当前位置:网站首页>[paper notes] multi goal reinforcement learning: challenging robotics environments and request for research
[paper notes] multi goal reinforcement learning: challenging robotics environments and request for research
2022-07-05 05:06:00 【See deer (Python version)】
Catalog
Abstract
First , It introduces a challenging system based on existing robot hardware Continuous control tasks ( from OpenAI Gym Integrate ).
All tasks have Sparse binary rewards , And follow a Multi-objective reinforcement learning (RL) frame , In this framework , An agent is told to use a Additional input What to do .
The second part of this paper proposes a set of improvement RL Algorithm Specific research ideas , Most of them are related to Multiple goals RL and Post experience playback of .
1 Environments
1.1 Fetch environments
The crawl environment is based on 7 Degree of freedom grasping robot arm , It has a two finger parallel gripper .
We added an extra arrive Mission ,pick and place The task is a little different .
In all acquisition tasks , It's all about goals The three-dimensional , And describes The desired position of the goal ( or To arrive End actuators ).
Rewards are sparse and binary : If the object is Target location ( stay 5 Within centimeters ), Agents get 0 Reward , otherwise −1.
The action is 4 Dimensional : Three dimensional assignment in Cartesian coordinates Gripper movement required in , The last dimension controls the On and off .
Before returning control to the agent , We are 20 In simulator steps ( Every δ = 0.002 \delta=0.002 δ=0.002) Apply the same action , That is, the action frequency of the agent is f = 25 H z f=25Hz f=25Hz.
Observations include the Cartesian position of the fixture 、 Linear velocity and the position and linear velocity of the robot fixture .
If an object exists , We also include Cartesian positions and rotations using Euler angles , Its linear and angular velocity , And its position and linear speed relative to the clamping .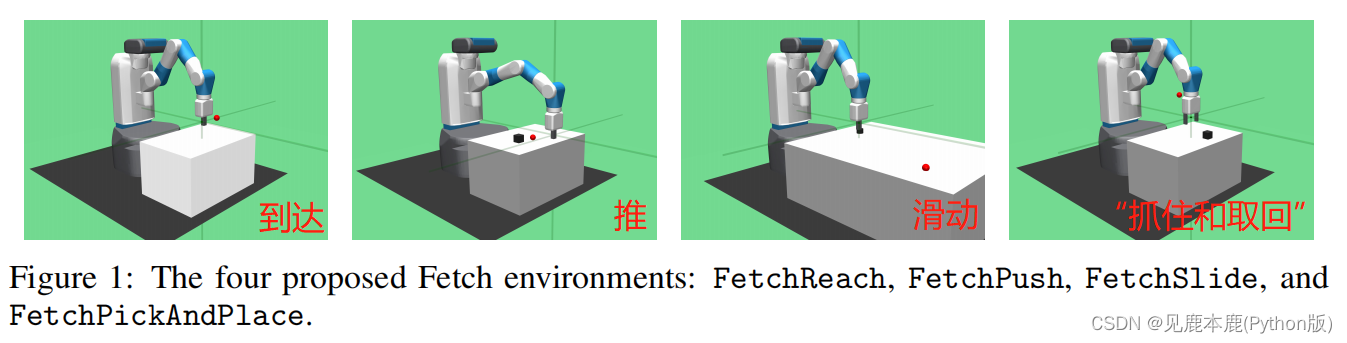
Reaching (FetchReach)
The task is to move the gripper to the target position . This task is very easy to learn , Therefore, it is a suitable benchmark , To ensure that a new idea works completely .
Pushing (FetchPush)
A box is placed on a table in front of the robot , Its task is to move it to a target location on the table . The fingers of the robot are locked , To prevent gripping . Learned behavior is usually a mixture of pushing and rolling .
Sliding (FetchSlide)
An ice hockey was placed on a long smooth table , The target position is beyond the reach of the robot , So it must use this Hit the ice hockey with strength , It slides , Then stop at the target position due to friction .
Pick & Place (FetchPickAndPlace)
The task is to grab a box , And move it to a target location that may be on the surface of the table or in the air above the table .
