当前位置:网站首页>Map of mL: Based on the adult census income two classification prediction data set (whether the predicted annual income exceeds 50K), use the map value to realize the interpretable case of xgboost mod
Map of mL: Based on the adult census income two classification prediction data set (whether the predicted annual income exceeds 50K), use the map value to realize the interpretable case of xgboost mod
2022-07-06 06:44:00 【A Virgo procedural ape】
ML And shap: be based on adult Census income two classification forecast data set ( Whether the predicted annual income exceeds 50k) utilize Shap It's worth it XGBoost A detailed introduction to interpretable cases of model implementation
Catalog
# 2.1、 Preliminary screening of modeling features
# 2.2、 Target feature binarization
# 2.3、 Category feature coding digitization
# 2.4、 Separate features from labels
#3、 Model training and reasoning
# 3.2、 Model building and training
#4、 Model feature importance interpretation visualization
#4.1、 Visualization of global feature importance
# T1、 Output the importance of features based on the model itself
# T2、 utilize Shap Value interpretation XGBR Model
#4.2、 Visualization of local feature importance
# (1)、 Single sample full feature bar graph visualization
# (2)、 One turn two feature full sample local independent graph scatter diagram visualization
# (3)、 Visualization of double feature full sample scatter diagram
# 4.3、 Model feature screening
# (1)、 Clustering based shap Feature filtering visualization
5、 Interpretability of model prediction ( It can mainly analyze misclassified samples )
(1)、 A single sample tries to visualize — Compare predictions
(2)、 Multiple samples try to visualize
# 5.2、 Visual analysis of decision diagram : How models make decisions
# (1)、 Single sample decision graph visualization
# (2)、 Visualization of multiple sample decision diagrams
be based on adult Census income two classification forecast data set ( Whether the predicted annual income exceeds 50k) utilize Shap It's worth it XGBoost Model implementation interpretability case
1、 Define datasets
dtypes_len: 15
| age | workclass | fnlwgt | education | education_num | marital_status | occupation | relationship | race | sex | capital_gain | capital_loss | hours_per_week | native_country | salary |
| 39 | State-gov | 77516 | Bachelors | 13 | Never-married | Adm-clerical | Not-in-family | White | Male | 2174 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 50 | Self-emp-not-inc | 83311 | Bachelors | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Husband | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 13 | United-States | <=50K |
| 38 | Private | 215646 | HS-grad | 9 | Divorced | Handlers-cleaners | Not-in-family | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 53 | Private | 234721 | 11th | 7 | Married-civ-spouse | Handlers-cleaners | Husband | Black | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 28 | Private | 338409 | Bachelors | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Prof-specialty | Wife | Black | Female | 0 | 0 | 40 | Cuba | <=50K |
| 37 | Private | 284582 | Masters | 14 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Wife | White | Female | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 49 | Private | 160187 | 9th | 5 | Married-spouse-absent | Other-service | Not-in-family | Black | Female | 0 | 0 | 16 | Jamaica | <=50K |
| 52 | Self-emp-not-inc | 209642 | HS-grad | 9 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Husband | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 45 | United-States | >50K |
| 31 | Private | 45781 | Masters | 14 | Never-married | Prof-specialty | Not-in-family | White | Female | 14084 | 0 | 50 | United-States | >50K |
| 42 | Private | 159449 | Bachelors | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Husband | White | Male | 5178 | 0 | 40 | United-States | >50K |
2、 Data set preprocessing
# 2.1、 Preliminary screening of modeling features
df.columns
14
# 2.2、 Target feature binarization
# 2.3、 Category feature coding digitization
filt_dtypes_len: 13 [('age', 'float32'), ('workclass', 'category'), ('fnlwgt', 'float32'), ('education_Num', 'float32'), ('marital_status', 'category'), ('occupation', 'category'), ('relationship', 'category'), ('race', 'category'), ('sex', 'category'), ('capital_gain', 'float32'), ('capital_loss', 'float32'), ('hours_per_week', 'float32'), ('native_country', 'category')]
# 2.4、 Separate features from labels
df_adult_display
| age | workclass | education_num | marital_status | occupation | relationship | race | sex | capital_gain | capital_loss | hours_per_week | native_country | salary | |
| 0 | 39 | State-gov | 13 | Never-married | Adm-clerical | Not-in-family | White | Male | 2174 | 0 | 40 | United-States | 0 |
| 1 | 50 | Self-emp-not-inc | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Husband | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 13 | United-States | 0 |
| 2 | 38 | Private | 9 | Divorced | Handlers-cleaners | Not-in-family | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | 0 |
| 3 | 53 | Private | 7 | Married-civ-spouse | Handlers-cleaners | Husband | Black | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | 0 |
| 4 | 28 | Private | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Prof-specialty | Wife | Black | Female | 0 | 0 | 40 | Cuba | 0 |
| 5 | 37 | Private | 14 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Wife | White | Female | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | 0 |
| 6 | 49 | Private | 5 | Married-spouse-absent | Other-service | Not-in-family | Black | Female | 0 | 0 | 16 | Jamaica | 0 |
| 7 | 52 | Self-emp-not-inc | 9 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Husband | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 45 | United-States | 1 |
| 8 | 31 | Private | 14 | Never-married | Prof-specialty | Not-in-family | White | Female | 14084 | 0 | 50 | United-States | 1 |
| 9 | 42 | Private | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Husband | White | Male | 5178 | 0 | 40 | United-States | 1 |
df_adult
| age | workclass | education_num | marital_status | occupation | relationship | race | sex | capital_gain | capital_loss | hours_per_week | native_country | salary | |
| 0 | 39 | 7 | 13 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2174 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 0 |
| 1 | 50 | 6 | 13 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 39 | 0 |
| 2 | 38 | 4 | 9 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 0 |
| 3 | 53 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 0 |
| 4 | 28 | 4 | 13 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | 37 | 4 | 14 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 0 |
| 6 | 49 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 23 | 0 |
| 7 | 52 | 6 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 39 | 1 |
| 8 | 31 | 4 | 14 | 4 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 14084 | 0 | 50 | 39 | 1 |
| 9 | 42 | 4 | 13 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 5178 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 1 |
# 2.5、 Data set segmentation
df_len: 32561 ,train_test_index: 30933
X.shape,y.shape: (30933, 12) (30933,)
X_test.shape,y_test.shape: (1628, 12) (1628,)
#3、 Model training and reasoning
# 3.1、 Data set segmentation
# 3.2、 Model building and training
# 3.3、 Model to predict
| age | workclass | education_num | marital_status | occupation | relationship | race | sex | capital_gain | capital_loss | hours_per_week | native_country | y_val_predi | y_val | |
| 11311 | 29 | 4 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| 12519 | 33 | 4 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 8614 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 1 | 1 |
| 29225 | 27 | 4 | 13 | 4 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| 5428 | 22 | 4 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| 2400 | 32 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| 4319 | 45 | 4 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 1 | 0 |
| 26564 | 43 | 4 | 9 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| 4721 | 60 | 0 | 13 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 39 | 0 | 1 |
| 19518 | 29 | 6 | 9 | 2 | 12 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 35 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| 25013 | 33 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
#4、 Model feature importance interpretation visualization
#4.1、 Visualization of global feature importance
# T1、 Output the importance of features based on the model itself
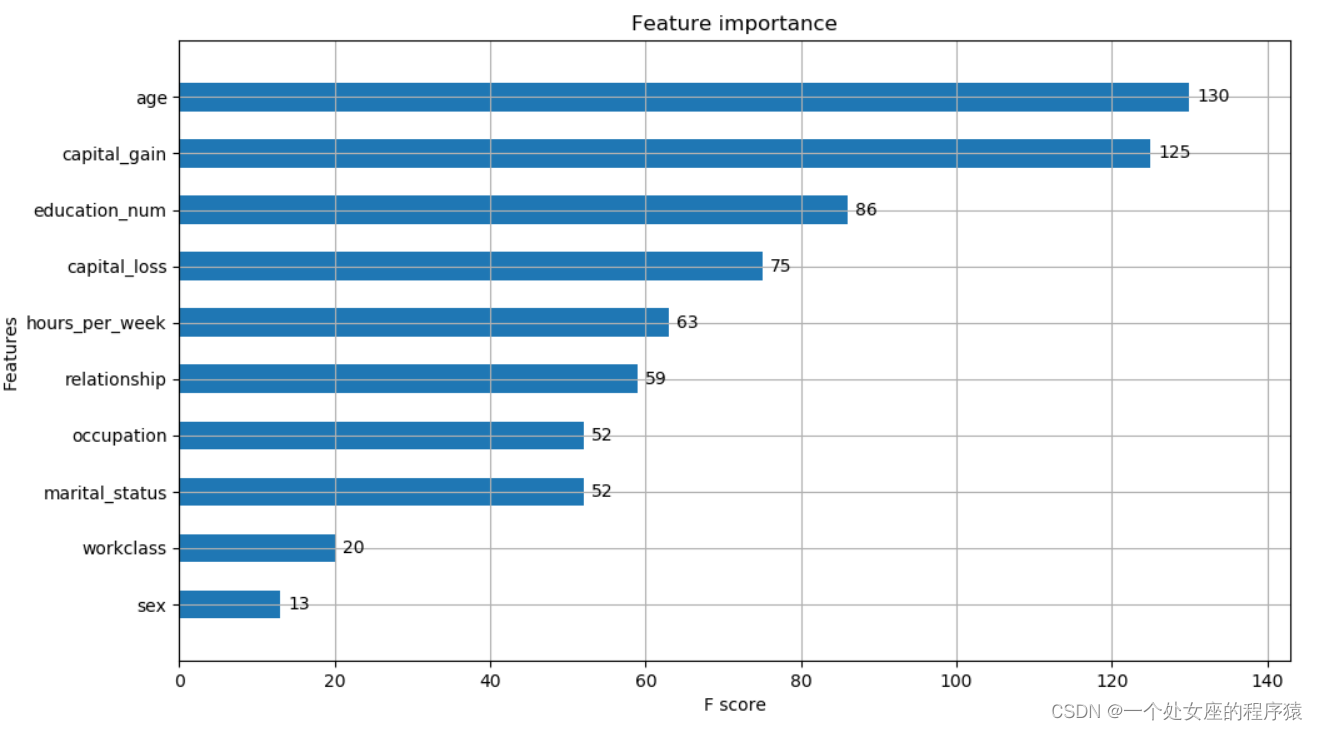
XGBR_importance_dict: [('age', 130), ('capital_gain', 125), ('education_num', 86), ('capital_loss', 75), ('hours_per_week', 63), ('relationship', 59), ('marital_status', 52), ('occupation', 52), ('workclass', 20), ('sex', 13), ('native_country', 10), ('race', 6)]
# T2、 utilize Shap Value interpretation XGBR Model
utilize shap The built-in function realizes the visualization of feature contribution —— The ranking of feature importance is similar to the above , But it's not the same
# (1)、 establish Explainer And calculate SHAP value

# T2.1、 Output shap.Explanation object
# T2,2、 Output numpy.array Array
shap2exp.values.shape (30933, 12)
[[ 0.31074238 -0.16607898 0.5617416 ... -0.04660619 -0.09465054
0.00530914]
[ 0.34912622 -0.16633348 0.65308005 ... -0.06718991 -0.9804511
0.00515459]
[ 0.21971266 0.02263742 -0.299867 ... -0.0583196 -0.09738331
0.00415599]
...
