当前位置:网站首页>Thread pool reject policy best practices
Thread pool reject policy best practices
2022-07-07 13:29:00 【Bug Commander】
Thread pool exhaustion occurs occasionally in projects on the front line , Recently, I finally have time to study it well , The problem is actually not complicated , Also thanks to Dubbo The rejection policy of thread pool can quickly find the general reason .
Through this question , I'm also curious about the thread pool rejection strategy used by various countries , Dig a hole 、 Dig soil , Let's see ~
The problem background
Thread pool exhaustion occurs occasionally on the front line , The phenomenon is as follows :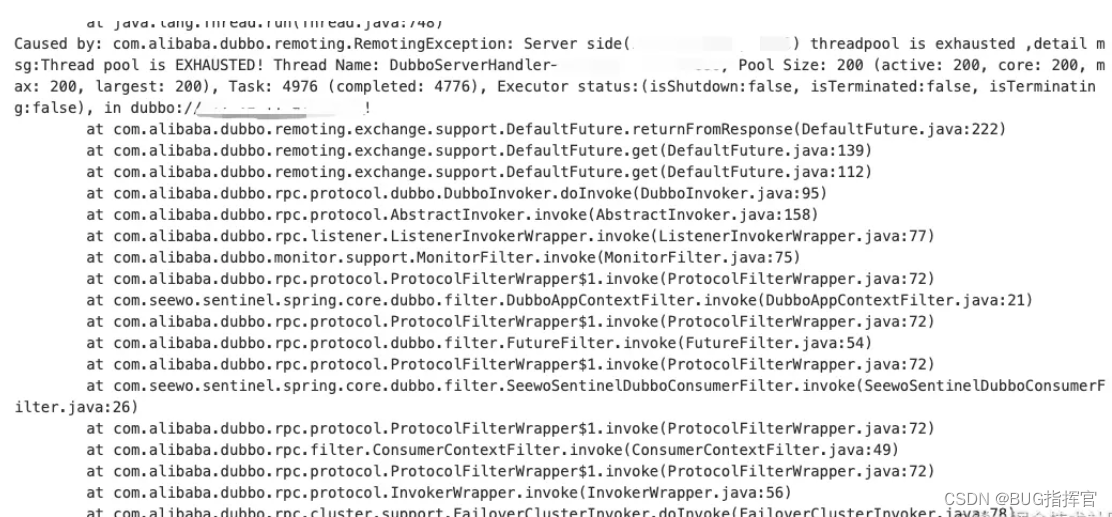
Downstream of the call Dubbo Interface , Tips Server The thread pool on the end is exhausted .
At first, I thought there was sudden traffic , But the monitoring shows that the flow is stable , And problems still exist after capacity expansion , Gradually realize that the problem is not simple .

Problem analysis
Since there are exception logs and stacks , First, let's see what scenario this exception will appear . stay Dubbo Source code , We can find this prompt in AbortPolicyWithReport in .
public class AbortPolicyWithReport extends ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy
AbortPolicyWithReport Inherited from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy, It is a thread pool rejection policy , When the buffer task queue in the thread pool is full , When the number of threads reaches the maximum , Will trigger the rejection policy , Invoking the rejection policy rejectedExecution() Methods to deal with .
that , What are the different rejection strategies ?
JDK Thread pool rejection policy
stay java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor, We can find JDK Four preset rejection strategies :
- CallerRunsPolicy - Caller thread processing
Under this strategy , If the thread pool is not closed , Then it will be handled by the current caller thread , Otherwise, discard the task directly .
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
- AbortPolicy - Throw an exception
If the rejection policy is not configured , The thread pool will use this policy by default , Direct selling rejectedExecution, Leave it to the upper business .
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("...");
}
- DiscardPolicy - Discard the current task
The simplest way to deal with it , Direct discarding .
// The actual method body is empty , That is, it is not processed in this scenario , Direct discarding
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
}
- DiscardOldestPolicy - Discard the next task to perform
This strategy is to discard the oldest task in the queue ( In fact, it is the next task to be performed ), And try to perform the current task .