1.2 Hand environments
These environments are based on Shadow Dexterous Hand, This is a Anthropomorphic , Yes 24 Two degrees of freedom manipulator . Here 24 In joints , Yes 20 One can be controlled independently , The other one is the coupling joint .
| Items | Contents |
|---|---|
| Rewards | The agent obtains a reward of 0 if the goal has been achieved (within some task-specific tolerance) and −1 otherwise. |
| Actions | 20-dimensional. Use absolute position control for all non-coupled joints of the hand. |
| Observations | include the 24 positions and velocities of the robot’s joints. In case of an object that is being manipulated, we also include its Cartesian position and rotation represented by a quaternion (hence 7-dimensional) as well as its linear and angular velocities. |
Reaching (HandReach)
A simple task , The goal is 15 Dimensional , And include the target Cartesian position of each fingertip of the hand . If the average distance between the fingertip and the desired position is less than 1 centimeter , It is considered that the goal has been achieved .
Block manipulation (HandManipulateBlock)
In the block operation task , A block is placed on the palm . then , Task is operation block , So as to achieve the target attitude .
HandManipulateBlockRotateZ
The target revolves around the block z The axis rotates randomly . There is no target location .
HandManipulateBlockRotateParallel
Around the block z The random target rotation of the axis and x Axis and y Axis target rotation of axis . There is no target location .
HandManipulateBlockRotateXYZ
Random target rotation for all axes of the block . There is no target location .
HandManipulateBlockFull
Random target rotation for all axes of the block . Random target location .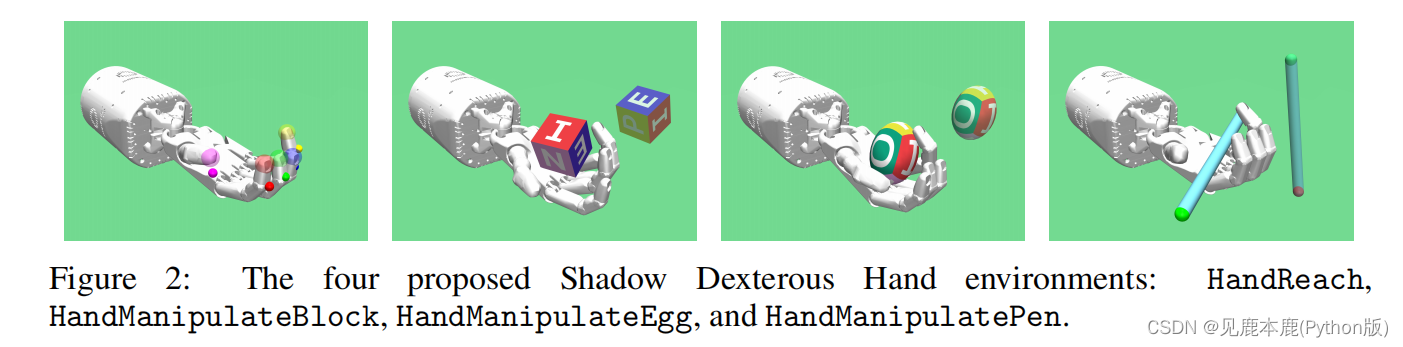
If the distance between the position of the block and its desired position is less than 1 centimeter ( Only for complete variants ), And the rotation difference is less than 0.1rad, It is considered that the goal has been achieved .
Egg manipulation (HandManipulateEgg)
The goal here is similar to the block task , But it's not Egg shaped objects The block .
The geometry of the object is significantly different from the difficulty of the problem , And eggs are probably the simplest object .
The goal is also 7 Dimensional , Including target location ( In Cartesian coordinates ) And target rotation ( Expressed in quaternions ).
HandManipulateEggRotate
Randomly rotate all the axes of the egg . There is no target location .
HandManipulateEggFull
Randomly rotate all the axes of the egg . Random target location .
If the distance between the position of the egg and its desired position is less than 1 centimeter ( Only for complete variants ), And the rotation difference is less than 0.1rad, It is considered that the goal has been achieved .
Pen manipulation (HandManipulatePen)
It's hard to grasp the pen , Because it's easy to fall off your hands , It's easy to collide and get stuck between other fingers .
Another operation , This time, use a pen instead of building blocks or eggs .
HandManipulatePenRotate
Random target rotation x and y Axis , There is no goal around z Shaft rotation . There is no target location .
HandManipulatePenFull
Random target rotation x and y Axis , There is no goal around z Shaft rotation . Random target location .