[-0.48140627 0.07019287 -0.30844492 ... -0.04253047 -0.10924102
0.00649792]
[ 0.39729887 -0.2313431 -0.45257783 ... -0.06502013 0.27416423
0.00587647]
[ 0.27594262 0.03170239 0.78293955 ... -0.06743324 0.31613
0.00530914]]
shap2array.shape (30933, 12)
[[ 0.31074238 -0.16607898 0.5617416 ... -0.04660619 -0.09465054
0.00530914]
[ 0.34912622 -0.16633348 0.65308005 ... -0.06718991 -0.9804511
0.00515459]
[ 0.21971266 0.02263742 -0.299867 ... -0.0583196 -0.09738331
0.00415599]
...
[-0.48140627 0.07019287 -0.30844492 ... -0.04253047 -0.10924102
0.00649792]
[ 0.39729887 -0.2313431 -0.45257783 ... -0.06502013 0.27416423
0.00587647]
[ 0.27594262 0.03170239 0.78293955 ... -0.06743324 0.31613
0.00530914]]
shap2exp.values And shap2array, Whether the two matrices are equal : True# (2)、 Characteristics of the whole sample shap Value bar graph visualization
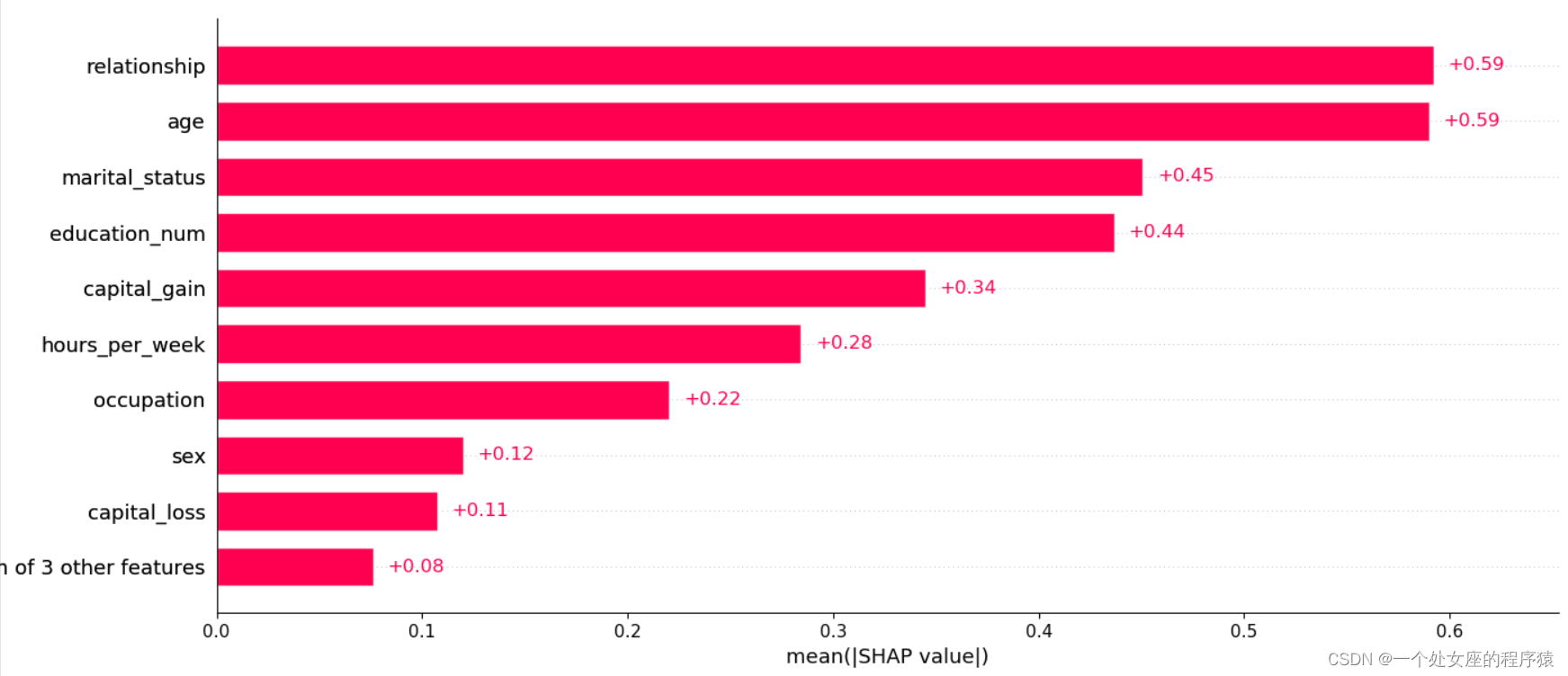
# shap Value high-order interactive visualization
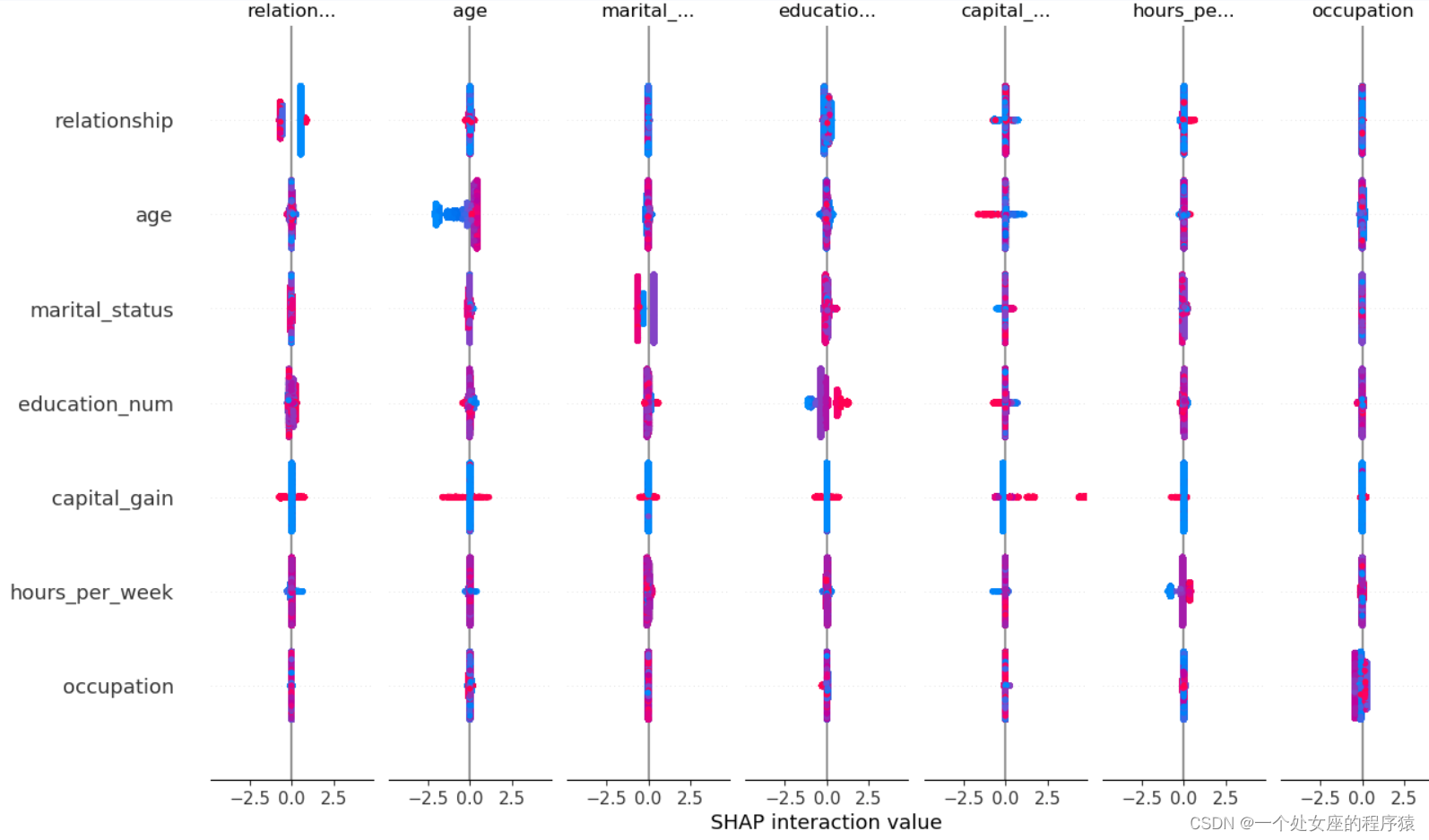
# (3)、 Characteristics of the whole sample shap Value colony graph visualization
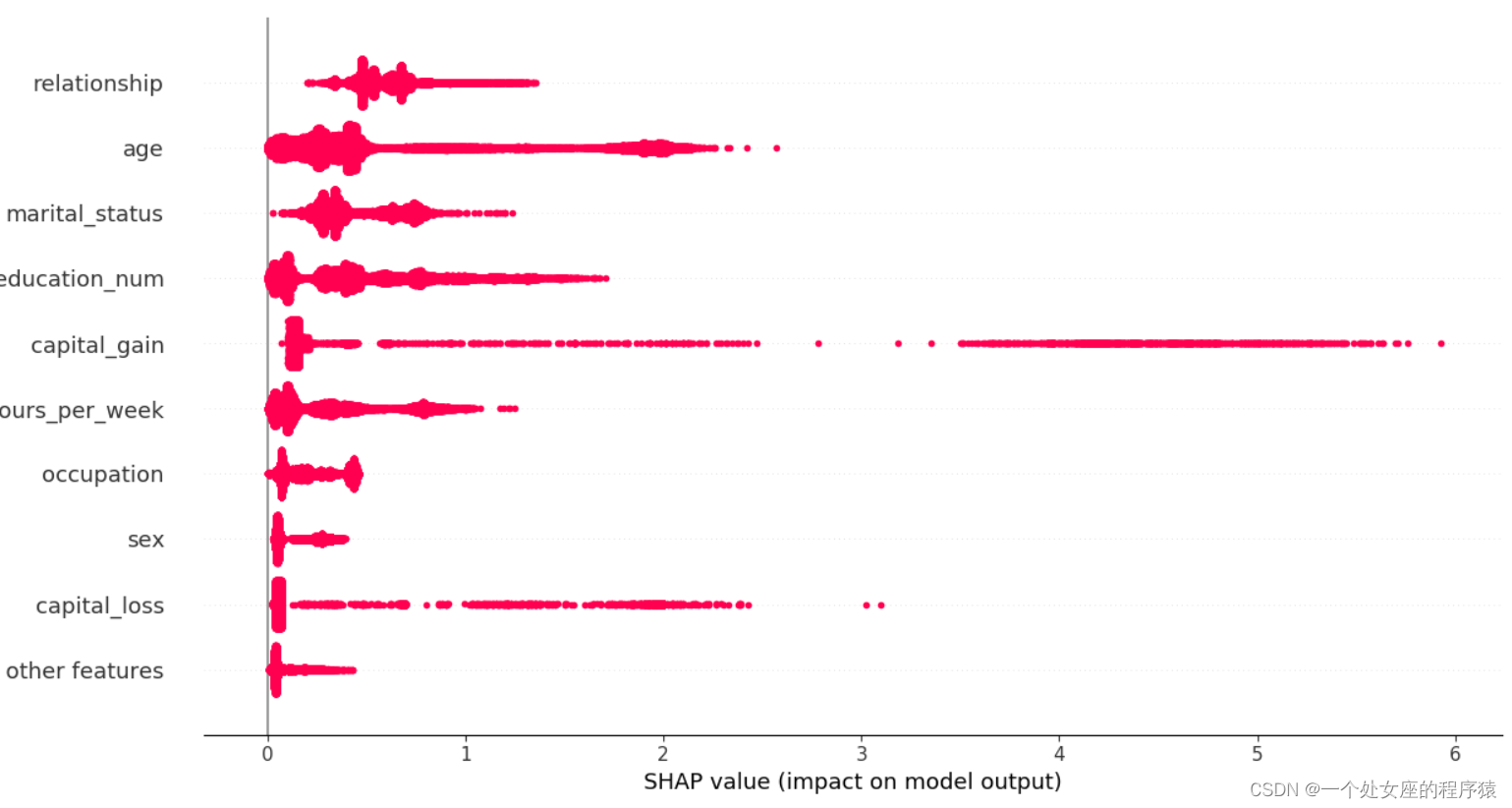
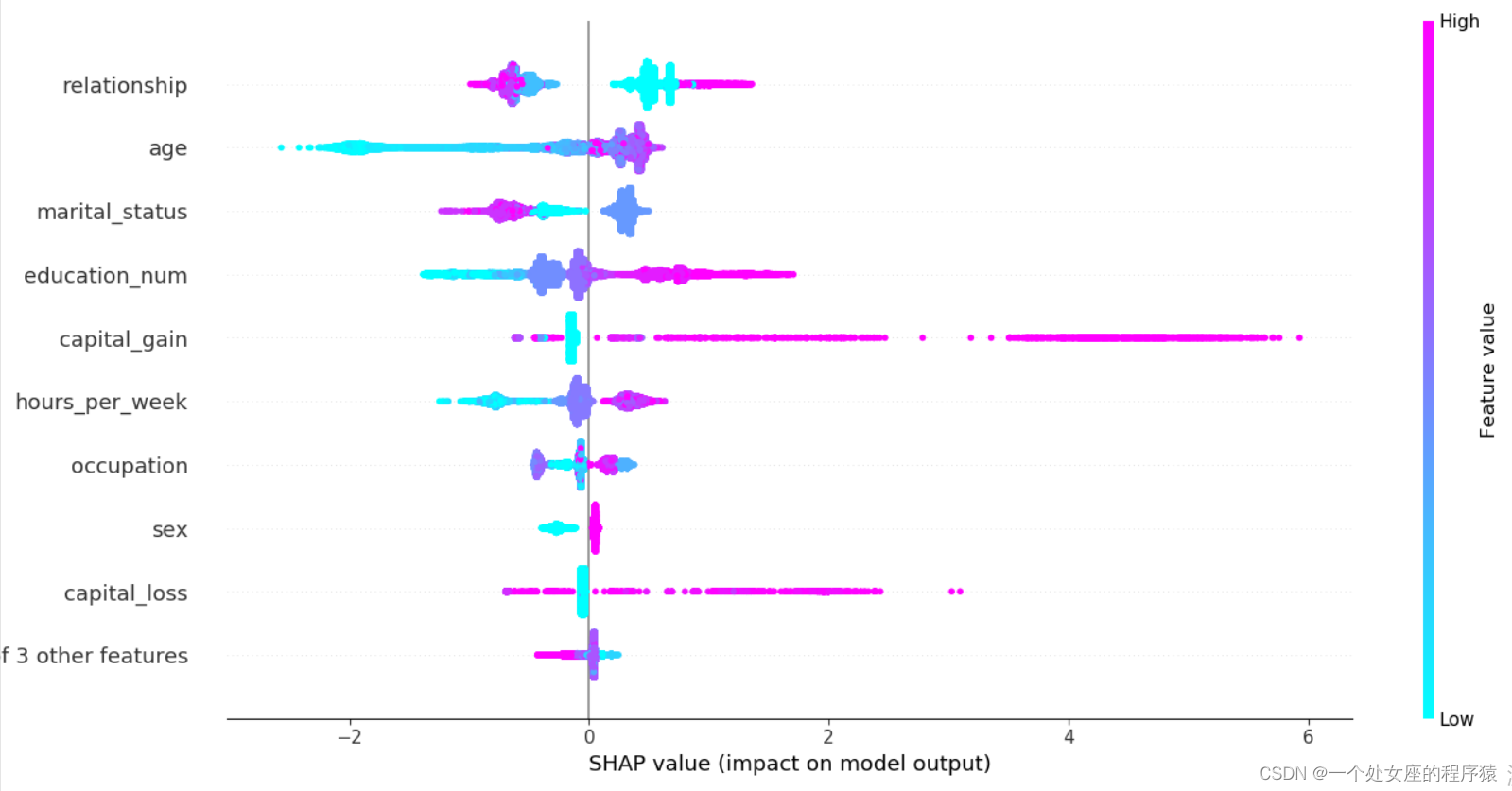
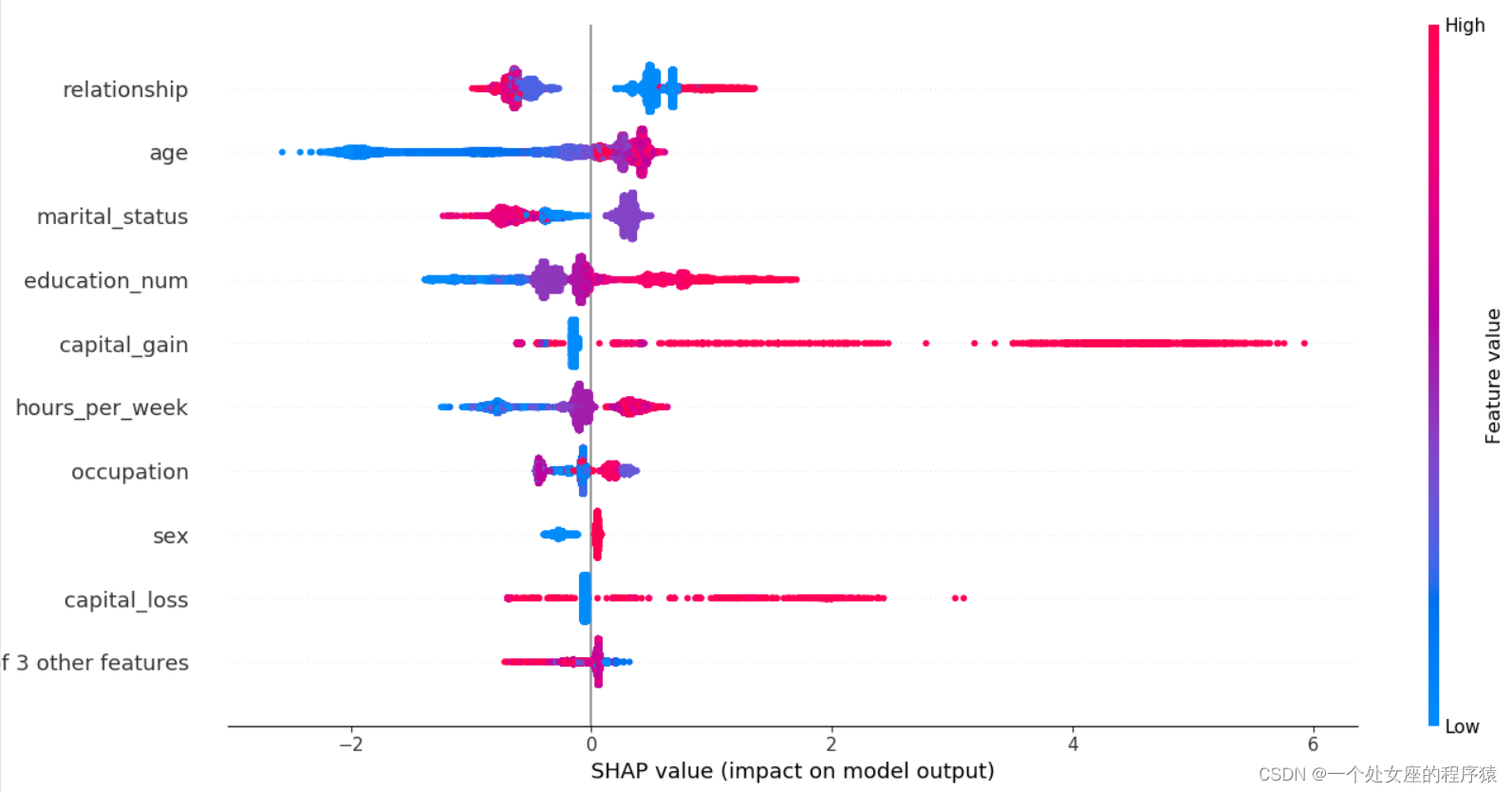
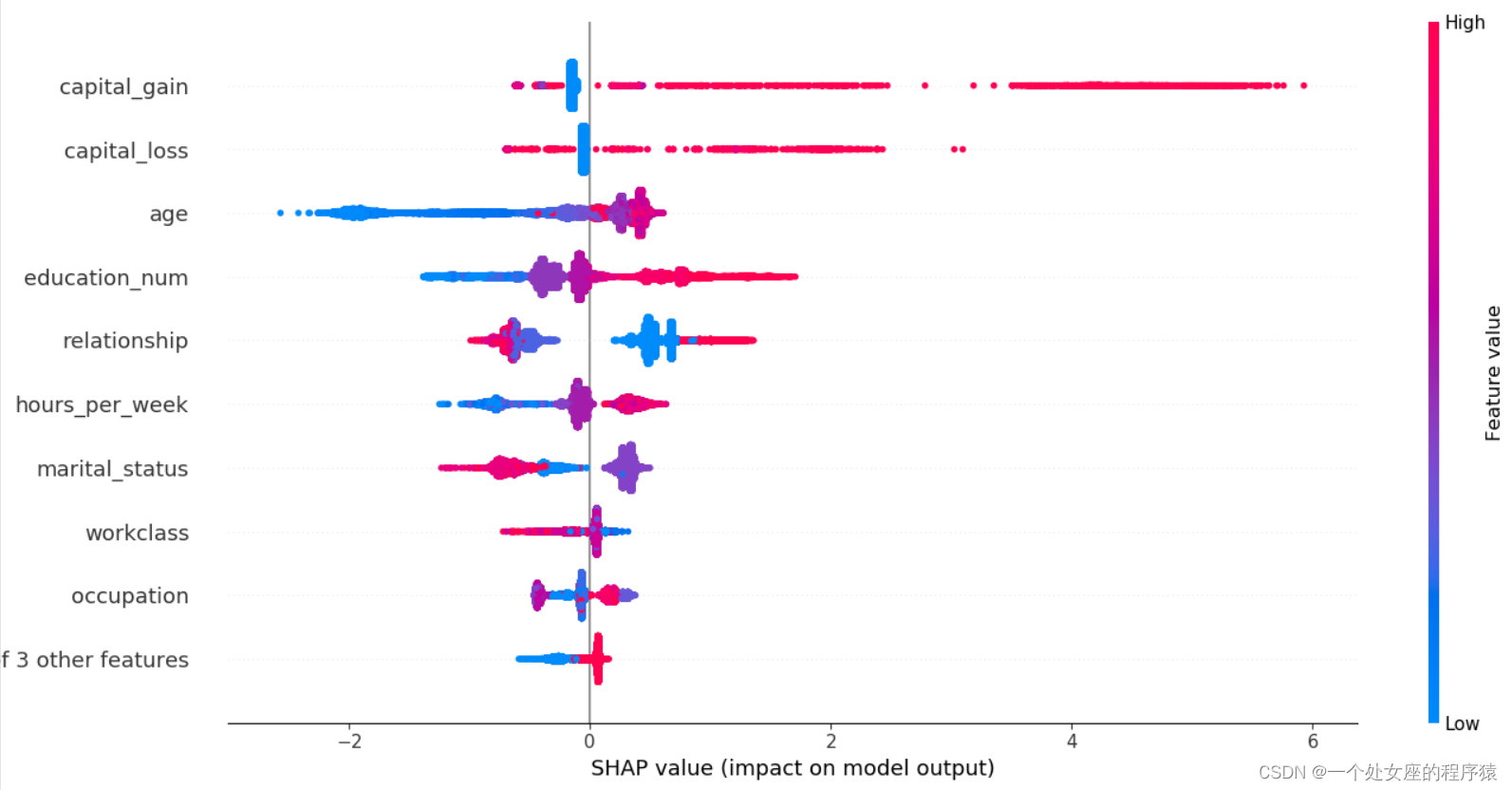
# (4)、 Global feature importance sorting scatter diagram visualization
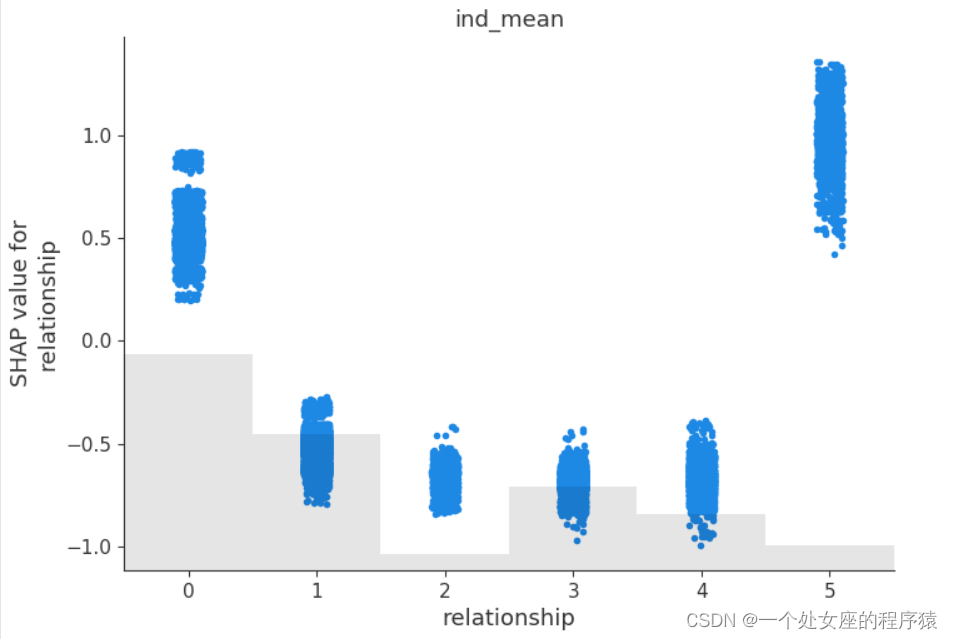
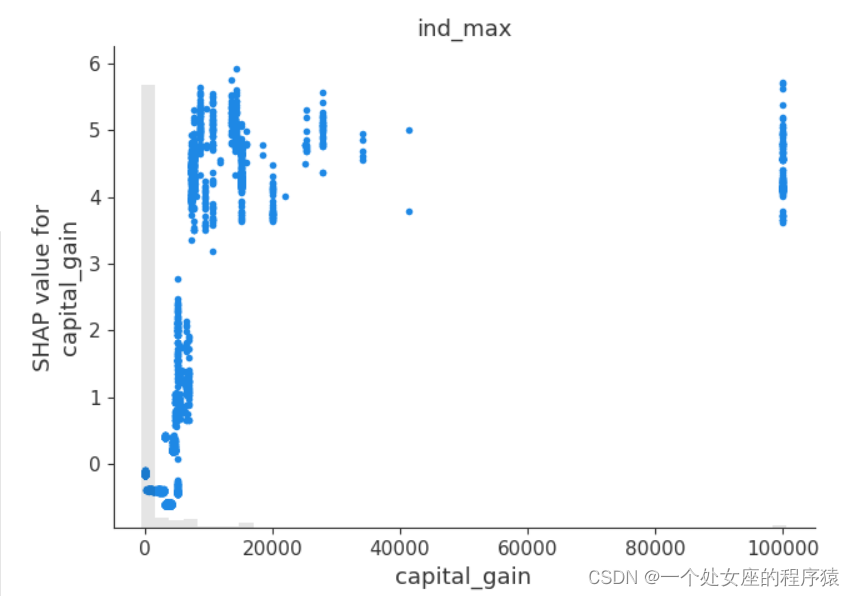
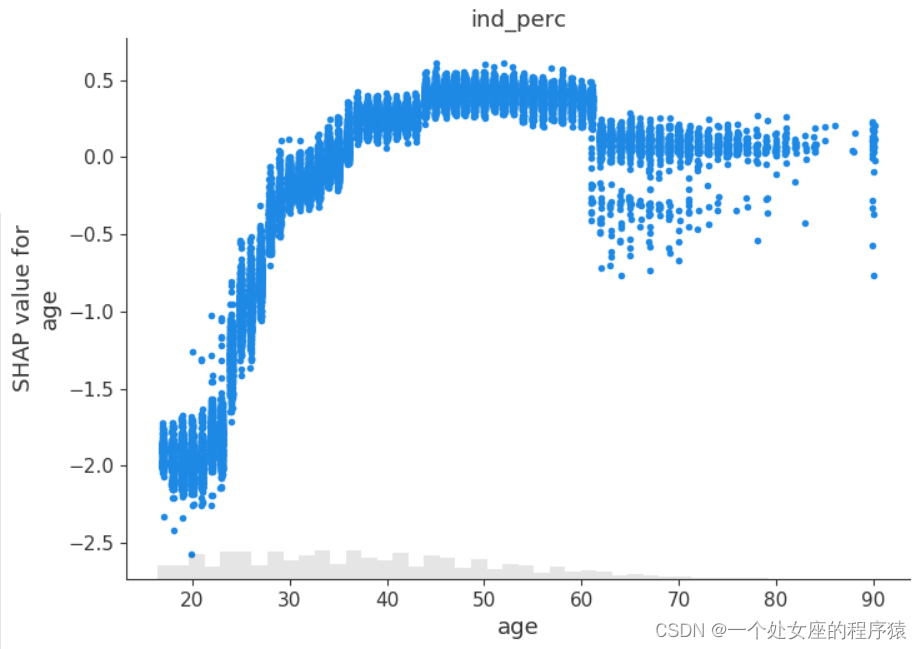
#4.2、 Visualization of local feature importance
# (1)、 Single sample full feature bar graph visualization
Pre test samples :0
.values =
array([ 0.31074238, -0.16607898, 0.5617416 , -0.58709425, -0.08897061,