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
Dubbo Thread pool rejection policy
that Dubbo What is your rejection strategy ?
In fact, it can be seen from the name ,AbortPolicyWithReport.
public class AbortPolicyWithReport extends ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy {
...
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
String msg = String.format("Thread pool is EXHAUSTED!" + ...);
logger.warn(msg);
dumpJStack();
dispatchThreadPoolExhaustedEvent(msg);
throw new RejectedExecutionException(msg);
}
...
}
Dubbo The rejection strategy of is to throw an exception RejectedExecutionException, At the same time, I will do one thing - dumpJStack(), Record the time JVM Thread stack .
dumpJStack
Let's look at the source code first .
private void dumpJStack() {
// some dump Time interval and concurrency control
...
// Create a new one-way pool for dump Stack
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
pool.execute(() -> {
...
try (FileOutputStream jStackStream = new FileOutputStream(
new File(dumpPath, "Dubbo_JStack.log" + "." + dateStr))) {
JVMUtil.jstack(jStackStream);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("dump jStack error", t);
}
...
});
...
}
It's very simple , The final call JVMUtil.jstack Put the present JVM The thread stack of dump Come down , And doing so has a great advantage , That is to know what other threads were doing at that time , Help analyze the cause of thread pool overflow .
Cause analysis
It's easy to have a thread stack , Look at what threads were doing at that time .
Dubbo Bottom use Netty Network communication , The thread pools involved include IO Thread pool (boss、worker) And business thread pool ( Handle business events ). From the previous log, we can see that Server Business thread pool on the end , namely DubboServerHandler Run out of , Then count , See what threads are doing .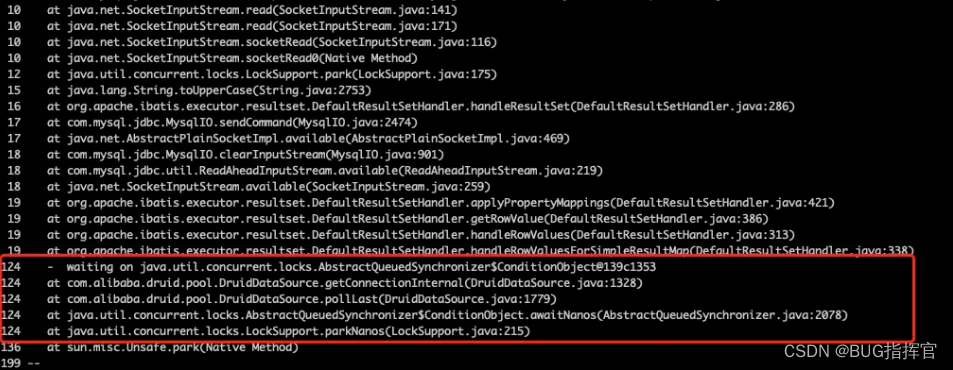
Obviously , A large number of threads are blocked in getting DB Connected to the . Then it's easy to do , You can check whether slow queries occupy the connection for a long time in the same time period , Or is it true that the connection pool is small , The thread pool and connection pool are mismatched , So far, the analysis will not continue ( It's not the point of discussion, haha ).
Different rejection strategies
You can see ,Dubbo By rewriting the reject policy , To help locate problems in abnormal scenarios , It has helped a lot .
So how do other mainstream components do it ?
RocketMQ
With Broker For example , It contains many thread pools for different message processing scenarios , contain send、put、pull、query wait .
Use of process pool ,RocketMQ adopt BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor Inheritance encapsulates a layer ThreadPoolExecutor, The upper layer can pass in parameters by itself , It also includes configurable RejectedExecutionHandler.