If the distance between the position of the pen and its desired position is less than 5 centimeter ( Only for complete variants ), And the difference in rotation , Ignore z Axis , Less than 0.1rad, It is considered that the goal has been achieved .
1.3 Multi-goal environment interface
Goal-aware observation space
It requires that the type of observation space is :gym.space.Dict
observtion
The state or posture of the robot .
desired_goal
What agents must achieve .
achieved_goal
What the agent has achieved . stay FetchReach in , This is the position of the robot end effector . Ideally , This will work with desired_goal identical .
Exposed reward function
secondly , We allow Recalculate rewards in a different way The way to show the reward function . This is an alternative target HER The necessary requirements of formula Algorithm .
Compatibility with standard RL algorithms
We include a simple wrapper , It will be new Target observation space based on dictionary Convert to a more common Array Express .
1.4 Benchmark results
Subjects
| DDPG+HER with sparse rewards | DDPG+HER with dense rewards | DDPG with sparse rewards | DDPG with dense rewards |
|---|
We pass on each MPI The worker performs 10 A deterministic test is derived to evaluate the performance after each stage , Then through the introduction and MPI Workers average to calculate the test success rate .
In all cases , We use it 5 Repeat an experiment with different random seeds , And report the results by calculating the median test success rate and the quartile range .
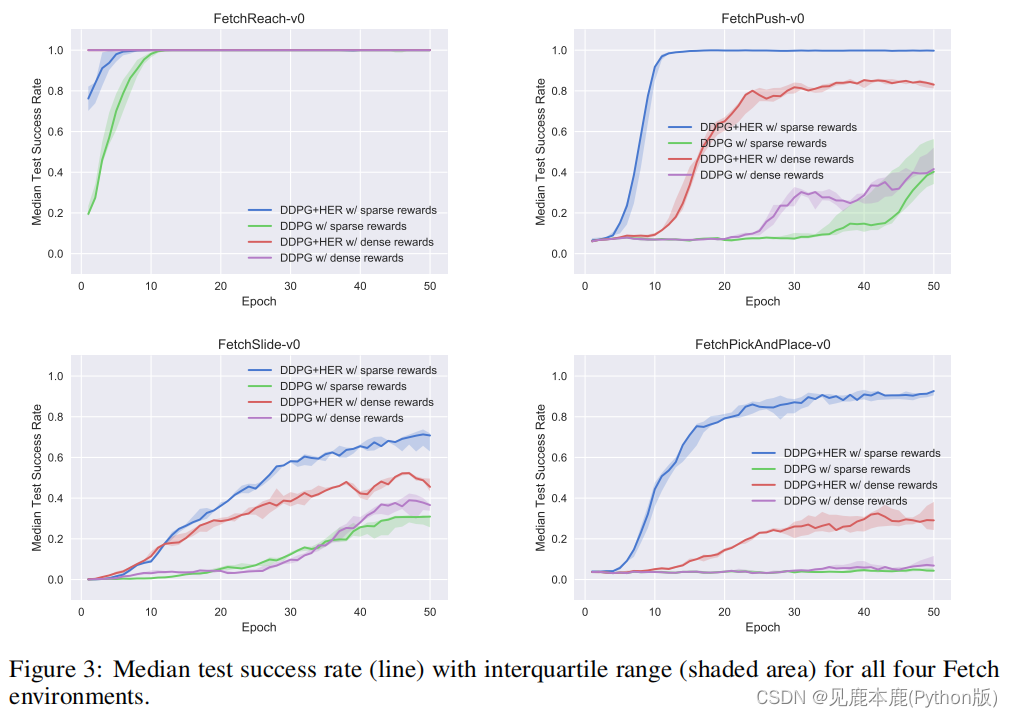
In the rest of the environment ,DDPG+HER Significantly better than all other configurations .
If the reward structure is sparse , But you can also successfully learn from intensive rewards , that DDPG+HER The best performance of .
For ordinary DDPG, It is usually easier to learn from intensive rewards , Sparse rewards are more challenging .