-0.6133537 , 0.01539118, 0.04758333, -0.3988452 , -0.04660619,
-0.09465054, 0.00530914], dtype=float32)
.base_values =
-1.3270257
.data =
array([3.900e+01, 7.000e+00, 1.300e+01, 4.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00,
4.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 2.174e+03, 0.000e+00, 4.000e+01, 3.900e+01])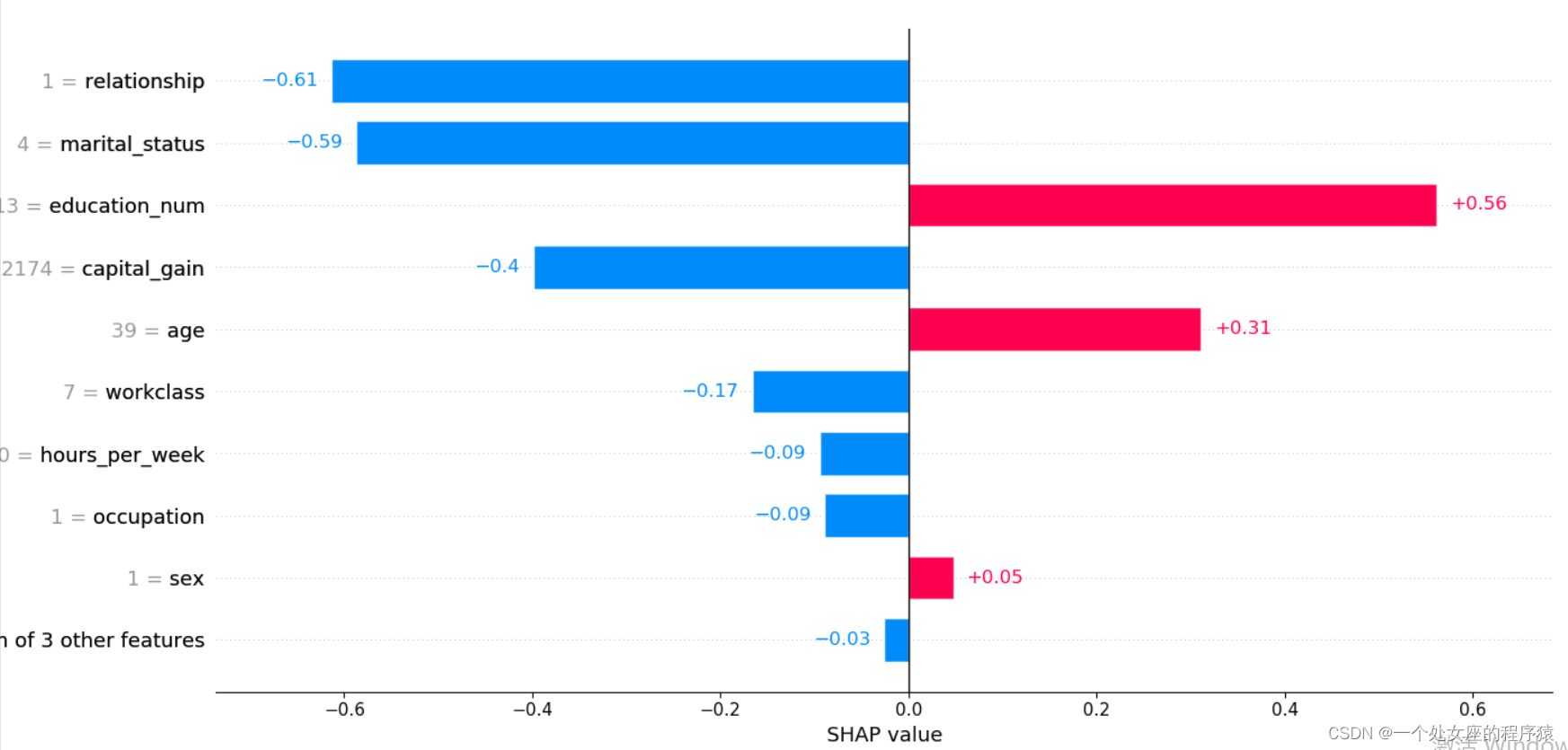
Pre test samples :1
.values =
array([ 0.34912622, -0.16633348, 0.65308005, 0.3069151 , 0.26878497,
0.5229906 , 0.01030679, 0.04531586, -0.15429462, -0.06718991,
-0.9804511 , 0.00515459], dtype=float32)
.base_values =
-1.3270257
.data =
array([50., 6., 13., 2., 4., 0., 4., 1., 0., 0., 13., 39.])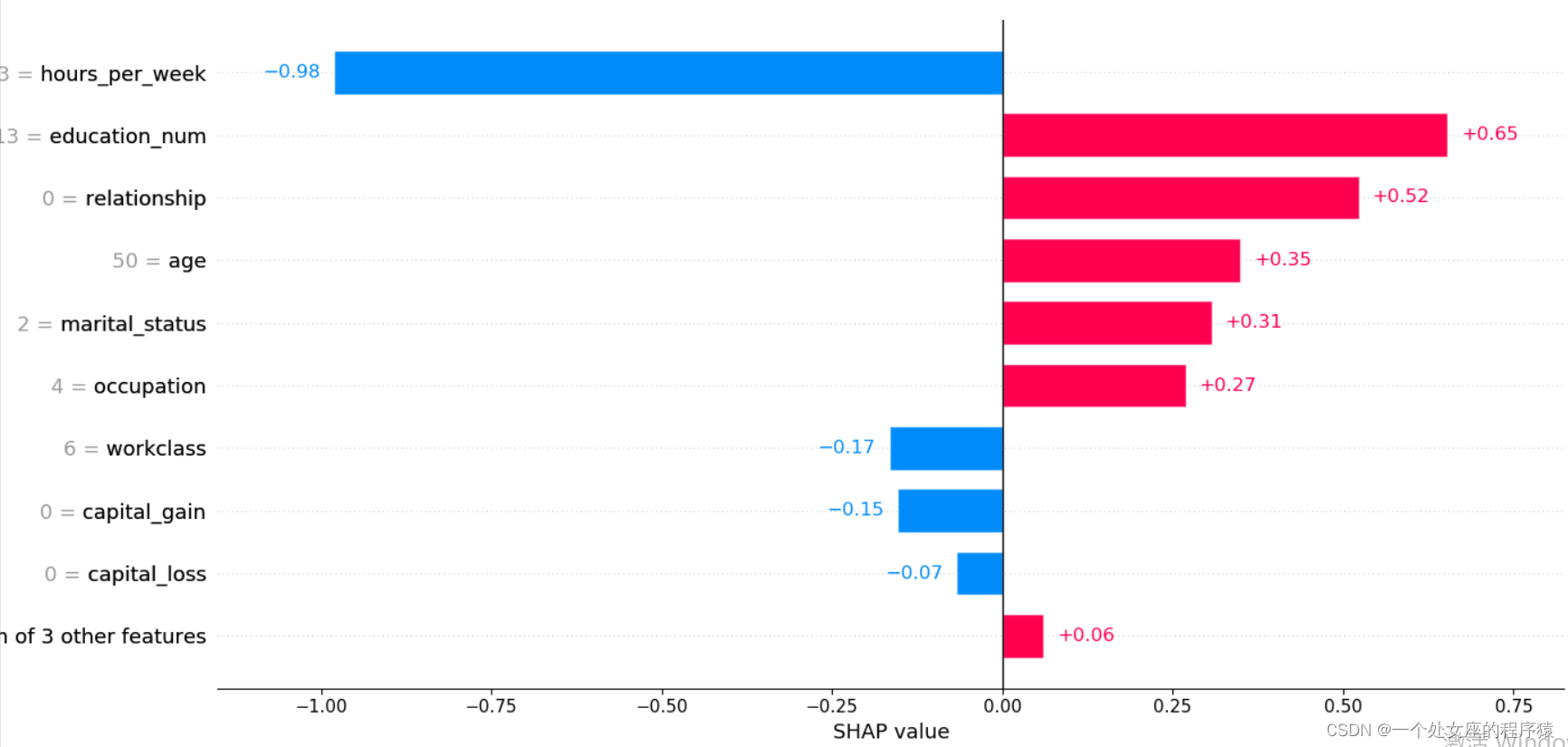
Pre test samples :10
.values =
array([ 0.27578622, 0.02686635, -0.0699547 , 0.2820353 , 0.3097189 ,
