当前位置:网站首页>Dynamic extensible representation for category incremental learning -- der
Dynamic extensible representation for category incremental learning -- der
2022-07-02 07:58:00 【MezereonXP】
Dynamic extensible representation for category incremental learning – DER
List of articles
This time, we introduce a training method similar to representation learning , For incremental learning of categories , From CVPR2021 An article from "DER: Dynamically Expandable Representation for Class Incremental Learning".
First , We need to add some pre concepts , Such as category incremental learning and representation learning .
Category incremental learning
In traditional classification learning , We usually have all categories when we train , When testing, it also tests all kinds of data .
In the real world , We often don't define all categories at the beginning , And collect all the corresponding data , The reality is that , We usually have some categories of data , Then train a classifier first , Wait until there is a new category , Then make adjustments to the network structure , Conduct data collection again 、 Training and testing .
Representational learning / Measure learning
Representational learning (Representation Learning), Or measure learning (Metric Learning), Its purpose is to , Learn a representation of data ( Usually in the form of a vector ), Make the representation of the same kind close , The representation of dissimilarity is far away , The distance here can be Euclidean distance, etc .
When doing category incremental learning , We can often reuse the previously trained representation extractor , Tune on new data (fine-tune).
here , The article divides representation learning into 3 class :
- Regularization based method
- Distillation based method
- Structure based approach
Regularization based methods generally have a strong assumption , It is mainly based on the estimation method , Fine tune the parameters .
Distillation based methods depend on the quantity and quality of the data used .
Structure based approach , Additional new parameters will be introduced , Used to model new categories of data .
The above classification is actually insufficient , If you use traditional measurement learning to learn a “ front end ”, To extract features , Then fine tuning the back-end classifier is also a method , But this article doesn't seem to discuss this method .
The basic flow