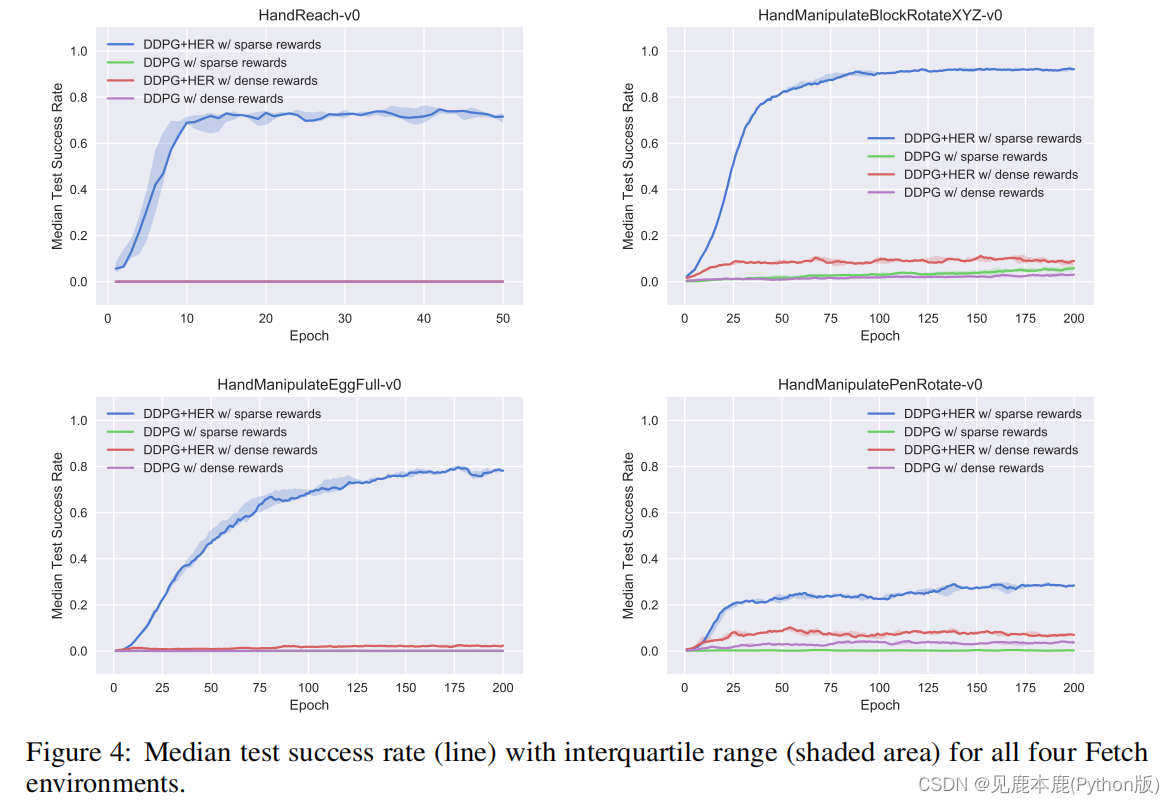
Similar to before , In the use of HER when , Sparse reward structure is obviously better than dense reward structure .
She can learn some successful policies in all environments , But especially HandManipulatePen Especially challenging .
Explanation of the reason :
- Learning sparse return is much simpler , Because critics only need to distinguish between the state of success and the state of failure .
- However , Intensive incentive policies encourage the choice of a strategy that directly achieves the desired goals .
2 Request for Research
Automatic hindsight goals generation
We can learn which goals are most valuable for experience replay .
The biggest problem is how to determine which targets are most valuable for replay . One option is training generator , To maximize Behrman error .
Unbiased HER
HER The joint distribution of replay tuples is changed in an unprincipled way .
Theoretically , This may make training impossible in an extremely random environment , Although we haven't noticed this in practice .
Consider an environment , There is a special action , Bring the agent to a random state , The incident ended after that .
In hindsight , If we replay the goals that agents will achieve in the future , Such action seems to be perfect .
How to avoid this problem ? One possible method is to use importance sampling to eliminate sampling bias , But this may lead to too high variance of the gradient .
HER+HRL
A possible extension of this work is to replace not only the goal , And a higher level of action , for example , If the high level requires a low level to reach the state , But other States B state , We can replay this process instead of high-level action B.
This can make a higher level of learning even though the low-level policy is very bad , But this is not very principled , It may make the training unstable .
Richer value functions
UVFA Extend the value function to multiple goals , and TDM Expand it to different time ranges .
Both of these innovations can make training easier , Although the function of learning is more complex .
