当前位置:网站首页>Es full text index
Es full text index
2022-07-06 14:37:00 【Xiaobai aYuan】
ES The benefits of full-text indexing :
1. As a database ( Instead of MySQL);
2. Do retrieval services under the condition of big data 、 Synonym processing 、 Relevance ranking 、 Complex data analysis 、 Near real time processing of massive data ;
3. Analysis of records and logs
4. Full text search
5. Supplement to relational database , Substitution of traditional database
6. On-site search 、 Vertical search
1.docker
Application container engine
“Docker Is an open source application container engine , Allows developers to package their applications and dependencies into a portable image , Then post to any popular Linux or Windows On the machine with the operating system , You can also implement virtualization . Containers are completely sandboxed using the sandbox mechanism , There will be no interface between them .”
2.docker install
a. Update source : apt-get update
b. install docker: apt-get install docker.io
c. see docker: docker ps # Check whether the installation is successful
# It depends on your own situation , Prompt that if you don't have permission, add sudo
3.docker install ES
1、 Pull es Mirror image
docker pull bitnami/elasticsearch
2、 establish es Containers
docker run -d -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 --name elasticsearch bitnami/elasticsearch
# It depends on your own situation , Prompt that if you don't have permission, add sudo
3. Test whether the installation is successful in the web page :

1. stay flask Project use ES Indexes
Create a story about es Indexed folder

es.py in
example es object 、 Initialize a connection Elasticsearch Action object 、 according to id Get document data and insert documents id
Establish and es Links to containers
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
from celery_task import celery_app
# Establishing a connection
es = Elasticsearch("http://101.42.224.35:9200/")
class ES(object):
"""
es object
"""
def __init__(self, index_name: str):
self.es = es
self.index_name = index_name
def get_doc(self, uid):
return self.es.get(index=self.index_name, id=uid)
def insert_one(self, doc: dict):
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, body=doc)
def insert_array(self, docs: list):
for doc in docs:
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, body=doc)
def search(self, query, count: int = 30, fields=None):
fields = fields if fields else ["title", 'pub_date']
dsl = {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": query,
"fields": fields
},
# 'wildcard': {
# 'content': {
# 'value': '*' + query + '*'
# }
# }
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
match_data = self.es.search(index=self.index_name, body=dsl, size=count)
return match_data
def _search(self, query: dict, count: int = 20, fields=None): # count: The size of the data returned
results = []
match_data = self.search(query, count, fields)
for hit in match_data['hits']['hits']:
results.append(hit['_source'])
return results
def create_index(self):
if self.es.indices.exists(index=self.index_name) is True:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
self.es.indices.create(index=self.index_name, ignore=400)
def delete_index(self):
try:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
except:
passone_scripts.py
Import database data es
# You need to pay attention to whether the port number and database are local databases, as well as the name of the database to be imported and the decoding method of the database
import pymysql
import traceback
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
def get_db_data():
# Open database connection (ip/ Database user name / The login password / Database name )
db = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", user=" user name ", password=" password ",
database=" Database name ", charset='utf8')
# Use cursor() Method to create a cursor object cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "SELECT * FROM course"
# Use execute() Method execution SQL Inquire about
cursor.execute(sql)
# Get a list of all records
results = cursor.fetchall()
# Close database connection
db.close()
return results
def insert_data_to_es():
es = Elasticsearch("http://101.42.224.35:9200/")
# Empty data
es.indices.delete(index='course')
try:
i = -1
for row in get_db_data():
print(row)
print(row[1], row[2])
i += 1
es.index(index='course', body={
'id': i,
'table_name': 'table_name',
'pid': row[4],
'title': row[5],
'desc': str(row[6]),
})
except:
error = traceback.format_exc()
print("Error: unable to fecth data", error)
if __name__ == "__main__":
insert_data_to_es()The index needs to be defined in the model class and set to support Chinese
__searchable__ = ['title'] # Search for related fields
__analyzer__ = ChineseAnalyzer()# Support Chinese index Use in view es Redefine the interface , Finally, return the data
stay python The method used in ----es.searche()
es = ES(index_name='Tag')
result = es._search(q, fields=['title', 'desc'])
import traceback
from common.es.es import ES
class GetTag(Resource):
def get(self):
"""
Get front-end data
Use es Full text search
"""
parser = reqparse.RequestParser()
parser.add_argument('q')
args = parser.parse_args()
q= args.get('q')
try:
es = ES(index_name='Tag')
result = es._search(q, fields=['title', 'desc'])
return marshal(result, tag_fields)
except:
error = traceback.format_exc()
print('111111111111', error)
return {'message': error}, 500Through the above configuration and rewritten interface, you can realize the full text es Use of index
边栏推荐
- Function: find the root of the equation by Newton iterative method
- Intel oneapi - opening a new era of heterogeneity
- Always of SystemVerilog usage_ comb 、always_ iff
- Overview of LNMP architecture and construction of related services
- This article explains in detail how mockmvc is used in practical work
- 《统计学》第八版贾俊平第十一章一元线性回归知识点总结及课后习题答案
- 使用 flask_whooshalchemyplus jieba实现flask的全局搜索
- Sword finger offer 23 - print binary tree from top to bottom
- An unhandled exception occurred when C connected to SQL Server: system Argumentexception: "keyword not supported:" integrated
- 《统计学》第八版贾俊平第八章假设检验知识点总结及课后习题答案
猜你喜欢
《统计学》第八版贾俊平第二章课后习题及答案总结
Attack and defense world misc practice area (GIF lift table ext3)

