当前位置:网站首页>Su embedded training - Day6
Su embedded training - Day6
2022-07-08 00:58:00 【Light chasing rain】
List of articles
One A function pointer
A function pointer : Essence is a pointer , Point to a function
The function name we define is actually a pointer , Save the first address of the current function code area
The purpose of function pointer learning is to solve whether a pointer can be defined , You can call the current function like the function name
Format defined by function pointer :
return type (* Variable name )( Parameters );
Function values really work : To pass a function as a parameter to another function, you need to define it as a function pointer , Also called callback function
#include <stdio.h>
typedef unsigned char uchar; // use uchar Express unsigned char
typedef int (*T)(int,int); // Statement T For function pointer type
void f1()
{
printf("hello world!\n");
}
int f2(int x,int y)
{
printf("this is f2\n");
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
void (*p1)(); // Define function pointers
p1 = f1;// Can not write p1 = f1(); ----> call f1 function , Assign return value to p1
p1();
// p1 = f2; // incompatible types
int (*p2)(int,int);
p2 = f2;
p2(1,2);
T p3; // Equivalent to int(*p3)(int,int)
p3 = f2;
p3(1,2);
return 0;
}
Two Callback function
#include <stdio.h>
int less(int x,int y)
{
return (x < y) ? 1 : 0;
}
int greater(int x,int y)
{
return (x > y) ? 1 : 0;
}
void Sort(int a[],int length,int (*p)(int,int))
{
int i,j;
for(i = 0 ; i < length - 1;i++)
{
for(j = 0 ; j < length - 1 - i;j++)
{
if(p(a[j],a[j+1]))
{
#if 0
int t = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = t;
#endif
a[j] = a[j] + a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = a[j] - a[j + 1];
a[j] = a[j] - a[j + 1];
}
}
}
}
void Print(int a[],int length)
{
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < length;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
putchar(10);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a[10] = {0};
printf(" Please enter 10 A digital :\n");
int i;
int length = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
for(i = 0 ; i < length;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
Sort(a,length,less);
Print(a,length);
return 0;
}
practice : Write function , Define an unsigned 4 The whole number of bytes , Then get the content of each byte , Then return to the sum of the addition
requirement : This integer needs to pass parameters , Returns the sum of each byte
458963212 —>0001 1011 0101 1011 0011 1001 0000 1100
0000 1100 —>12
0011 1001 —> 57
0101 1011 —>91
0001 1011 —> 27
12+57+91+27 = 187
#include <stdio.h>
int GetByteSum(unsigned int num)
{
int sum = 0;
#if 0
// Will each 8 Take it out
int byte1,byte2,byte3,byte4;
byte1 = num & 0xff;
byte2 = (num >> 8) & 0xff;
byte3 = (num >> 16) & 0xff;
byte4 = (num >> 24) & 0xff;
sum = byte1 + byte2 + byte3 + byte4;
#endif
unsigned char *p = (unsigned char)#
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i < 4; i++)
{
sum += *p;
p++;
}
p = NULL;
return sum;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
unsigned int num = 458963212;
int n = GetByteSum(num);
printf("n = %d\n",n);
return 0;
}
Interview questions :
define and typedef The difference between ?
1.#define It's a preprocessing instruction , Simple replacement of strings in the preprocessing stage , Does not participate in the compilation phase ,typedef Is the redefinition of type , The type was redefined during compilation
2. When using #define and typedef When defining multiple pointers ,define What is defined is the first pointer , It's all variables , and typedef All definitions refer to