Actually Broker When creating different thread pools for message processing , No special rejection policy is specified , So the default is AbortPolicy, Throw an exception .
this.sendMessageExecutor = new BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getSendMessageThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getSendMessageThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.sendThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("SendMessageThread_")
// No rejection policy is set
);
At the same time, in order to avoid task overflow , A larger task queue size is set for each thread pool by default .
private int sendThreadPoolQueueCapacity = 10000;
private int putThreadPoolQueueCapacity = 10000;
private int pullThreadPoolQueueCapacity = 100000;
private int replyThreadPoolQueueCapacity = 10000;
private int queryThreadPoolQueueCapacity = 20000;
private int clientManagerThreadPoolQueueCapacity = 1000000;
private int consumerManagerThreadPoolQueueCapacity = 1000000;
private int heartbeatThreadPoolQueueCapacity = 50000;
private int endTransactionPoolQueueCapacity = 100000;
Sum up ,RocketMQ The rejection strategy of uses AbortPolicy, Throw an exception , At the same time, in order to avoid task queue overflow , Set a large task queue .
Netty
With EventLoopGroup For example , By default, the reject policy of the thread pool uses RejectedExecutionHandlers, Provide... Through singleton mode Handler To deal with .
public final class RejectedExecutionHandlers {
private static final RejectedExecutionHandler REJECT = new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
@Override
public void rejected(Runnable task, SingleThreadEventExecutor executor) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException();
}
};
private RejectedExecutionHandlers() { }
public static RejectedExecutionHandler reject() {
return REJECT;
}
...
}
It can be seen that ,Netty By default, the rejection policy of also throws an exception , And RocketMQ The difference in comparison is , The size of the task queue will take max(16, maxPendingTasks),io.netty.eventLoop.maxPengdingTasks It can be configured through environment variables .
Doris
The team has been using Doris, It belongs to computing storage separation 、MPP Analytical storage components of the architecture , Take a look at FE Rejection strategy in , Officially, there are two :
LogDiscardPolicy
static class LogDiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
private static final Logger LOG = LogManager.getLogger(LogDiscardPolicy.class);
private String threadPoolName;
public LogDiscardPolicy(String threadPoolName) {
this.threadPoolName = threadPoolName;
}
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
LOG.warn("Task " + r.toString() + " rejected from " + threadPoolName + " " + executor.toString());
}
}
It's understandable that DiscardPolicy, Discarding the task , Simultaneous recording warn journal .
BlockedPolicy
static class BlockedPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
private String threadPoolName;
private int timeoutSeconds;
public BlockedPolicy(String threadPoolName, int timeoutSeconds) {
this.threadPoolName = threadPoolName;
this.timeoutSeconds = timeoutSeconds;
}
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
try {
executor.getQueue().offer(r, timeoutSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("Task " + r.toString() + " wait to enqueue in " + threadPoolName + " " + executor.toString() + " failed");
}
}
}
This strategy will be special , It will block the current thread , Try your best to put the task in the queue . If the specified blocking time is exceeded timeoutSeconds( Default 60s), Still unable to put the task in the queue , Record warn journal , And discard the task .
These two strategies are Doris It is actually used in , At the same time, the task queue size of the thread pool is set to 10.
ElasticSearch
ES The rejection strategy of is relatively complex , Its customization implements two rejection policies .
- EsAbortPolicy
public class EsAbortPolicy extends EsRejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
if (r instanceof AbstractRunnable) {
if (((AbstractRunnable) r).isForceExecution()) {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = executor.getQueue();
if ((queue instanceof SizeBlockingQueue) == false) {
throw new IllegalStateException("forced execution, but expected a size queue");
}
try {
((SizeBlockingQueue<Runnable>) queue).forcePut(r);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new IllegalStateException("forced execution, but got interrupted", e);
}
return;
}
}
incrementRejections();
throw newRejectedException(r, executor, executor.isShutdown());
}
}
It's essentially AbortPolicy, But there will be some special treatment , Include forceExecution Judgment of enforcement 、 Statistics of task rejection times , Finally throw an exception .
