当前位置:网站首页>Common fault analysis and Countermeasures of using MySQL in go language
Common fault analysis and Countermeasures of using MySQL in go language
2022-07-08 01:14:00 【Baidu geek said】
Reading guide : Many students are using it Go In the process of dealing with the database , I often encounter some exceptions and don't know why , This paper starts from SQL The principle of connection pool is analyzed , Some examples are simulated to interpret and analyze abnormal phenomena , And give some common countermeasures , I hope I can help you .
The full text 12795 word , Estimated reading time 32 minute
Many students met MySQL Slow query problems , It may appear as SQL The sentence is very simple , But the query takes a long time . It may be caused by such reasons .
1、 Resources are not released in time
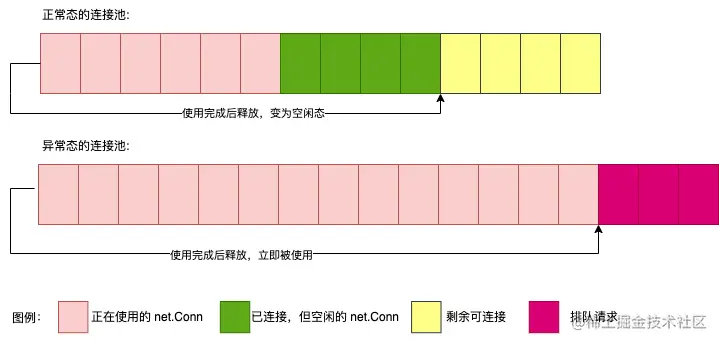
Go Of sql The package uses a long connection to make Client and SQL Server Interaction , for fear of SQL Server Too many links , Usually in Client The terminal limits the maximum number of connections .
Here is sql State diagram of the connection pool ( Set the maximum number of open connections ):
SQL Client and Server After interaction , Some results return a stream (Stream), Network connection at this time (Conn) Be being Stream Object continues to be used ,Client The results need to be read iteratively , The stream should be closed immediately after reading to reclaim resources ( Release conn).
For example, the longest DB.QueryContext The method is like this :
// QueryContext Query some results
// query:select * from test limit 10
func (db *DB) QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
type Rows struct{
Close( ) error
ColumnTypes( ) ( [ ]*ColumnType, error)
Columns( ) ( [ ]string, error)
Err( ) error
Next( ) bool
NextResultSet( ) bool
Scan(dest ...any) error
}
When there are still results ( namely Rows.Next()==true when ), It means that there are still results that have not been read , At this point, you must call Rows.Close() Method to close the stream to release the connection ( Make the current connection idle to Make this connection available to other logic ).
1.1 experiment 1- Do not call Rows.Close()
If you don't call Close What will happen ? Let's do an experiment to observe :
select * from user;
+----+-------+---------------------+----------+--------+
| id | email | register_time | password | status |
+----+-------+---------------------+----------+--------+
| 2 | dw | 2011-11-11 11:01:00 | d | 0 |
+----+-------+---------------------+----------+--------+
1 row in set (0.03 sec)
package main
import (
"context"
"database/sql"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"sync"
"time"
_ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql"
)
func main() {
db, err := sql.Open("mysql", "root:@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/test")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
db.SetMaxOpenConns(1)
// Start a separate collaboration , For output DB Status information
go func() {
tk := time.NewTicker(3 * time.Second)
defer tk.Stop()
for range tk.C {
bf, _ := json.Marshal(db.Stats())
fmt.Println("db.Stats=", string(bf))
}
}()
// start-up 10 Collaborators cheng , Query data at the same time
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go func(id int) {
defer wg.Done()
queryOne(id, db)
}(i)
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println("finish")
}
func queryOne(id int, db *sql.DB) {
start := time.Now()
rows, err := db.QueryContext(context.Background(), "select * from user limit 1")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// defer rows.Close()
// Not from Rows Read the results in , No call rows.Close
fmt.Println("id=", id, "hasNext=", rows.Next(), "cost=", time.Since(start))
}
After execution, the following contents will be entered :
id= 0 hasNext= true cost= 9.607371ms
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
Read the status data :
{
"MaxOpenConnections": 1, // Maximum number of open connections , Consistent with the code settings , yes 1
"OpenConnections": 1, // Number of open connections
"InUse": 1, // Number of connections in use
"Idle": 0, // Number of idle connections
"WaitCount": 9, // Number of waiting connections
"WaitDuration": 0, // The total waiting time ( Count while waiting for exit )
"MaxIdleClosed": 0, // Exceed the maximum idle Count the total number of closed connections
"MaxIdleTimeClosed": 0, // Overtake and catch up idle Total number of connections closed at time
"MaxLifetimeClosed": 0 // The total number of connections closed over the maximum lifetime
}
As can be seen from the above output , All in all 10 Collaborators cheng , There is only one co process queryOne Method successfully executed , other 9 All processes are in a waiting state .