Binary search tree concept

Intranet information collection of Intranet penetration (3)
《统计学》第八版贾俊平第十一章一元线性回归知识点总结及课后习题答案
图书管理系统
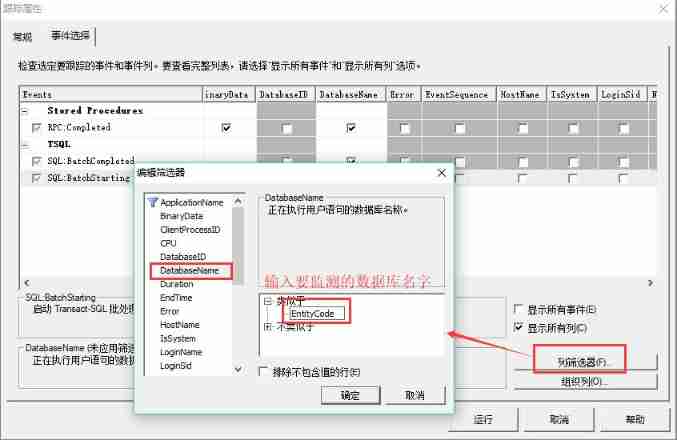
Database monitoring SQL execution
Keil5-MDK的格式化代码工具及添加快捷方式
![Harmonyos application development -- address book management system telmanagesys based on listcontainer [phonebook][api v6]](/img/0b/ddbee0b8a34627e13bff5598bbaed8.jpg)
Harmonyos application development -- address book management system telmanagesys based on listcontainer [phonebook][api v6]
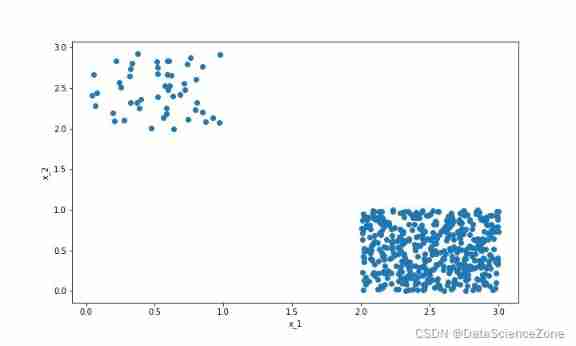
Data mining - a discussion on sample imbalance in classification problems
随机推荐
Statistics 8th Edition Jia Junping Chapter 7 Summary of knowledge points and answers to exercises after class
Binary search tree concept
Apache APIs IX has the risk of rewriting the x-real-ip header (cve-2022-24112)
List and data frame of R language experiment III
Record an API interface SQL injection practice
数字电路基础(二)逻辑代数
[pointer] find the value of the largest element in the two-dimensional array
Function: find 1-1/2+1/3-1/4+1/5-1/6+1/7-... +1/n
四元数---基本概念(转载)
Solutions to common problems in database development such as MySQL
Matplotlib绘图快速入门
Statistics 8th Edition Jia Junping Chapter 10 summary of knowledge points of analysis of variance and answers to exercises after class
函数:用牛顿迭代法求方程的根
数字电路基础(五)算术运算电路
Pointers: maximum, minimum, and average
后台登录系统,JDBC连接数据库,做小案例练习
函数:求两个正数的最大公约数和最小公倍
Data mining - a discussion on sample imbalance in classification problems
On the idea of vulnerability discovery
Attack and defense world misc practice area (GIF lift table ext3)