ES in , Thread pool
forceExecutionWhat is it? ?When the conditions are met , That is to use ES Self defined
AbstractRunnablePerform task encapsulation 、SizeBlockingQueueAs a task queue , You can determine whether to force it into the task queue according to the task configuration . For some important tasks , When it cannot be discarded , Can beforceExecutionSet to true.The effect of being forced into the task queue depends on
SizeBlockingQueueQueue types encapsulated in , If the package isArrayBlockingQueue, Then the waiting queue will be blocked and free ; If the package isLinkedTransferQueue, Because the queue size is infinite , And put It uses ASYNC Pattern , So it will be put in the queue immediately and return .
- ForceQueuePolicy
static class ForceQueuePolicy extends EsRejectedExecutionHandler {
...
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable task, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
if (rejectAfterShutdown) {
if (executor.isShutdown()) {
reject(executor, task);
} else {
put(executor, task);
if (executor.isShutdown() && executor.remove(task)) {
reject(executor, task);
}
}
} else {
put(executor, task);
}
}
private static void put(ThreadPoolExecutor executor, Runnable task) {
final BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = executor.getQueue();
// force queue policy should only be used with a scaling queue
assert queue instanceof ExecutorScalingQueue;
try {
queue.put(task);
} catch (final InterruptedException e) {
assert false : "a scaling queue never blocks so a put to it can never be interrupted";
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
private void reject(ThreadPoolExecutor executor, Runnable task) {
incrementRejections();
throw newRejectedException(task, executor, true);
}
}
}
This policy does not close the thread pool , And used ES Self defined ExecutorScalingQueue Task queue of , Will force the task to be placed in the thread pool queue . among ,ExecutorScalingQueue It's also inherited from LinkedTransferQueue, The final call put Methods to ASYNC Put the mode into the task queue .
It looks like