1.2 experiment 2- call Rows.Close()
If the queryOne Methodical ,“// defer rows.Close()” Remove comments from , That is to say :
func queryOne(id int, db *sql.DB) {
start := time.Now()
rows, err := db.QueryContext(context.
Background(), "select * from user limit 1")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer rows.Close() // Opened the comment here ,Close Methods release resources
fmt.Println("id=", id, "hasNext=", rows.Next(), "cost=", time.Since(start))
}
After execution , Will output the following :
# go run main.go
id= 9 hasNext= true cost= 4.082448ms
id= 3 hasNext= true cost= 5.670052ms
id= 8 hasNext= true cost= 5.745443ms
id= 5 hasNext= true cost= 6.238615ms
id= 6 hasNext= true cost= 6.520818ms
id= 7 hasNext= true cost= 6.697782ms
id= 4 hasNext= true cost= 6.953454ms
id= 1 hasNext= true cost= 7.1079ms
id= 0 hasNext= true cost= 7.3036ms
id= 2 hasNext= true cost= 7.464726ms
finish
The above output results indicate all 10 All the processes have been successfully executed .
1.3 experiment 3- Use the... With timeout Context
Add , Above call QueryContext Method time , It uses context.Background(), So it's the effect of consistent blocking . Actually in use , Incoming context It usually has timeout or supports cancellation , Like this :
func queryOne(id int, db *sql.DB) {
start := time.Now()
ctx,cancel:=context.WithTimeout(context.Background(),time.Second) // The key
defer cancel() // The key . If you replace this line with _=cancel, Another result
rows, err := db.QueryContext(ctx , "select * fro m user limit 1")
if err != nil {
// panic (err)
fmt.Println("BeginTx failed:",err)
return
}
// defer rows.Close () // Opened the note here Interpretation of the ,Close Methods release resources
fmt.Println("id=" , id, "hasNext=", rows.Next(), "cost=", time.Since (start))
}
After operation, it can be observed that , be-all 10 All the cooperation projects have been successfully implemented :
id= 9 hasNext= true cost= 1.483715ms
id= 3 hasNext= true cost= 175.675µs
id= 6 hasNext= true cost= 1.277596ms
id= 1 hasNext= true cost= 174.307µs
id= 7 hasNext= true cost= 108.061µs
id= 4 hasNext= true cost= 115.072µs
id= 2 hasNext= true cost= 104.046µs
id= 0 hasNext= true cost= 96.833µs
id= 8 hasNext= true cost= 123.758µs
id= 5 hasNext= true cost= 92.791µs
finish
because context It is with timeout , And when the execution is completed, it will call defer cancel() take ctx Cancel , So even if not used rows.Close Release resources ,ctx In being cancel Resources will also be released immediately after .
If will defer cancel() Replace with _=cancel , Another result 了 , What we're going to see is :
d= 9 hasNext= true cost= 2.581813ms
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
BeginTx failed: context deadline exceeded
1.4 Solution
Summary :
We should use QueryContext This class supports incoming context Function of , And pass in the... With timeout control context, And after the logic execution is completed , You should use defer Methods will context Cancel .
For results that return a stream type , After use, you must call Close Method to free resources .
all *sql.DB、*sql.Tx、*sql.Stmt Return *Conn、*Stmt、*Rows These types all need Close:
type DB/Tx/Stmt struct{
Conn(ctx context.Context) (*Conn, error)
Prepare(query string) (*Stmt, error)
PrepareContext(ctx context.Context, query string) (*Stmt, error)
Query(query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
}
To avoid this problem , Generally, you only need to follow the example above , add defer rows.Close() that will do .
