoring address of ,0.0.0.0 For all addresses
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
--28-- uncomment , To configure es Server's ip, If it is a cluster, configure it master Node ip
elasticsearch.url: ["http://20.0.0.5:9200","http://20.0.0.6:9200"]
--37-- uncomment , Set in the elasticsearch Add .kibana Indexes
kibana.index: ".kibana"
--96-- uncomment , To configure kibana Log file path for ( You need to create... Manually ), Otherwise, the default is messages Keep a log in the library
logging.dest: /var/log/kibana.log
6.3、 Create a log file , start-up Kibana service
touch /var/log/kibana.log
chown kibana:kibana /var/log/kibana.log
systemctl start kibana.service
systemctl enable kibana.service
netstat -natp | grep 5601
6.4、 verification Kibana
Browser access http://20.0.0.5:5601
The first time you log in, you need to add a Elasticsearch Indexes :
Index name or pattern
// Input :system-* # Enter the previously configured... In the index name Output Prefix “system”
single click “create” Button to create , single click “Discover” Button to view chart information and log information .
Data display can be classified , stay “Available Fields” Medium “host”, And then click “add” Button , You can see the following “host” The result of screening
6.5、 take Apache Log of the server ( Access to the 、 FALSE ) Add to Elasticsearch And pass Kibana Show
vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/apache_log.conf
input {
file{
path => "/etc/httpd/logs/access_log"
type => "access"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file{
path => "/etc/httpd/logs/error_log"
type => "error"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "access" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["20.0.0.5:9200","20.0.0.6:9200"]
index => "apache_access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["20.0.0.5:9200","20.0.0.6:9200"]
index => "apache_error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
cd /etc/logstash/conf.d/
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f apache_log.conf
Browser access http://20.0.0.5:9100 Check whether the index is created
Browser access http://20.0.0.5:5601 Sign in Kibana, single click “Index Pattern -> Create Index Pattern” Button to add an index , Enter the previously configured... In the index name Output Prefix apache_access-*, And click “Create” Button . Add... In the same way apache_error-* Indexes .
choice “Discover” tab , Select the newly added... From the middle drop-down list apache_access-* 、apache_error-* Indexes , You can view the corresponding charts and log information .
边栏推荐
- Virtual memory, physical memory /ram what
- 有钱人买房就是不一样
- OpenGL common functions
- Android -- jetpack: the difference between livedata setValue and postvalue
- Syntaxhighlight highlights the right scroll bar
- Yunxiaoduo software internal test distribution test platform description document
- How to build your own super signature system (yunxiaoduo)?
- 一个普通人除了去工厂上班赚钱,还能干什么工作?
- Three. JS introductory learning notes 19: how to import FBX static model
- 【微信小程序】Chapter(5):微信小程序基础API接口
猜你喜欢
Three. JS introductory learning notes 18: how to export JSON files with Blender
The rebound problem of using Scrollview in cocos Creator
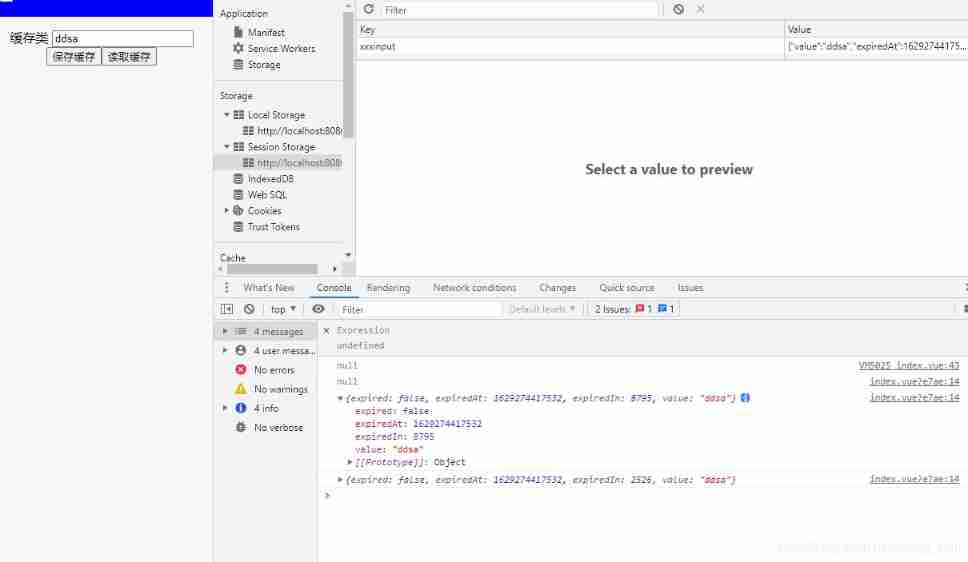
TS as a general cache method

Webgl texture
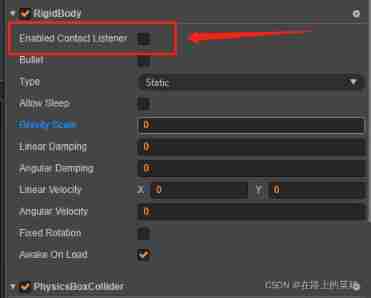
Cocos creator collision and collision callback do not take effect

强化实时数据管理,英方软件助力医保平台安全建设

Async and await
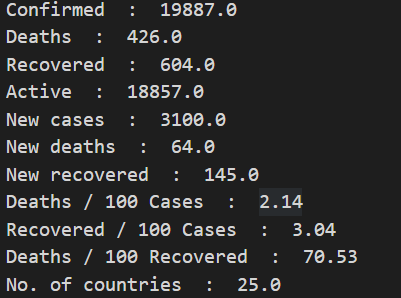
Numpy -- epidemic data analysis case

Ue4/ue5 multi thread development attachment plug-in download address

numpy--疫情数据分析案例
随机推荐
Getting started with webgl (3)
Syntaxhighlight highlights the right scroll bar
Points for attention in porting gd32 F4 series programs to gd32 F3 series
神经网络c语言中的指针是怎么回事
numpy--数据清洗
Postman generate timestamp, future timestamp
持续创作,还得靠它!
星瑞格数据库入围“2021年度福建省信息技术应用创新典型解决方案”
TS typescript type declaration special declaration field number is handled when the key key
Cocos makes Scrollview to realize the effect of zooming in the middle and zooming out on both sides
Asynchronous application of generator function
numpy--疫情数据分析案例
Three. JS introductory learning notes 19: how to import FBX static model
C Alibaba cloud OSS file upload, download and other operations (unity is available)
尤雨溪,来了!
【微信小程序】Chapter(5):微信小程序基础API接口
It's different for rich people to buy a house
Use moviepy Editor clips videos and intercepts video clips in batches
LeetCode2_ Add two numbers
山东老博会,2022中国智慧养老展会,智能化养老、适老科技展