3.define Generally used to represent constants , And the replacement of functions ,typedef Used for type redefinition
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Method 1:({})
// Method 2:do{}while(0)
int min;
#define MAX(a,b) ({int max;if(a > b)max=a;else max=b;max;}) //({}) There can be multiple statements , The last sentence is the return value of the macro
#define MIN(a,b) do{if(a < b) min = a;else min = b;}while(0)
#define PRINT_MSG(msg) do{printf("%s\n",msg);return -1;}while(0)
#define S(n) #n //# Represents string
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int *p = NULL;
int hello = 100;
printf("max = %d\n",MAX(100,200));
MIN(100,200);
printf("min = %d\n",min);
p = (int *)malloc(4);
if(p == NULL)
{
PRINT_MSG("malloc failed!\n");
}
printf("%s\n",S(10)); // String
return 0;
}
3、 ... and Storage type
auto:
register: Define variables on registers , Fast running speed , But the number of registers of the chip is limited , Cannot be used indefinitely
Register variables cannot take addresses
extern: The variables or files used are defined in other files
static:
1. Limit scope :( Modified variables or functions can only be used in this document )
2. Extending the life cycle
volatile: Ensure that data is fetched from memory every time , Instead of fetching data from the cache , Prevent the compiler from optimizing the code
1. When multiple threads access the same variable
2. Use C When the language operates the hardware address
#include <stdio.h>
int a = 100;
void fun()
{
static int i = 0;
printf("i = %d\n",i++);
printf("a = %d\n",a);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a = 200;
printf("a = %d\n",a);
{
int a = 300;
printf("a = %d\n",a);
}
printf("i = %d\n",i);
fun();
fun();
fun();
return 0;
}
Four memory management
The stack area : local variable , The function being called , The formal parameters are all on the stack
The stack area will not be cleared when it is released 0, So when defining variables, do not initialize , They are all random values ,
Stack space is automatically applied by the system , Automatic release
Heap area : Use malloc The allocated memory is in the heap , Manual application , Hand release
Static zone |.bss: Use static Decorated uninitialized variables and global uninitialized variables are in .bss paragraph
|----------------------------
|.data: Use static Decorated initialized variables and global initialized variables are in .data paragraph
|----------------------------
|.text: Code segment , Text segment
|----------------------------
|.ro: Read only data segment
|const int a;
|char *p = “helloworld”;
#include <stdio.h>
int a; //.bss paragraph
static int w = 4; //.data
int b = 1234; //.data
const int g = 789; //.ro
void func(void)
{
const int y = 1234; //.ro
int *p = &y; // The stack area
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char ch; //.stack
char ch1 = 'a'; //.stack
char *p = "aaaa"; //P .stack "aaaa":.ro
return 0;
}
Thinking questions 1
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char *p = NULL;
char *tmp = "helloworld";
p = (tmp + 4);
//p[-1] = ? p[-5] = ?
printf("p[-1] = %c,p[-5] = %c\n",p[-1],p[-5]);
return 0;
}
Thinking questions 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char *data = "12345678";
short *tmp = NULL;
char p[6] = {0};
tmp = (short *)&p[2];
*tmp = atoi(&data[4]);
printf("*tmp = %d\n",*tmp);//“5678”,atoi Until '\0' end
//p[0],p[1],p[2],p[3],p[4],p[5]?
int i = 0 ;
for(i = 0 ; i < 5;i++)
{
printf("p[%d] = %#x\n",i,p[i]);
}
return 0;
}
[email protected]:~/jsetc/208/day6$ ./8- Thinking questions 2
*tmp = 5678