If used GDP frame , Read Rows result , have access to mysql.ReadRowsClose Method , After reading , It's automatic Close. such as :
type user struct {
ID int64 `ddb:"id"`
Status uint8 `ddb:"status"`
}
func readUsers(ctx context.Context)([]*user,error)
rows, err := cli.QueryContext(ctx, "select * from user where status=1 limit 5")
if err != nil {
return nil,err
}
var userList []*user
err=mysql.ReadRowsClose(rows, &userList)
return userList,err
}
Or is it QueryWithBuilderScan:
b := &SimpleBuilder{
SQL: "SELECT id,name from user where id=1",
}
type user struct{
Name string `ddb:"name"`
ID int `ddb:"id"`
}
var us []*user
err = mysql.QueryWithBuilderScan(ctx, client, b, &us)
2、 The transaction is incomplete
Open a transaction (Tx) after , Must submit (Commit) Or rollback (Rollback), Otherwise, the transaction will be incomplete , It can also lead to Client End resources ( Connect ) Don't release .
func (db *DB) BeginTx(ctx context.Context, opts *TxOptions) (*Tx, error)
type Tx
func (tx *Tx) Commit() error // Commit transaction
func (tx *Tx) Rollback ( ) error // Roll back the transaction
func (tx *Tx) Exec(query string, args ...any) (Result, error)
func (tx *Tx) ExecContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (Result, error)
func (tx *Tx) Prepare(query string) (*Stmt, error)
func (tx *Tx) PrepareContext(ctx context.Context, query string) (*Stmt, error)
func (tx *Tx) Query(query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
func (tx *Tx) QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)
func (tx *Tx) QueryRow(query string, args ...any) *Row
func (tx *Tx) QueryRowContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) *Row
func (tx *Tx) Stmt(stmt *Stmt) *Stmt
func (tx *Tx) StmtContext(ctx context.Context, stmt *Stmt) *Stmt
2.1 and PHP The difference between
Another thing to note , Use Go Standard library DB.BeginTx Method to start a transaction , You will get a transaction object Tx, Let a batch of SQL Executing in a transaction requires that these SQL Here it is Tx Object . This and PHP It's not the same , For example PHP This is how transactions are used in :
<?php
/* Start a transaction , Turn off auto submit */
$dbh->beginTransaction();
/* Insert multiple rows of records based on all or nothing ( Or insert them all , Or not to insert them all ) */
$sql = 'INSERT INTO fruit(name, colour, calories) VALUES (?, ?, ?)';
$sth = $dbh->prepare($sql);
foreach ($fruits as $fruit) {
$sth->execute(array(
$fruit->name,
$fruit->colour,
$fruit->calories,
));
}
/* Submit changes */
$dbh->commit();
// This code comes from https://www.php.net/manual/zh/pdo.commit.php
While using Go Our business is like this :
import (
"context"
"database/sql"
"log"
)
var (
ctx context.Context
db *sql.DB
)
func main() {
tx, err := db.BeginTx(ctx, &sql.TxOptions{Isolation: sql.LevelSerializable})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
id := 37
// Use Tx perform Update sentence , Instead of continuing to use db.Exec
_, execErr := tx.Exec(`UPDATE users SET status = ? WHERE id = ?`, "paid", id)
if execErr != nil {
_ = tx.Rollback()
log.Fatal(execErr)
}
if err := tx.Commit(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
// This code comes from :https://pkg.go.dev/database/[email protected]#example-DB.BeginTx
2.2 experiment
Let's continue to experiment with the impact of incomplete transactions , The main part is the same as above ,queryOne The method becomes as follows :
func queryOne(id int, db *sql.DB) {
tx,err:=db.BeginTx(context.Background(),nil)
if err!=nil{
panic(err)
}
// defer tx.Rollback()
start := time.Now()
rows, err := tx.QueryContext(context.Background(), "select * from user limit 1")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer rows.Close()
// The transaction did not roll back 、 Submit
fmt.Println("id=", id, "hasNext=", rows.Next(), "cost=", time.Since(start))
}
After execution, the input and the above have no rows.Close similar :
id= 9 hasNext= true cost= 11.670369ms
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
db.Stats= {"MaxOpenConnections":1,"OpenConnections":1,"InUse":1,"Idle":0,"WaitCount":9,"WaitDuration":0,"MaxIdleClosed":0,"MaxIdleTimeClosed":0,"MaxLifetimeClosed":0}
Again , All in all 10 Collaborators cheng , There is only one co process queryOne Method successfully executed , other 9 All processes are in a waiting state .