As shown in the figure above , In fact, it is a process of feature splicing , First , We use some categories of data for training , Get a feature extractor Φ t − 1 \Phi_{t-1} Φt−1, For a new feature F t \mathcal{F}_t Ft , Given a picture x ∈ D ~ t x\in \tilde{\mathcal{D}}_t x∈D~t , The features after splicing can be expressed as :
u = Φ t ( x ) = [ Φ t − 1 ( x ) , F t ( x ) ] u = \Phi_{t}(x)=[\Phi_{t-1}(x), \mathcal{F}_t(x)] u=Φt(x)=[Φt−1(x),Ft(x)]
Then the feature will be input into a classifier H t \mathcal{H}_t Ht On , Output is :
p H t ( y ∣ x ) = S o f t m a x ( H t ( u ) ) p_{\mathcal{H}_t}(y|x)=Softmax(\mathcal{H}_t(u)) pHt(y∣x)=Softmax(Ht(u))
The predicted result is :
y ^ = arg max p H t ( y ∣ x ) \hat{y} = \arg\max p_{\mathcal{H}_t}(y|x) y^=argmaxpHt(y∣x)
therefore , The basic training error is simple cross entropy error :
L H t = − 1 ∣ D ~ t ∣ ∑ i = 1 ∣ D ~ t ∣ log ( p H t ( y = y i ∣ x i ) ) \mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{H}_t}=-\frac{1}{|\tilde{\mathcal{D}}_t|}\sum_{i=1}^{|\tilde{\mathcal{D}}_t|}\log(p_{\mathcal{H}_t}(y=y_i|x_i)) LHt=−∣D~t∣1i=1∑∣D~t∣log(pHt(y=yi∣xi))
We will classify H t \mathcal{H}_t Ht Replace with a classifier for the new category feature H a \mathcal{H}_a Ha , You can get an error for the characteristics of the new category L H a \mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{H}_a} LHa
The error form of fusion is ;
L E R = L H t + λ a L H a \mathcal{L}_{ER} = \mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{H}_t} + \lambda_a\mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{H}_a} LER=LHt+λaLHa
In order to reduce the parameter increment caused by category increment , Here a kind of Mask Mechanism , That is to learn one Mask, For the channel Mask, Use a variable e l e_l el Control .
f l ′ = f l ⊙ m l m l = σ ( s e l ) f_l'=f_l\odot m_l\\ m_l=\sigma(se_l) fl′=fl⊙mlml=σ(sel)
among σ ( ⋅ ) \sigma(\cdot) σ(⋅) Express sigmoid Activation function , s s s Is a scaling factor .
Introduce a sparsity error , It is used to encourage the model to compress parameters as much as possible ,Mask Drop more channels :
L S = ∑ l = 1 L K l ∣ ∣ m l − 1 ∣ ∣ 1 ∣ ∣ m l ∣ ∣ 1 ∑ l = 1 L K l c l − 1 c l \mathcal{L}_S = \frac{\sum_{l=1}^LK_l||m_{l-1}||_1||m_l||_1}{\sum_{l=1}^LK_lc_{l-1}c_{l}} LS=∑l=1LKlcl−1cl∑l=1LKl∣∣ml−1∣∣1∣∣ml∣∣1
among , L L L Is the number of layers , K l K_l Kl It's No l l l Layer convolution Kernel Size.
Final , Get a comprehensive error expression :
L D E R = L H t + λ a L H t a + λ s L S \mathcal{L}_{DER} = \mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{H}_t} +\lambda_a\mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{H}_t^a} + \lambda_s\mathcal{L}_S LDER=LHt+λaLHta+λsLS
experimental analysis
The first is the setting of data set , Three data sets are used :
- CIFAR-100
- ImageNet-1000
- Imagenet-100
about CIFAR-100 Of 100 class , Will be based on 5,10,20,50 Incremental processes to train . here , about 5 Incremental processes , That is, it will increase every time 20 Class new category data . Such a data set segmentation method is recorded as CIFAR100-B0.
Another incremental method is , First in 50 Training on class , And then the rest 50 class , according to 2、5、10 An incremental process for training . Write it down as CIFAR100-B50.
We only give here CIFAR-100 Result of dataset , More detailed , You can see the paper .
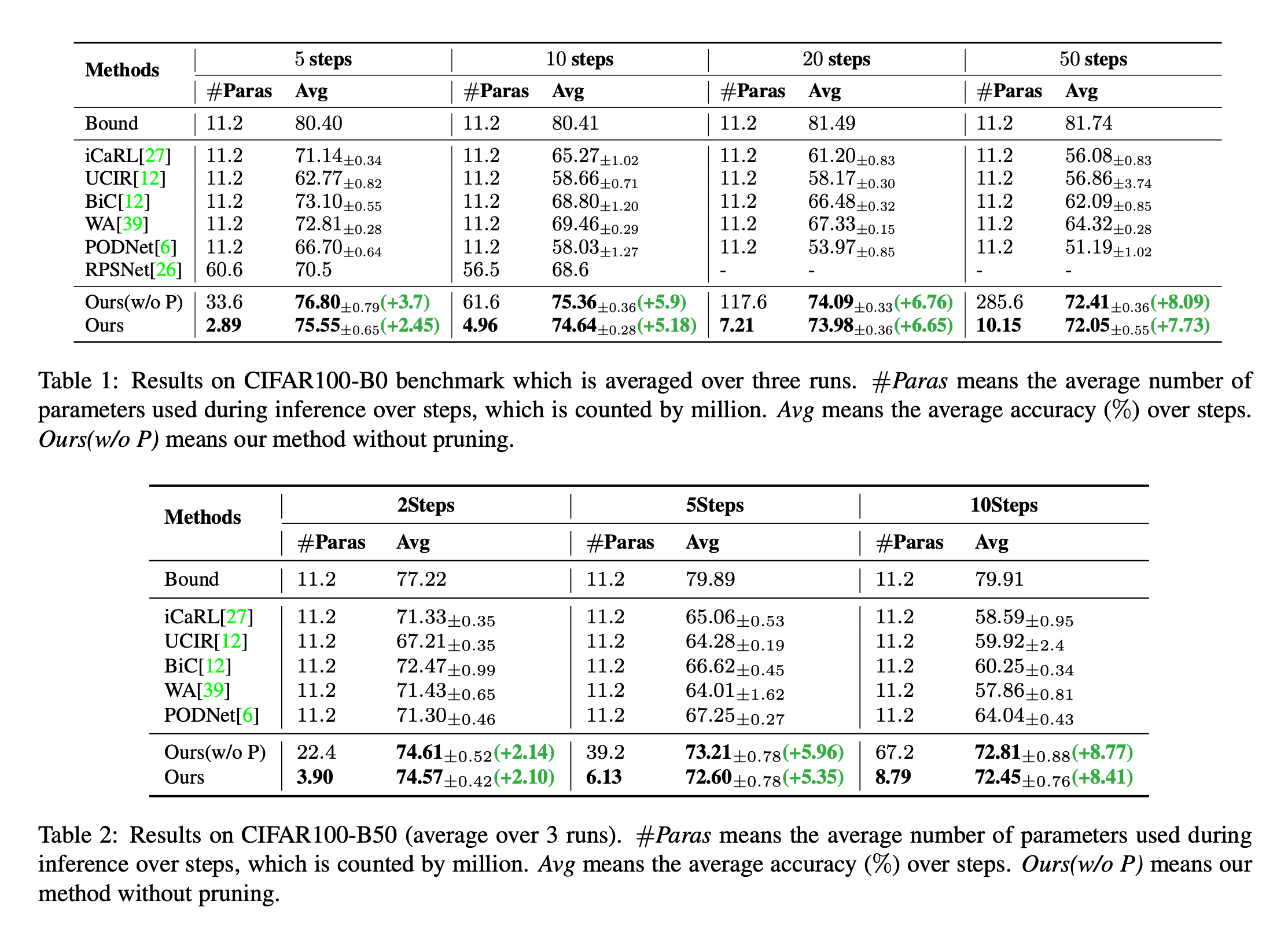
As shown in the figure above , The final average accuracy of this method is higher than that of other incremental learning methods . It should be noted that , When using Mask The mechanism is , That is to use Mask The result of is to cut the parameters , The parameters of the obtained model are greatly reduced , The accuracy can still be maintained .
边栏推荐
- label propagation 标签传播
- Common CNN network innovations
- [binocular vision] binocular correction
- 【DIoU】《Distance-IoU Loss:Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression》
- 论文tips
- open3d学习笔记三【采样与体素化】
- E-R画图明确内容
- 【Batch】learning notes
- Correction binoculaire
- 【Cutout】《Improved Regularization of Convolutional Neural Networks with Cutout》
猜你喜欢