p[0] = 0
p[1] = 0
p[2] = 0x2e
p[3] = 0x16
p[4] = 0
5、 ... and Structure
A structure is a construction type , The members of the structure are continuous in memory ,
But the members of the structure can be of different types .
The key words of the structure are struct To label .
Format :
struct Type name {
member 1;
member 2;
...
};
(1) Use of structures struct To mark
(2)struct Followed by the type name of the structure , Not variable names
(3) The members of the structure are {} Included
(4){} Add... To the back ;
(5) The members of the structure can be different
(6) The members of the structure are separated by semicolons
(7) You cannot assign values when defining a structure
(8) You cannot write functions in a structure , Because the bytes occupied by the function are not fixed , But you can write function pointers
(9) How the structure accesses members “ Variable . member ”
(10) Structure pointer to the way to access members “ Variable -> member ”
5.1 The use of structures
5.1.1 Definition and assignment of structure
#include <stdio.h>
struct person{
char name[32];
char sex;
int age;
int high;
float weight;
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
struct person p1;
strcpy(p1.name," Zhang San ");
p1.sex = 'm';
p1.age = 18;
p1.high = 189;
p1.weight = 80;
struct person *p2 = NULL;
p2 = (struct person *)malloc(sizeof(*p2));
if(p2 == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failure");
}
strcpy(p2->name," Zhang San ");
p2->sex = 'm';
p2->age = 18;
p2->high = 189;
p2->weight = 80;
return 0;
}
5.1.2 Define the structure and assign values at the same time
#include <stdio.h>
struct person{
char name[32];
char sex;
int age;
int high;
float weight;
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
struct person p1 = {"zhangsan",'m',20,186,80}; // Initialize all members
struct person p2 = { // Select member initialization
.name = "zhangsan",
.weight = 80
};
return 0;
}
5.1.3 Array of structs
struct person p1[3]; // This is the structure array , There are three in the array strcut person
5.2 How the structure is defined
5.2.1 Nameless structure
struct{
char name[32];
int age;
float weight;
} Variable 1, Variable 2;
struct Variable 1;-----》 This is the wrong way to write it
typedef struct{
char name[32];
int age;
float weight;
}student_t; // Type name
student_t Variable 1, Variable 2;
Be careful : The structure can be assigned as a whole , Array cannot be assigned as a whole after definition
5.2.2 The famous structure
typedef struct student{
char name[32];
int age;
float weight;
}student_t; // Type name
student_t Variable 1, Variable 2;
5.2.3 struct Special assignment method of
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct person{
char name[32];
char sex;
int age;
int high;
float weight;
}person;
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
person p;
p = (person){" Zhang an ",'m',20,189,80};
printf("name = %s,sex = %c age = %d high = %d weight = %f\n",p.name,p.sex,p.age,p.high,p.weight);
// Structure array assignment
// Method 1
person p1[2] = {
{
.name = "zhangsan",
.age = 19
},
{
.name = "zhangsi",
.age = 20
}
};
// Method 2:
person p2[3] = {
[0] = {
.name = "zhangsan",
.age = 19
},
[2] = {
.name = "zhangsi",
.age = 20
}
};
return 0;
}
// Method 3:
person p3[3];
p3[0].name
5.3 The size of bytes occupied by the structure
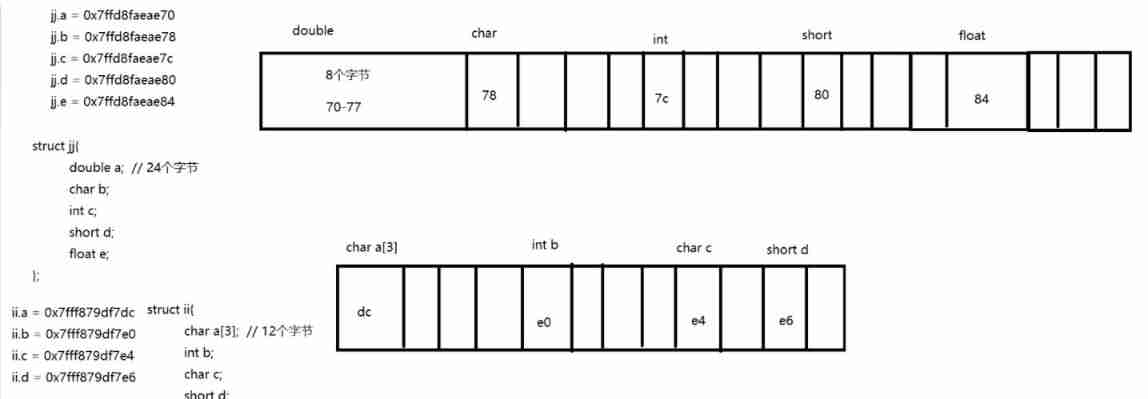
The rules :
The formula for the size of bytes occupied by structures is :
1. If the maximum member of the variable type inside the structure is less than or equal to 4 byte , Just align the memory according to the largest type