If the above queryOne Methods // defer tx.Rollback() The comment opens , Then all 10 Each collaboration can be successfully executed .
2.3 Solution
Avoid incomplete transactions , Make sure that the transaction is either Commit, Or be Rollback.
If used GDP frame , have access to mysql.BeginTx Method to use transactions . This scheme can use transactions more safely , Will automatically be based on Function returns a value to determine whether it is Commit still Rollback, If business function appears panic It will also be automatic Rollback.
// Definition of business logic function , In this function, you can add, delete, change and query in the transaction
// return error==nil be tx.Commit(), otherwise tx.Rollback()
type doFunc func(ctx context.Context, qe QueryExecuto r) error
func BeginTx(ctx context.Context, cli CanBeginTx, opts *sql.TxOptions, do doFunc) error
var cli mysql.Client
updateUserNameByID := func(ctx context.Context, id uint64, name string) error {
// Use BeginTx Method , Can handle affairs more easily
err := mysql.BeginTx(ctx, cli, nil, func(ctx context.Context, qe mysq.QueryExecutor) error {
// Other database update logic is omitted
b1 := &mysql.SimpleBuilder{}
b1.Append("select name from user where uid=?", id)
var oldName string
if err := mysql.QueryRowWithBuilderScan(ctx, qe, b1, &oldName); err != nil {
return err
}
if oldName == " Zhugeliang " || oldName == name {
// return err,mysql.BeginTx Method will rollback the transaction
return fmt.Errorf(" No need to update , Overall transaction rollback ")
}
b2 := &mysql.SimpleBuilder{}
b2.Append("update user set name=? where id=?", name, id)
_, err := mysql.ExecWithBuilder(ctx, qe, b2)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// return nil,mysql.BeginTx Method will commit the transaction
return nil
})
return err
}
3、 Other reasons
3.1 Preprocessing is not supported
By default, preprocessing is usually used to promote SQL The security of , Avoid producing SQL Injection problem .
If the cluster version is used in the factory MySQL:DDBS(DRDS), the prepare The support is not good , The performance will be especially poor after use . May behave as , Queries that should have returned in milliseconds , It actually takes hundreds of milliseconds or even seconds to return . In this case, you need to add a configuration item to the parameter interpolateParams=true , close prepare Function .
Name = "demo"
# Other configuration items are omitted
[MySQL]
Username = "example"
# Other parameters are omitted
DSNParams ="charset=utf8&timeout=90s&collation=utf8mb4_unicode_ci&parseTime=true&interpolateParams=true"
4、 How to check
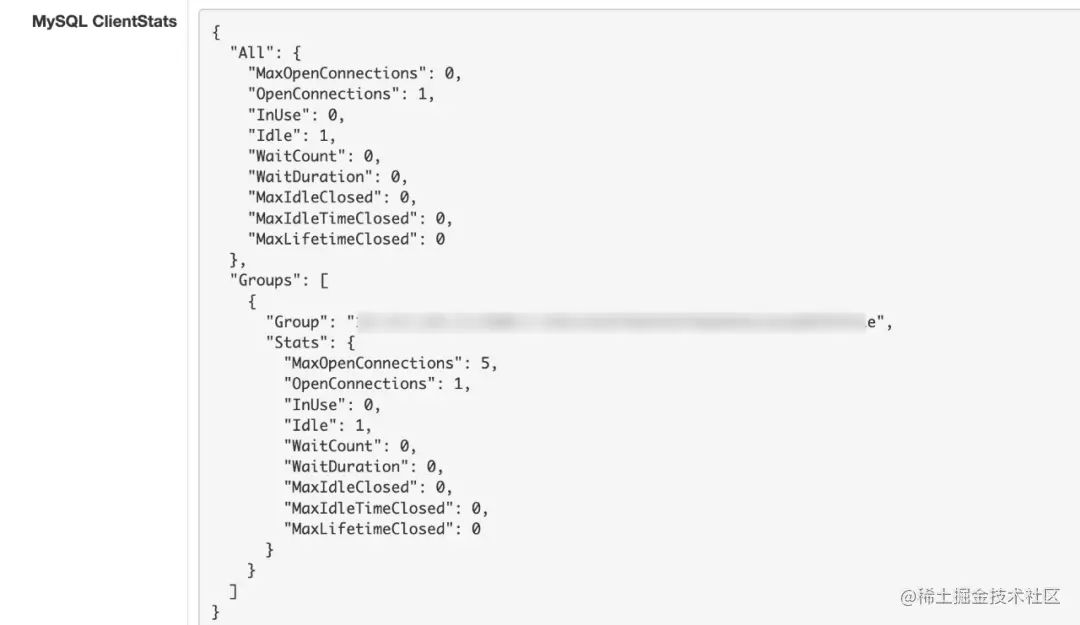
We can use DB Of Stats() Interface to analyze whether the above problems exist . In the above chapters , We just print this data to observe Client Status information .