0.55229187, -0.03686382, 0.05135565, -0.1607191 , -0.06321771,
0.38190693, 0.02023092], dtype=float32)
.base_values =
-1.3270257
.data =
array([37., 4., 10., 2., 4., 0., 2., 1., 0., 0., 80., 39.])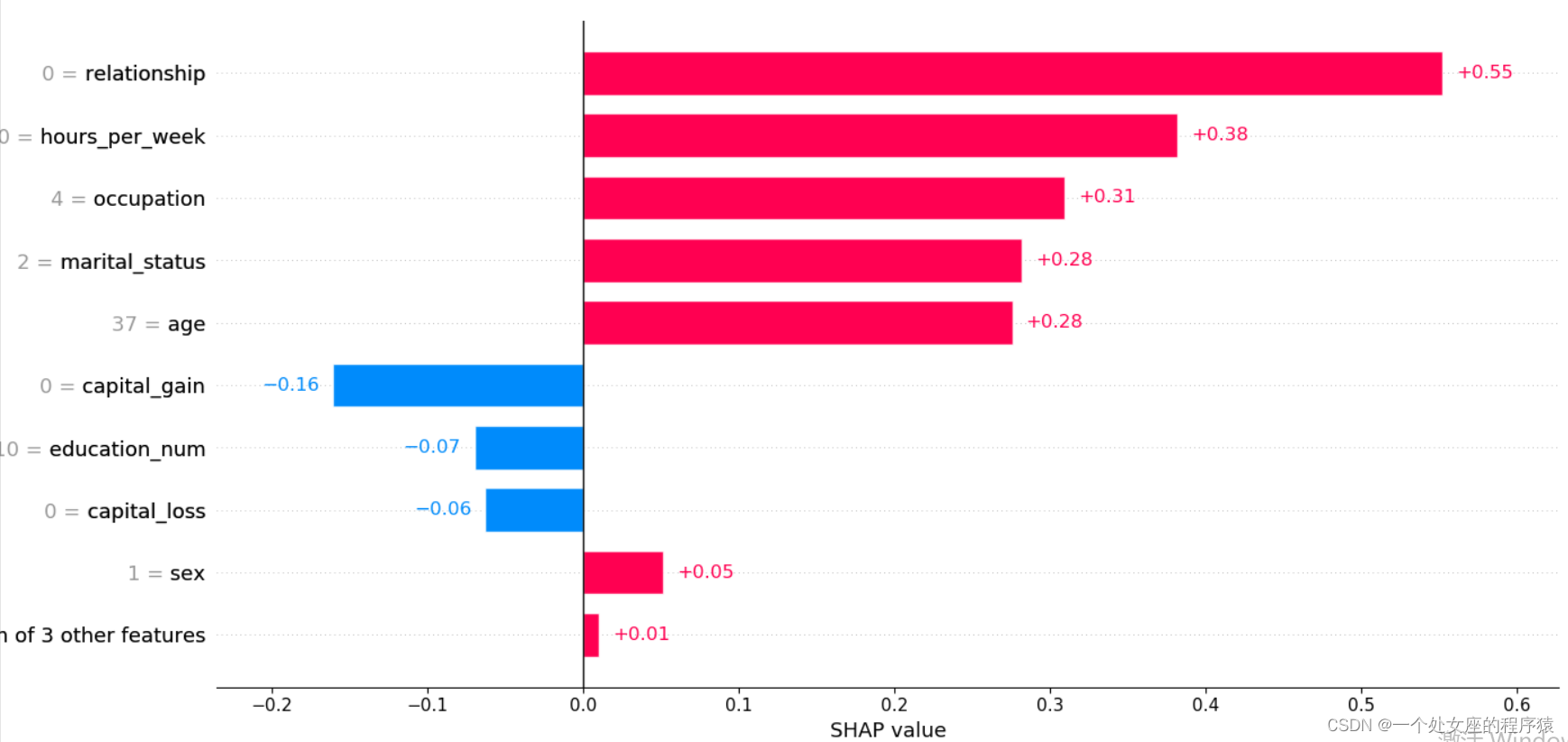
Pre test samples :20
.values =
array([ 0.31008577, 0.00316932, 1.3133987 , 0.16768128, 0.18239255,
0.6863757 , 0.00508371, 0.05159741, -0.15813455, -0.06736177,
0.31327826, 0.01936885], dtype=float32)
.base_values =
-1.3270257
.data =
array([40., 4., 16., 2., 10., 0., 4., 1., 0., 0., 60., 39.])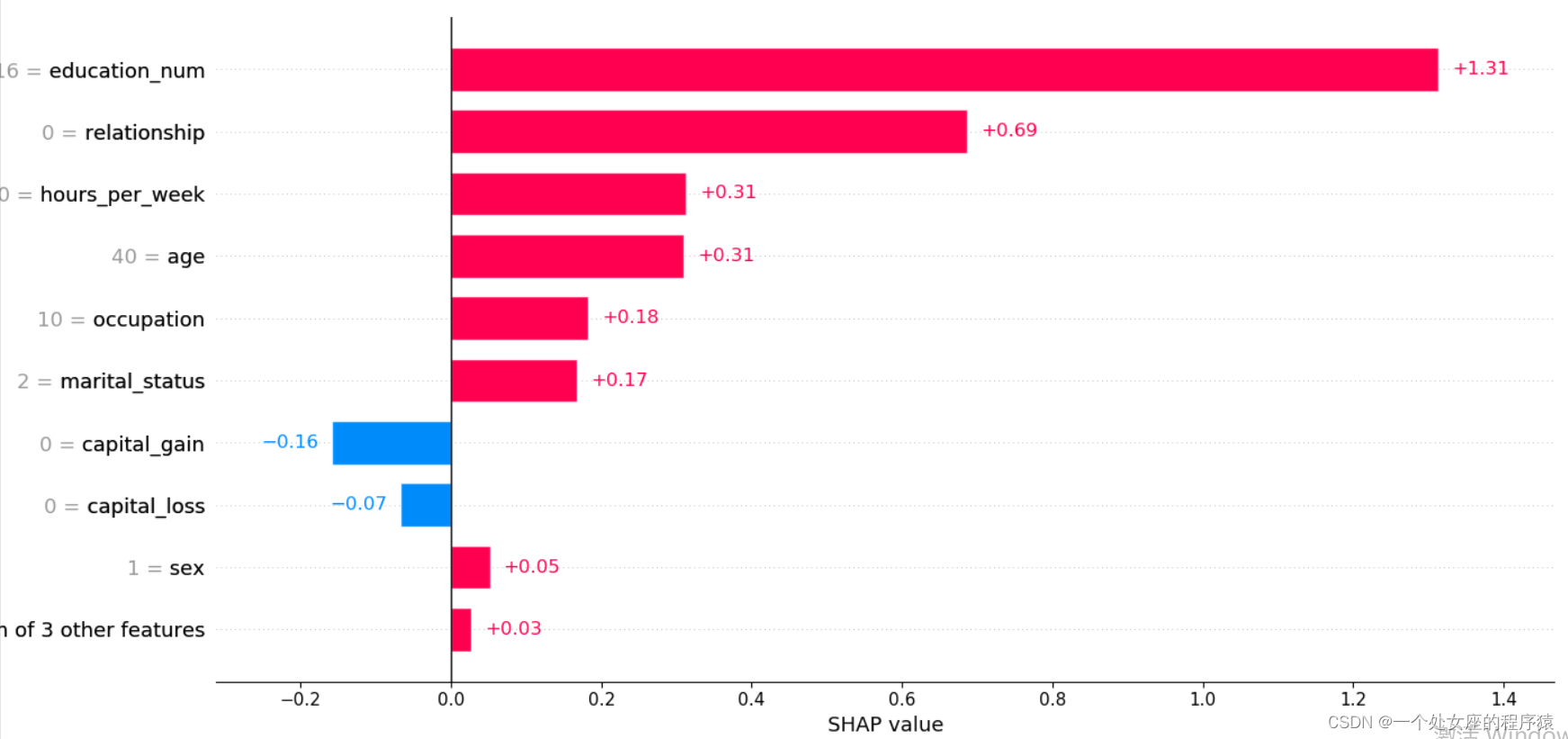
# (2)、 One turn two feature full sample local independent graph scatter diagram visualization
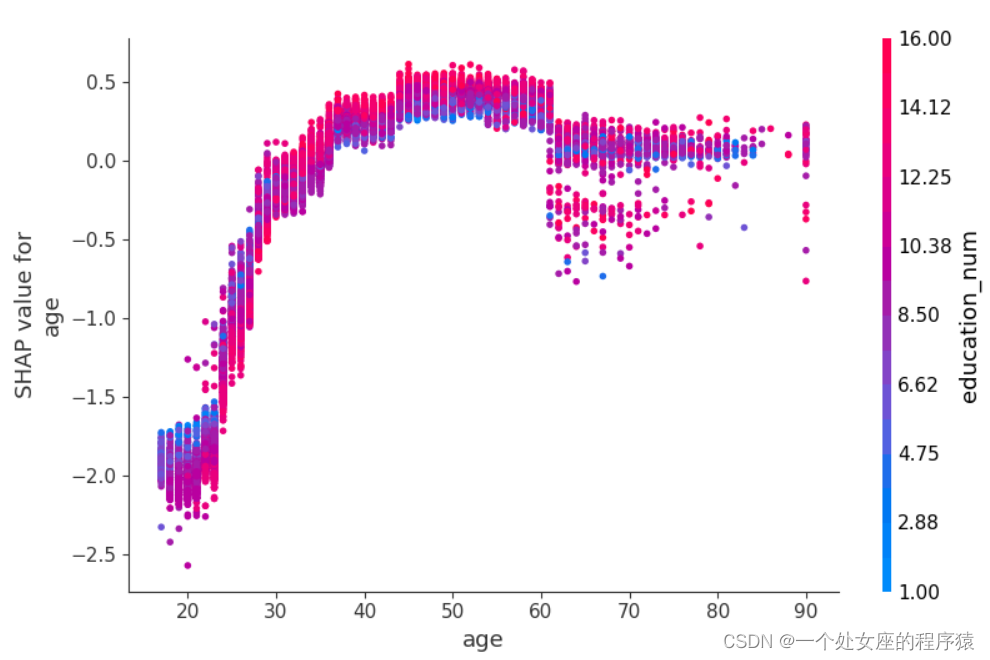
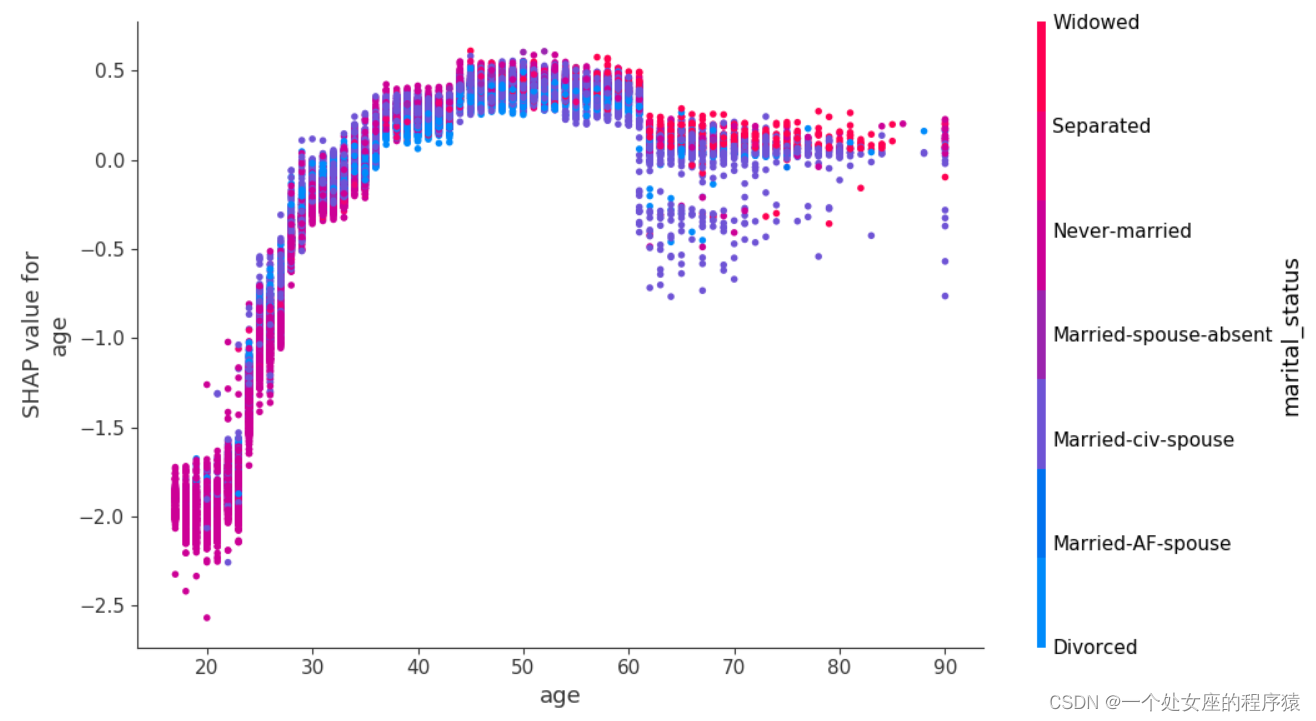