2. If the variable type inside the structure is greater than four bytes , Just align according to four bytes
3. The final size of the structure is aligned with the maximum type of members in the structure (32 Bit and 4 Byte alignment ,64 Bit and 8 Byte alignment )
#include <stdio.h>
struct aa{
char a; //1 Bytes
};
struct bb{
short a; //2 Bytes
};
struct cc{
int a; //4 Bytes
};
struct dd{
char a; // 2 Bytes
char b;
};
struct ee{
int a; // 8 Bytes
char b;
};
struct ff{
char a; // 6 Bytes
short b;
char c;
};
struct gg{
char a; // 8 Bytes
short b;
int c;
};
struct hh{
short a; // 8 Bytes
char b;
int c;
};
struct ii{
char a[3]; // 12 Bytes
int b;
char c;
short d;
};
struct jj{
double a; // 24 Bytes
char b;
int c;
short d;
float e;
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
struct ff a;
struct gg b;
struct jj c;
struct ii d;
printf("aa = %ld\n",sizeof(struct aa));
printf("bb = %ld\n",sizeof(struct bb));
printf("cc = %ld\n",sizeof(struct cc));
printf("dd = %ld\n",sizeof(struct dd));
printf("ee = %ld\n",sizeof(struct ee));
printf("ff = %ld\n",sizeof(struct ff));
printf("gg = %ld\n",sizeof(struct gg));
printf("hh = %ld\n",sizeof(struct hh));
printf("ii = %ld\n",sizeof(struct ii));
printf("jj = %ld\n",sizeof(struct jj));
printf("ff.a = %p\nff.b = %p\nff.c = %p\n",&a.a,&a.b,&a.c);
printf("gg.a = %p\ngg.b = %p\ngg.c = %p\n",&b.a,&b.b,&b.c);
printf("jj.a = %p\njj.b = %p\njj.c = %p\njj.d = %p\njj.e = %p\n\n",&c.a,&c.b,&c.c,&c.d,&c.e);
printf("ii.a = %p\nii.b = %p\nii.c = %p\nii.d = %p\n",d.a,&d.b,&d.c,&d.d);
return 0;
}
5.3.1 The bit field of the structure
A way to compress the size of a structure
#include <stdio.h>
struct aa{
char a:1;
char b:5;
char c:3;
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
printf("sizeof(aa) = %ld\n",sizeof(struct aa));
return 0;
}
1. When performing bit field operations inside the structure , It starts from the lowest position in memory , If this variable has
The symbol of , Then its highest bit is the sign bit , If there is only one bit in this bit field , It is both a symbol bit and a data bit
2. Members of the structure bit domain cannot get addresses
6、 ... and Shared body
6.1 Basic usage
union Internal members share the same memory space , The size of the community is the internal memory space of the largest member
No matter union How many members ,union The memory space of is the memory space of the largest member
Format :
union Type name {
char a;
short b;
int c;
};
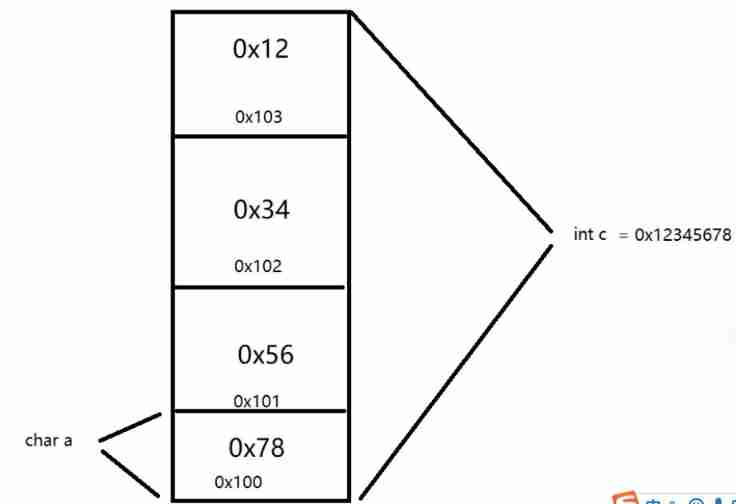
6.2 Judgment of size end
Byte order :
big-endian : The high byte is stored in the low address , The low byte is stored in the high address ( Network order )
Small end of the sequence : The high byte is stored in the high address , The low byte is stored in the low address
#include <stdio.h>
typedef union aa{
unsigned char a;
int c;
}aa_t;
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
aa_t a;
a.c = 0x12345678;
if(a.a == 0x12)
{
printf(" This is a big end machine \n");
}
else if(a.a == 0x78)
{
printf(" This is a small end machine \n");
}
return 0;
}
6.3 Define the consortium in the structure
Make the structure more versatile
#include <stdio.h>
struct aa
{
char a;
union{
int b;
char c;
};
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
struct aa a;
a.a = 10;
a.b = 0xaabb;
printf(“size = %ld\n”,sizeof(a));
printf(“c = %#x\n”,a.c);
return 0;
}
7、 ... and Enumeration type
Enumeration is the listing of finite data , For example, seven days a week , In a year 12 Months ,
These are all limited lists , Suitable for enumeration
Format :
enum Type name {
member 1,
member 2,
member 3,
member 4 = 10,
member 5,
...