{
"MaxOpenConnections" : 1 , // Maximum number of open connections , Consistent with the code settings , yes 1
"OpenConnections" : 1 , // Number of open connections
"InUse" : 1 , // Number of connections in use
"Idle" : 0 , // Number of idle connections
"WaitCount" : 9 , // Number of waiting connections
"WaitDuration" : 0 , // The total waiting time ( Count while waiting for exit )
"MaxIdleClosed" : 0 , // Exceed the maximum idle Count the total number of closed connections
"MaxIdleTimeClosed" : 0 , // Overtake and catch up idle Total number of connections closed at time
"MaxLifetimeClosed" : 0 // The total number of connections closed over the maximum lifetime
}
If you use GDP frame , We can observe this data through the following methods .
4.1 Integrate GDP Application panel
In Baidu factory ,GDP frame ( Inside Baidu Go Develop Platform, Easy to use 、 Easy to expand 、 Easy to observe 、 Stable and reliable characteristics , Used by thousands of modules ) There's a name "GDP Application panel " Functional module of , This module provides visual UI So that we can easily view 、 Observe various status information of the application . For example, you can view system information 、 File system information 、 Network status information 、 Compile information 、go runtime Information 、 Status information of various components in the framework ( Such as the operation status found by the service 、MySQL、Redis etc. Various Client Connection pool information, etc ).
Integrating this functionality is very simple , Just add 2 Line configurable code .
After integration , Can pass http://ip:port/debug/panel/?tab=servicer To access this panel , Find the corresponding servicer after ( The address of the page is /debug/panel/?tab=servicer&key={servicer_name} ), On the page “MySQL ClientStats” The paragraph is the current MySQL Client Of Stats Information . such as :
4.2 Integrated monitoring
GDP The framework's standardized indicator monitoring capability has been applied to all MySQL Client Of Stats Information is collected and output . We can use prometheus perhaps bvar Format output .
After integration , visit http://ip:port/metrics/service You can view the corresponding indicator items , It looks something like this :
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="ConnType"} 1
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="IPTotal"} 1
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="InUseAvg"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="InUseMax"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="InUseTotal"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="NumOpenAvg"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="NumOpenCfg"} 100
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="NumOpenMax"} 0
client_connpool{servicer="demo_mysql",stats="NumOpenTotal"} 0
You can add alarms to the above indicators , To help us find and locate problems faster .
4.3 Output to log
If the above 2 Kind of plan , You can also start an asynchronous coroutine , On a regular basis Stats Information output to the log , So that we can analyze the positioning problem .