forceExecution, And they all end up usingLinkedTransferQueueOf put Methods to ASYNC Mode non blocking queue . thatEsAbortPolicyandForceQueuePolicyWhat's the difference ?There are many similarities between the two , There are
forceExecutionThe judgment of the , And when you refuse, you throwRejectedExecutionException.The difference is ,
ForceQueuePolicyThe default mode is enforcement , And it is still possible to put tasks into the queue when the process pool is closed .
other
stay GitHub I flipped it casually , There are also ways to use the strategy chain , The implementation is also simple , Different strategies can be combined and configured at will .
public class RejectedExecutionChainPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
private final RejectedExecutionHandler[] handlerChain;
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
for (RejectedExecutionHandler handler : handlerChain) {
handler.rejectedExecution(r, executor);
}
}
}
summary
The rejection policy is mainly used in the case of resource overflow in the thread pool , In addition to the common reasons JDK In addition to the four rejection strategies provided , Different components will also try to use different rejection strategies to apply .
JDK The rejection policy provided
| type | explain |
|---|---|
| CallerRunsPolicy | JDK Provide , Caller thread processing |
| AbortPolicy | JDK Thread pool is used by default , Throw out RejectedExecutionException abnormal |
| DiscardPolicy | JDK Provide , Discard the current task |
| DiscardOldestPolicy | JDK Provide , Discard the next task to perform |
Custom reject policy
| Components | type | explain |
|---|---|---|
| RocketMQ | AbortPolicy | The thread pool used is slightly rejected by default , namely AbortPolicy |
| Dubbo | AbortPolicyWithReport | Throw out RejectedExecutionException abnormal , And report overflow , Record JVM Thread stack |
| Netty | RejectedExecutionHandlers | Logic and AbortPolicy Agreement , Throw an exception , Encapsulation is a single example Handler Use |
| Doris | LogDiscardPolicy | Logic and DiscardPolicy Agreement , Discarding the task , And record warn journal |
| Doris | BlockedPolicy | Try your best to put the task in the queue for execution , Waiting for the most 60s, Record after timeout warn journal , And discard the task |