# (3)、 Visualization of double feature full sample scatter diagram
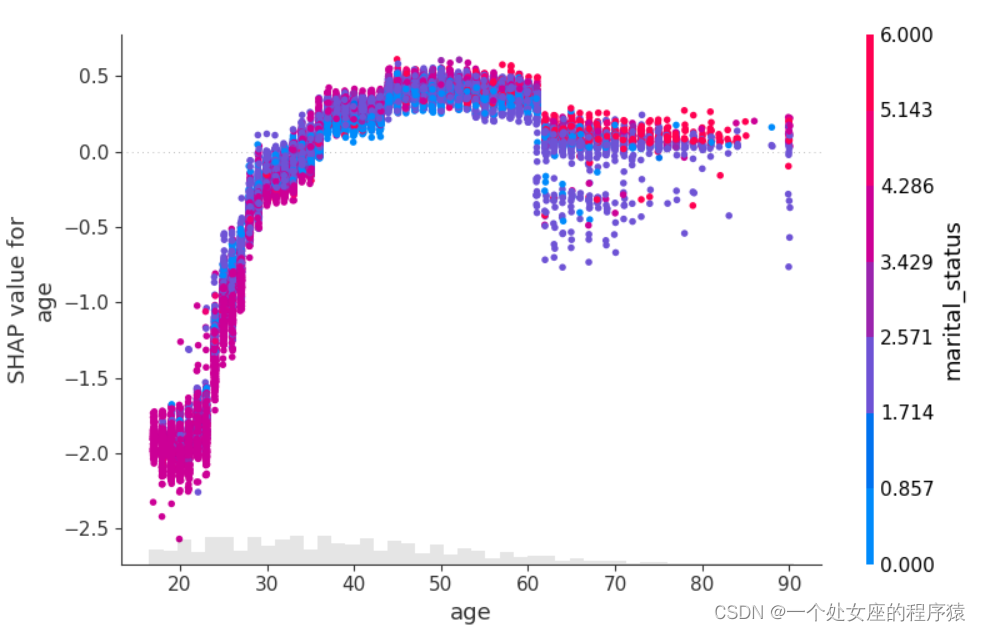
# 4.3、 Model feature screening
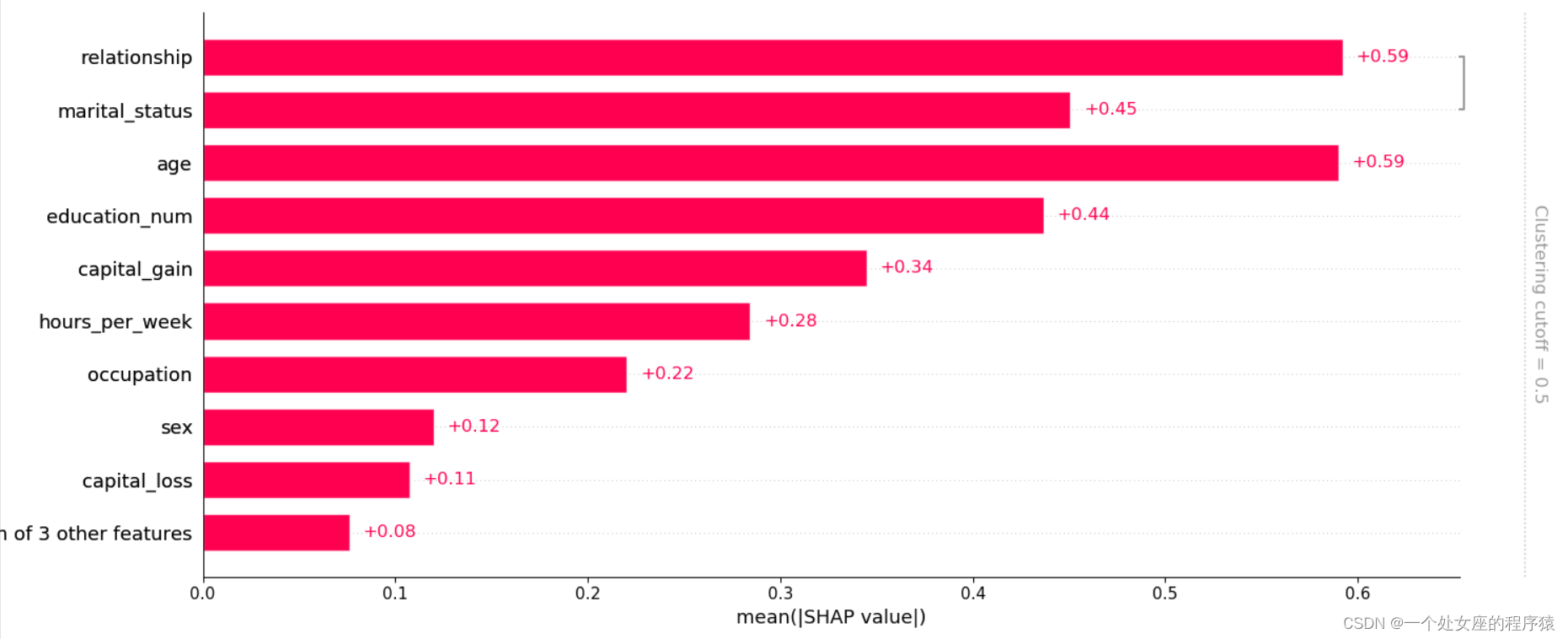
# (1)、 Clustering based shap Feature filtering visualization
5、 Interpretability of model prediction ( can The main Analyze misclassified samples )
Provides details of the forecast , Focus on explaining how individual forecasts are generated . It can help decision makers trust models , And explain how each feature affects the single decision of the model .
# 5.1、 Try to visualize analysis : Visualize the contribution of each feature in a single or multiple samples and Compare the predicted value of the model —— Explore misclassification samples
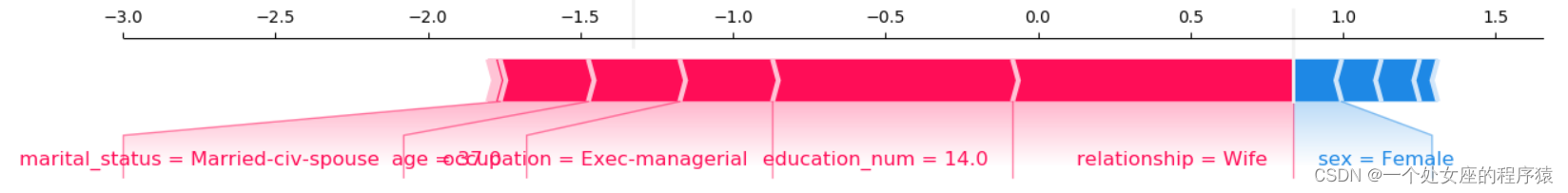
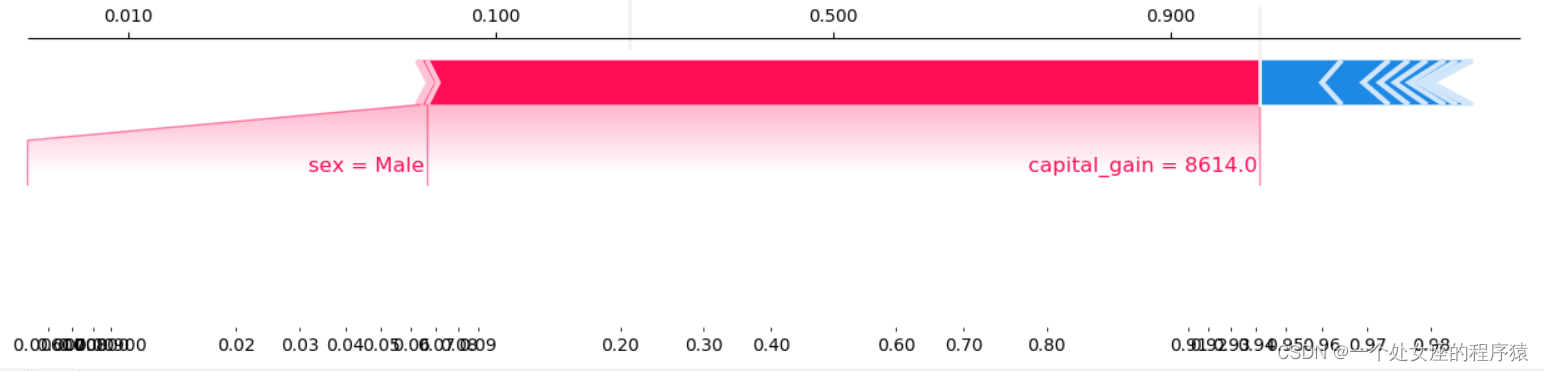
It provides the explicability of single model prediction , It can be used for error analysis , Find an explanation for the prediction of a particular instance . For example 0 Shown :
(1)、 Model output :5.89;
(2)、 Base value :base value namely explainer.expected_value, That is, the average value of model output and training data ;
(3)、 The number below the drawing arrow is the characteristic value of this instance . Such as Age=39;
(4)、 Red Indicates the Contribution is positive ( Will forecast Push up Characteristics of ), Blue Representing this feature The contribution is negative ( Will forecast PUSH low Characteristics of ). Length indicates influence ; The longer the arrow , The influence of features on output ( contribution ) The bigger it is . adopt x The scale value on the axis can see the reduction or increase of influence .