【Random Erasing】《Random Erasing Data Augmentation》

In the era of short video, how to ensure that works are more popular?

【AutoAugment】《AutoAugment:Learning Augmentation Policies from Data》
【学习笔记】Matlab自编图像卷积函数

用MLP代替掉Self-Attention

CVPR19-Deep Stacked Hierarchical Multi-patch Network for Image Deblurring论文复现
Pointnet understanding (step 4 of pointnet Implementation)
【Cascade FPD】《Deep Convolutional Network Cascade for Facial Point Detection》
【MagNet】《Progressive Semantic Segmentation》
Embedding malware into neural networks
随机推荐
Latex formula normal and italic
图像增强的几个方法以及Matlab代码
The difference and understanding between generative model and discriminant model
[in depth learning series (8)]: principles of transform and actual combat
Machine learning theory learning: perceptron
w10升级至W11系统,黑屏但鼠标与桌面快捷方式能用,如何解决
【DIoU】《Distance-IoU Loss:Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression》
【Cutout】《Improved Regularization of Convolutional Neural Networks with Cutout》
【Sparse-to-Dense】《Sparse-to-Dense:Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth Samples and a Single Image》
【Mixup】《Mixup:Beyond Empirical Risk Minimization》
open3d学习笔记五【RGBD融合】
What if a new window always pops up when opening a folder on a laptop
Thesis tips
【Mixup】《Mixup:Beyond Empirical Risk Minimization》
【双目视觉】双目矫正
It's great to save 10000 pictures of girls
Embedding malware into neural networks
笔记本电脑卡顿问题原因
open3d环境错误汇总
open3d学习笔记四【表面重建】