Faster information propagation
Most of the most advanced non strategies RL The algorithm uses the target network to stabilize the training .
However , This is at the cost of limiting the maximum learning speed of the algorithm , Because each target network update only returns the returned information one step in time ( If you use one-step guidance ).
We noticed that , In the early stages of training ,DDPG+HER The learning speed of is often proportional to the frequency of updating the target network , But the frequency of target network updates / Excessive amplitude will lead to unstable training , The final performance is worse .
HER + multi-step returns
HER The generated data deviates greatly from the strategy , Therefore, multi-step regression cannot be used , Unless we use some correction factors , Such as importance sampling .
Although there are many non strategic solutions for processing data , However, it is not clear whether they will perform well in the setting of training data far from strategy .
It may be beneficial to use multi-step return , Because the reduction of the guiding frequency can lead to less bias gradient .
Besides , It accelerates the reverse transmission of information about the return in time , According to our experiment , This is often DDPG+HER Limitations of training ( Compare the previous paragraph ).
On-policy HER
Rauber Et al. Put forward some preliminary results about the general policy gradient , But this method needs to be tested in a more challenging environment , As proposed in this report . One possible option is to use something similar to IPG The technique used in .
Combine HER with recent improvements in RL
RL with very frequent actions
In the continuous control domain , When the frequency of action approaches infinity , Performance will approach zero , This is caused by two factors .
- Inconsistent exploration and the need to guide more time to spread information about return back in time . How to design a sample with high efficiency RL Algorithm , Even if the frequency of action tends to infinity , It can also maintain its performance ? The exploration and utilization problem can be solved by using parameter noise , Using multi-step return can achieve faster information dissemination .
- The other method can be an adaptive and learnable frame skipping .
Appendix A
Appendix B
边栏推荐
- BUUCTF MISC
- Grail layout and double wing layout
- AutoCAD - full screen display
- Generate filled text and pictures
- Establish cloth effect in 10 seconds
- On-off and on-off of quality system construction
- AutoCAD - command repetition, undo and redo
- [leetcode] integer inversion [7]
- PR first time
- Kali 2018 full image download
猜你喜欢
Panel panel of UI
![Rip notes [rip message security authentication, increase of rip interface measurement]](/img/89/f70af97676496d7b9aa867be89f11d.jpg)
Rip notes [rip message security authentication, increase of rip interface measurement]
win10虚拟机集群优化方案

【论文笔记】Multi-Goal Reinforcement Learning: Challenging Robotics Environments and Request for Research

2022/7/2 question summary
AutoCAD - stretching
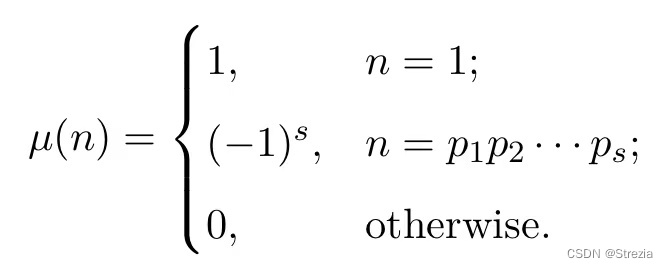
Number theoretic function and its summation to be updated
Detailed introduction of OSPF header message
AutoCAD -- dimension break
Séparation et combinaison de la construction du système qualité
随机推荐
Rip notes [rip three timers, the role of horizontal segmentation, rip automatic summary, and the role of network]
Grail layout and double wing layout
Panel panel of UI
Sqlserver stored procedures pass array parameters
2021-10-29
2022 / 7 / 1 Résumé de l'étude
【论文笔记】Multi-Goal Reinforcement Learning: Challenging Robotics Environments and Request for Research
Do a small pressure test with JMeter tool
2022/7/1学习总结
中国金刚烷行业研究与投资预测报告(2022版)
PostgreSQL 超越 MySQL,“世界上最好的编程语言”薪水偏低
Data is stored in the form of table
cocos2dx_ Lua card flip
Understand encodefloatrgba and decodefloatrgba
Time format conversion
2022/7/2 question summary
Unity parallax infinite scrolling background
The difference between heap and stack
3dsmax scanning function point connection drawing connection line
Dotween usage records ----- appendinterval, appendcallback