member n,
};
(2) The key to enumerating types is enum
(2) Enum members have no variable types
(3) Members are distinguished by commas
(4) The values of the enumerated members are incremented downward 1
(5) The member access in enumeration is not through . perhaps -> To visit , Use it directly with members
(6) The size of the enumeration type is 4 Bytes
(7) If the enumeration type is not assigned an initial value , The default from the 0 Start
practice :
Instance of a :
#include <stdio.h>
enum week{
MON = 1,
TUS,
WED,
THU,
FRI,
SAT,
SUN
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
enum week day;
printf("day size = %ld\n",sizeof(day));
day = TUS;
printf("day = %d\n",day);
day = 10; // Although the compiler does not report errors , But you can't assign values like this
// When assigning values to enumeration type variables , Only enumeration constants can be assigned
printf("day = %d\n",day);
return 0;
}
Example 2
#include <stdio.h>
#define S(n) case n: return #n
typedef enum leds{
RED,
GREEN,
BLUE,
}leds;
char *led_type_to_str(enum leds led)
{
switch(led)
{
S(RED);
S(GREEN);
S(BLUE);
default:
return " There is no the ";
}
}
leds led_open(leds led)
{
printf(" open %s The lamp \n",led_type_to_str(led));
return led;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
#if 0
char *p = NULL;
enum leds led;
led = led_open(RED);
p = led_type_to_str(led);
printf(" open %s-ok!\n",p);
#endif
printf(" open %s-ok!\n",led_type_to_str(led_open(RED)));
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- 3.MNIST数据集分类
- 【愚公系列】2022年7月 Go教学课程 006-自动推导类型和输入输出
- 13. Enregistrement et chargement des modèles
- jemter分布式
- 11.递归神经网络RNN
- How is it most convenient to open an account for stock speculation? Is it safe to open an account on your mobile phone
- NTT template for Tourism
- SDNU_ACM_ICPC_2022_Summer_Practice(1~2)
- 2022-07-07: the original array is a monotonic array with numbers greater than 0 and less than or equal to K. there may be equal numbers in it, and the overall trend is increasing. However, the number
- New library online | information data of Chinese journalists
猜你喜欢
NVIDIA Jetson test installation yolox process record
基于卷积神经网络的恶意软件检测方法
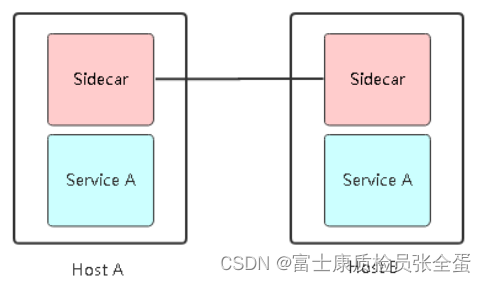
Service mesh introduction, istio overview
完整的模型训练套路
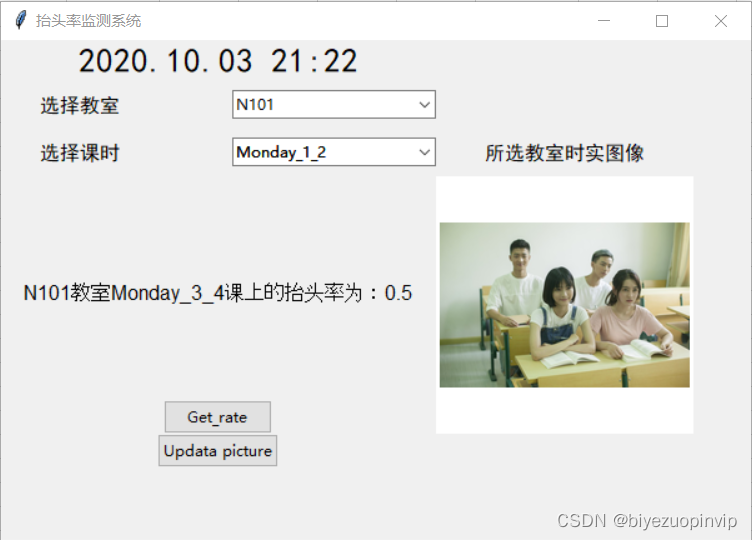
基于人脸识别实现课堂抬头率检测
![[necessary for R & D personnel] how to make your own dataset and display it.](/img/50/3d826186b563069fd8d433e8feefc4.png)
[necessary for R & D personnel] how to make your own dataset and display it.

How does starfish OS enable the value of SFO in the fourth phase of SFO destruction?
基于微信小程序开发的我最在行的小游戏
5g NR system messages
Application practice | the efficiency of the data warehouse system has been comprehensively improved! Data warehouse construction based on Apache Doris in Tongcheng digital Department
随机推荐
fabulous! How does idea open multiple projects in a single window?
ReentrantLock 公平锁源码 第0篇
Password recovery vulnerability of foreign public testing
What has happened from server to cloud hosting?
Course of causality, taught by Jonas Peters, University of Copenhagen
韦东山第二期课程内容概要
6.Dropout应用
3.MNIST数据集分类
AI zhetianchuan ml novice decision tree
Basic mode of service mesh
The weight of the product page of the second level classification is low. What if it is not included?
2.非线性回归
"An excellent programmer is worth five ordinary programmers", and the gap lies in these seven key points
[Yugong series] go teaching course 006 in July 2022 - automatic derivation of types and input and output
SDNU_ACM_ICPC_2022_Summer_Practice(1~2)
大二级分类产品页权重低,不收录怎么办?
Four stages of sand table deduction in attack and defense drill
Fofa attack and defense challenge record
What if the testing process is not perfect and the development is not active?
华泰证券官方网站开户安全吗?