| Elastic | EsAbortPolicy | Under normal circumstances, it is similar to AbortPolicy Agreement , If thread marking is enforced , Then it is forced to execute or put into the task queue , The performance of the actual queue depends on the queue type , May block or return immediately |
| Elastic | ForceQueuePolicy | By default, the task is enforced or placed in the task queue , Asynchronous non-blocking |
| other | PolicyChain | Policy chain , Contains a variety of rejection policies , Determine the final performance according to the conditions and node processing results |
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Storage principle inside mongodb
![Scripy tutorial classic practice [New Concept English]](/img/bc/f1ef8b6de6bfb6afcdfb0d45541c72.png)
Scripy tutorial classic practice [New Concept English]
Ogre introduction
![[Presto profile series] timeline use](/img/c6/83c4fdc5f001dab34ecf18c022d710.png)
[Presto profile series] timeline use

为租客提供帮助
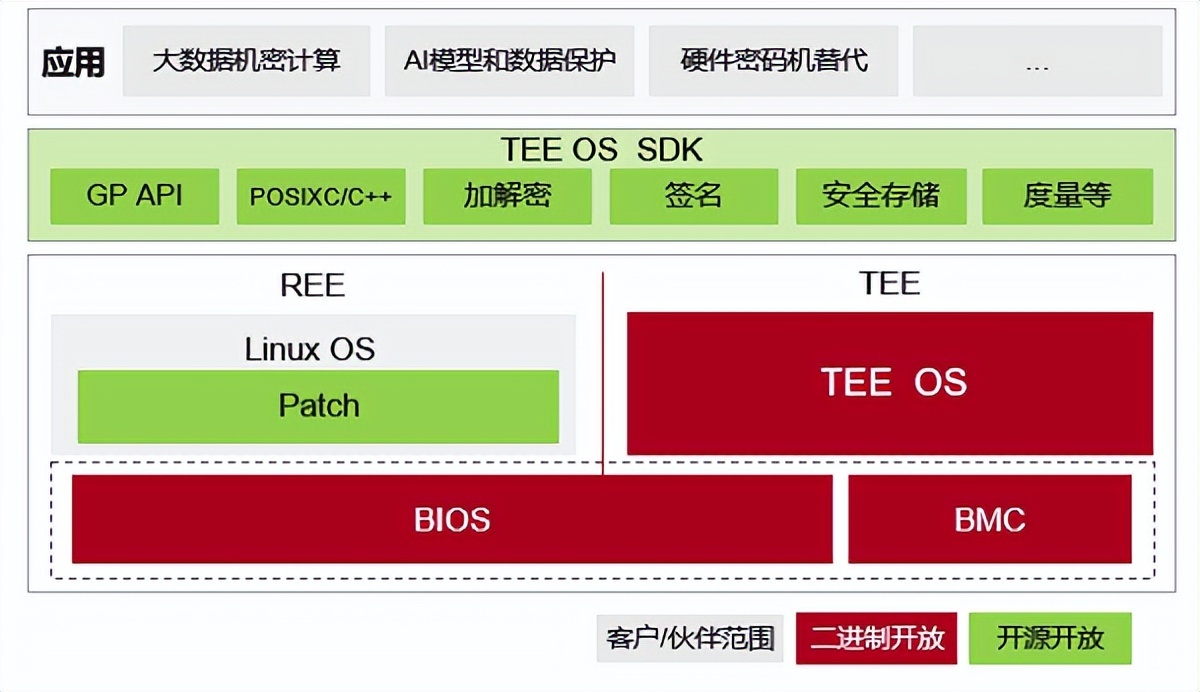
基于鲲鹏原生安全,打造安全可信的计算平台
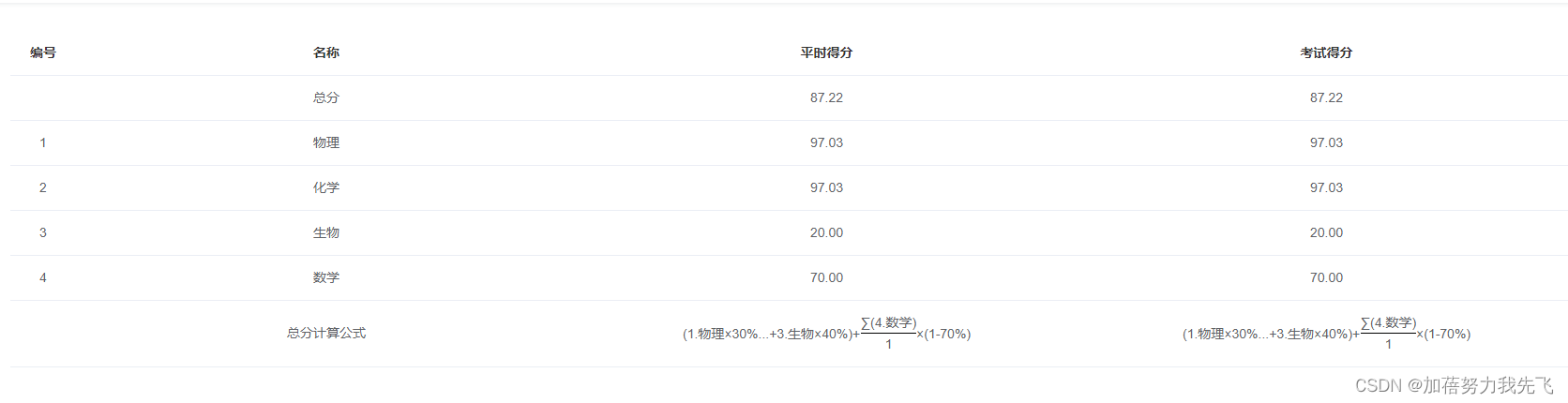
将数学公式在el-table里面展示出来

Per capita Swiss number series, Swiss number 4 generation JS reverse analysis
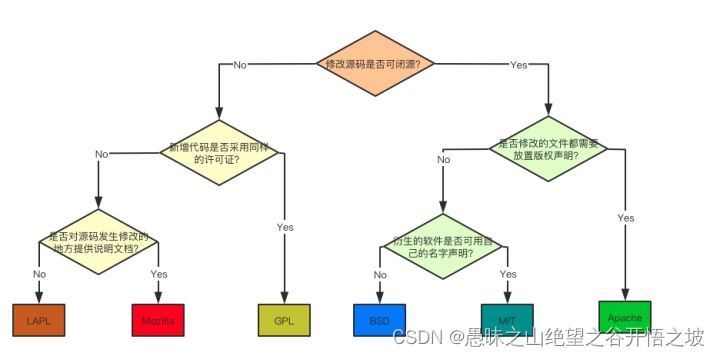
Introduce six open source protocols in detail (instructions for programmers)
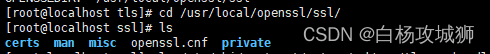
centso7 openssl 报错Verify return code: 20 (unable to get local issuer certificate)
随机推荐
LIS longest ascending subsequence problem (dynamic programming, greed + dichotomy)
为租客提供帮助
Vscode编辑器ESP32头文件波浪线不跳转彻底解决
JNA学习笔记一:概念
My "troublesome" subordinates after 00: not bad for money, against leaders, and resist overtime
shell 批量文件名(不含扩展名)小写改大写
RecyclerView的数据刷新
MongoDB优化的几点原则
Navicat运行sql文件导入数据不全或导入失败
如何让electorn打开的新窗口在window任务栏上面
【黑马早报】华为辟谣“军师”陈春花;恒驰5预售价17.9万元;周杰伦新专辑MV 3小时播放量破亿;法华寺回应万元月薪招人...
MongoDB的导入导出、备份恢复总结
ESP32 ① 编译环境
国泰君安证券开户怎么开的?开户安全吗?
Shell batch file name (excluding extension) lowercase to uppercase
高端了8年,雅迪如今怎么样?
10 张图打开 CPU 缓存一致性的大门
Error lnk2019: unresolved external symbol
【学习笔记】AGC010
Coscon'22 community convening order is coming! Open the world, invite all communities to embrace open source and open a new world~