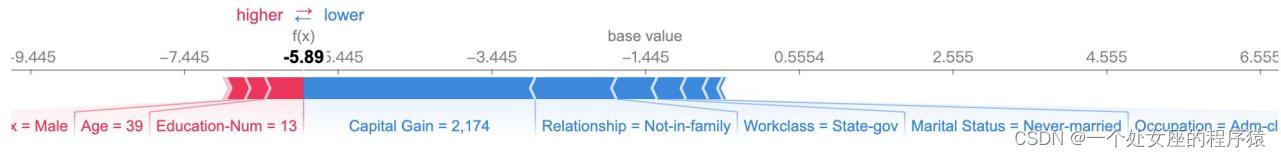
(1)、 A single sample Try to visualize — Compare predictions
Output the current test sample :0

mode_exp_value: -1.3270257
<IPython.core.display.HTML object>
Output the current test sample :0
age 29.0
workclass 4.0
education_num 9.0
marital_status 4.0
occupation 1.0
relationship 3.0
race 2.0
sex 0.0
capital_gain 0.0
capital_loss 0.0
hours_per_week 60.0
native_country 39.0
y_val_predi 0.0
y_val 0.0
Name: 11311, dtype: float64
Output the true of the current test sample label: 0
Output the prediction probability of the current test sample : 0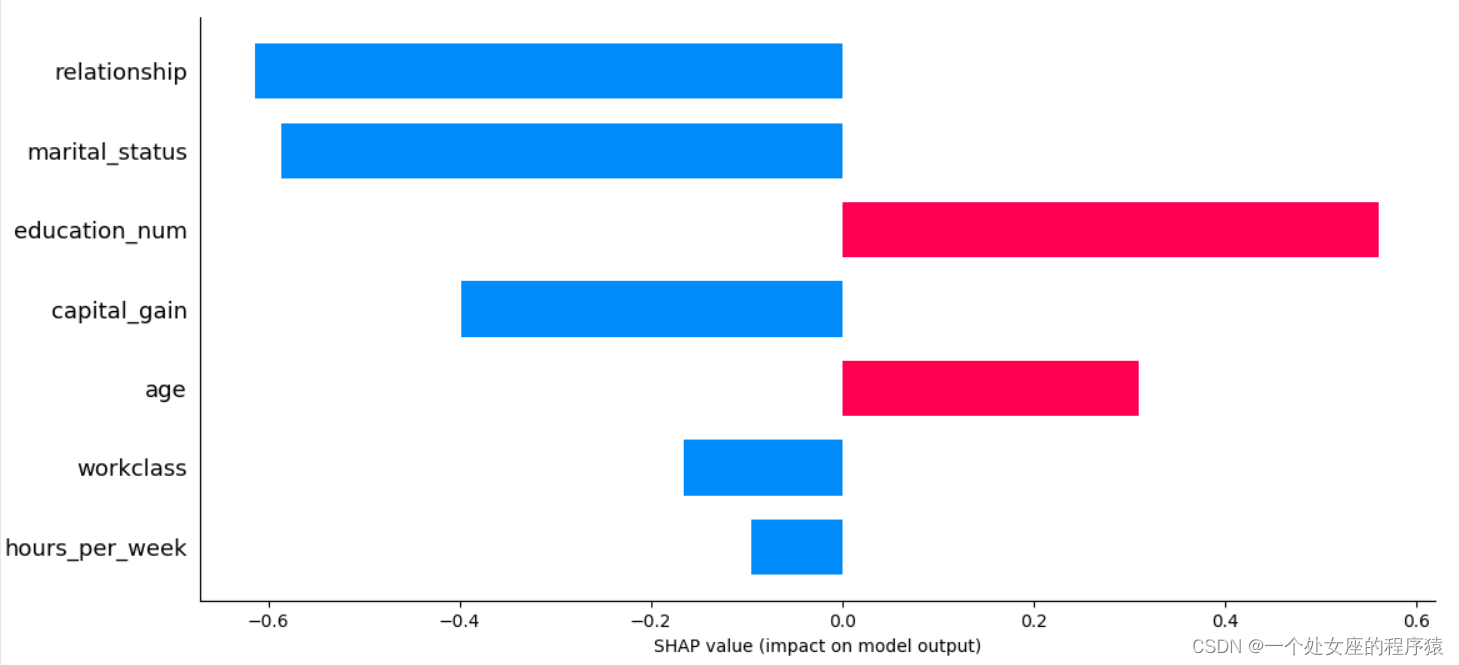
Output the current test sample :1

Output the current test sample :1
age 33.0
workclass 4.0
education_num 10.0
marital_status 4.0
occupation 3.0
relationship 1.0
race 2.0
sex 1.0
capital_gain 8614.0
capital_loss 0.0
hours_per_week 40.0
native_country 39.0
y_val_predi 1.0
y_val 1.0
Name: 12519, dtype: float64
Output the true of the current test sample label: 1
Output the prediction probability of the current test sample : 1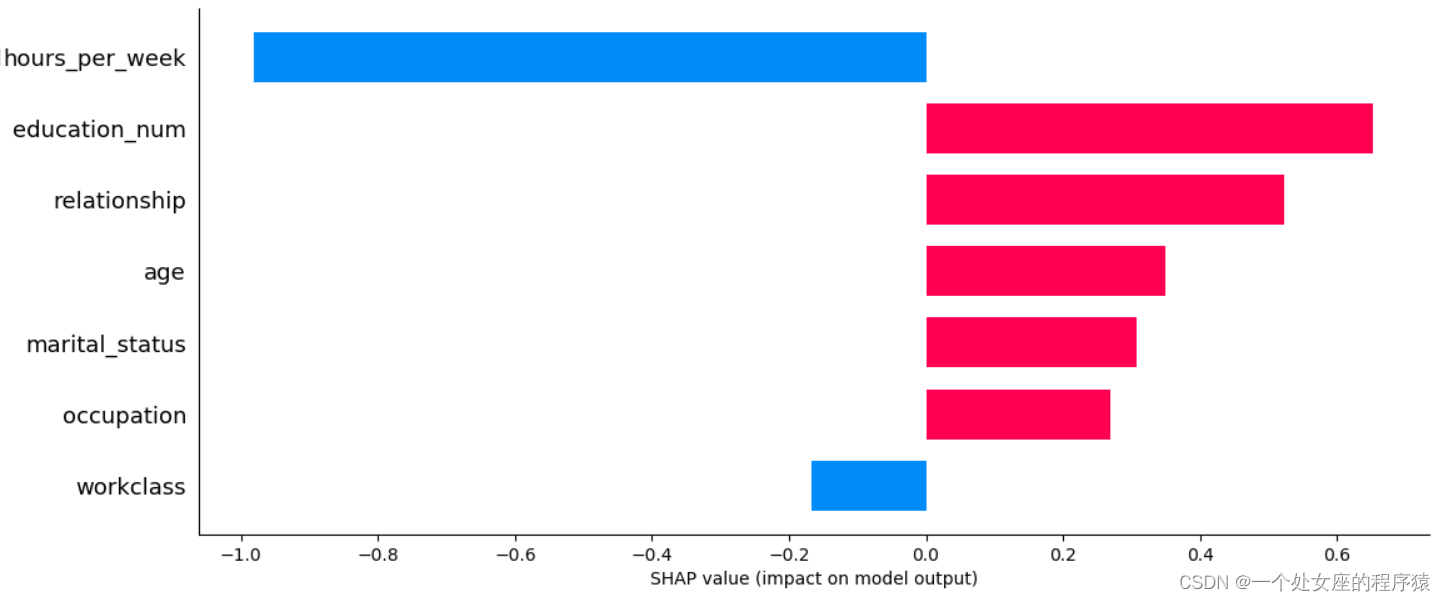
Output the current test sample :5
Output the current test sample :5
age 45.0
workclass 4.0
education_num 10.0
marital_status 2.0
occupation 4.0
relationship 0.0
race 4.0
sex 1.0
capital_gain 0.0
capital_loss 0.0
hours_per_week 40.0
native_country 39.0
y_val_predi 1.0
y_val 0.0
Name: 4319, dtype: float64
Output the true of the current test sample label: 0
Output the prediction probability of the current test sample : 1
Output the current test sample :7
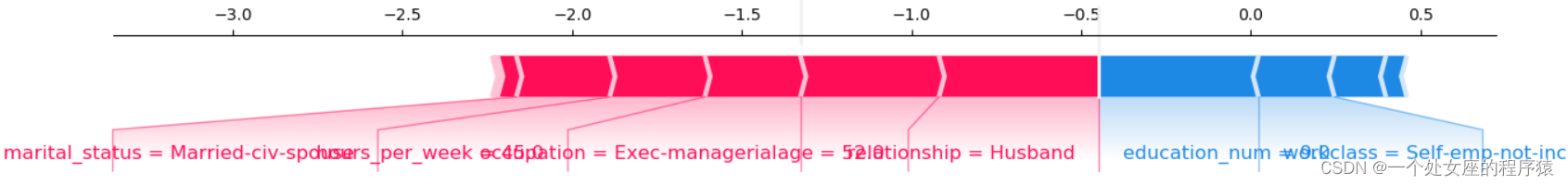
Output the current test sample :7
age 60.0
workclass 0.0
education_num 13.0
marital_status 2.0
occupation 0.0
relationship 0.0
race 4.0
sex 1.0
capital_gain 0.0
capital_loss 0.0
hours_per_week 8.0
native_country 39.0
y_val_predi 0.0
y_val 1.0
Name: 4721, dtype: float64
Output the true of the current test sample label: 1
Output the prediction probability of the current test sample : 0
(2)、 Multiple samples Try to visualize
# (2.1)、 Visualization of feature contribution , Use the dark red and dark blue map to visualize the front 5 A prediction explanation , have access to X Data sets .
# (2.2)、 Misclassification attempts to visualize , Definitely X_val Data sets , Because it involves model prediction .
If multiple samples are interpreted , Rotate the above form 90 Degrees and then placed horizontally side by side , Get the variant of the effort
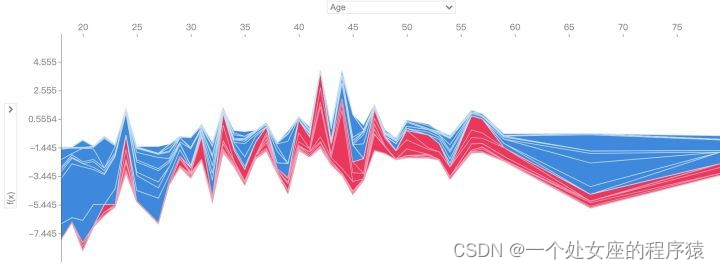
# 5.2、 Visual analysis of decision diagram : How models make decisions
# (1)、 Single sample decision Figure Visualization
# (2)、 Multiple sample decisions Figure Visualization
# (2.1)、 Visualization of some sample decision diagrams
# (2.2)、 Misclassification sample decision graph visualization
边栏推荐
- Attributeerror successfully resolved: can only use cat accessor with a ‘category‘ dtype
- Market segmentation of supermarket customers based on purchase behavior data (RFM model)
- 基於JEECG-BOOT的list頁面的地址欄參數傳遞
- Summary of leetcode's dynamic programming 4
- Py06 dictionary mapping dictionary nested key does not exist test key sorting
- MySQL high frequency interview 20 questions, necessary (important)
- 专业论文翻译,英文摘要如何写比较好
- [mqtt from getting started to improving series | 01] quickly build an mqtt test environment from 0 to 1
- Defense (greed), FBI tree (binary tree)
- CS passed (cdn+ certificate) PowerShell online detailed version
猜你喜欢

商标翻译有什么特点,如何翻译?

How to translate professional papers and write English abstracts better
![[ 英語 ] 語法重塑 之 動詞分類 —— 英語兔學習筆記(2)](/img/3c/c25e7cbef9be1860842e8981f72352.png)
[ 英語 ] 語法重塑 之 動詞分類 —— 英語兔學習筆記(2)
On the first day of clock in, click to open a surprise, and the switch statement is explained in detail

字幕翻译中翻英一分钟多少钱?

Is it difficult for girls to learn software testing? The threshold for entry is low, and learning is relatively simple

Changes in the number of words in English papers translated into Chinese

LeetCode 732. My schedule III
Phishing & filename inversion & Office remote template

The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
随机推荐
Apache DolphinScheduler源码分析(超详细)
Day 248/300 关于毕业生如何找工作的思考
Lesson 7 tensorflow realizes convolutional neural network
【软件测试进阶第1步】自动化测试基础知识
Monotonic stack
SAP SD发货流程中托盘的管理
[ 英语 ] 语法重塑 之 英语学习的核心框架 —— 英语兔学习笔记(1)
org. activiti. bpmn. exceptions. XMLException: cvc-complex-type. 2.4. a: Invalid content beginning with element 'outgoing' was found
(practice C language every day) reverse linked list II
MySQL is sorted alphabetically
ECS accessKey key disclosure and utilization
Difference between backtracking and recursion
女生学软件测试难不难 入门门槛低,学起来还是比较简单的
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
On the first day of clock in, click to open a surprise, and the switch statement is explained in detail
Leetcode daily question (1997. first day where you have been in all the rooms)
成功解决TypeError: data type ‘category‘ not understood
Advanced MySQL: Basics (1-4 Lectures)
Luogu p2089 roast chicken
Engineering organisms containing artificial metalloenzymes perform unnatural biosynthesis