————————END————————
Recommended reading :
Analysis on the wallet system architecture of Baidu trading platform
Wide table based data modeling application
Design and exploration of Baidu comment center
Data visualization platform based on template configuration
How to correctly evaluate the video quality
Small program startup performance optimization practice
How do we get through low code “⽆⼈ District ” Of :amis The key design of love speed
Mobile heterogeneous computing technology -GPU OpenCL Programming ( The basic chapter )
边栏推荐
- Smart grid overview
- Su embedded training - Day5
- 9. Introduction to convolutional neural network
- Multi purpose signal modulation generation system based on environmental optical signal detection and user-defined signal rules
- Leetcode notes No.21
- EDP to LVDS conversion design circuit | EDP to LVDS adapter board circuit | capstone/cs5211 chip circuit schematic reference
- swift获取url参数
- 2. Nonlinear regression
- Markdown learning (entry level)
- Analysis of 8 classic C language pointer written test questions
猜你喜欢
14.绘制网络模型结构
133. 克隆图
Capstone/cs5210 chip | cs5210 design scheme | cs5210 design data

13.模型的保存和载入
9. Introduction to convolutional neural network
Semantic segmentation model base segmentation_ models_ Detailed introduction to pytorch
NVIDIA Jetson test installation yolox process record
Complete model verification (test, demo) routine
Redis, do you understand the list
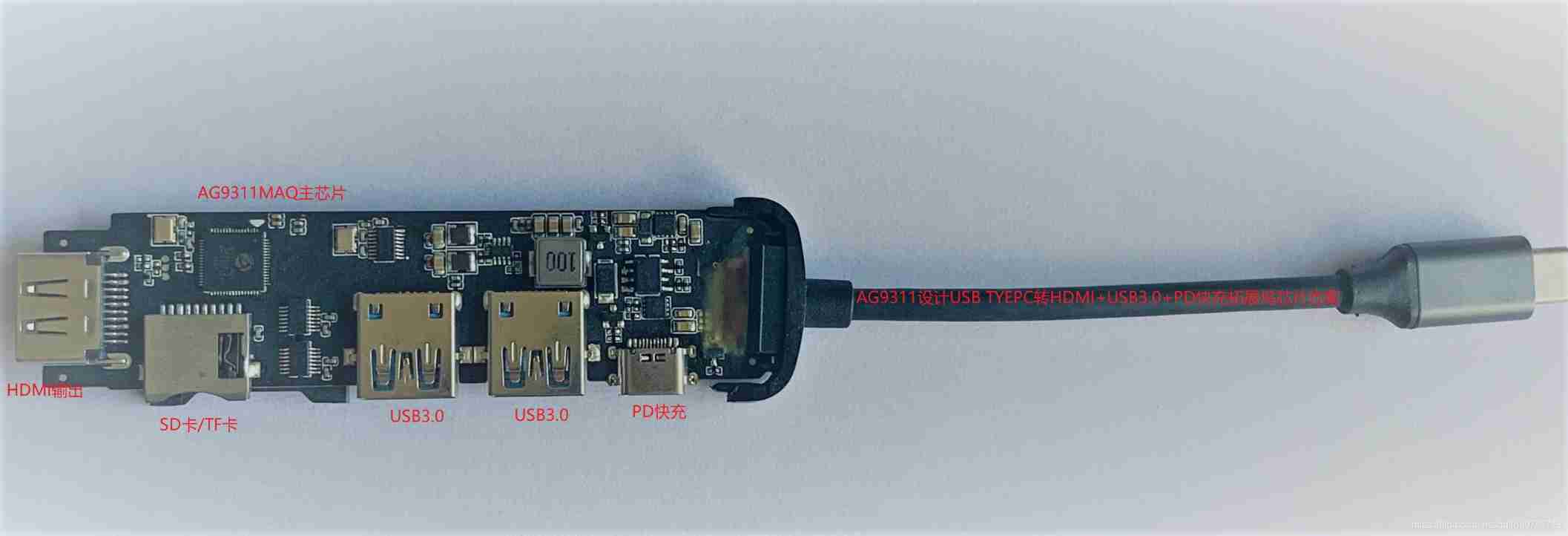
Ag9311maq design 100W USB type C docking station data | ag9311maq is used for 100W USB type C to HDMI with PD fast charging +u3+sd/cf docking station scheme description
随机推荐
A speed Limited large file transmission tool for every major network disk
Several frequently used OCR document scanning tools | no watermark | avoid IQ tax
Analysis of 8 classic C language pointer written test questions
General configuration tooltip
[deep learning] AI one click to change the sky
Jemter distributed
How to write mark down on vscode
130. Surrounding area
6. Dropout application
Understanding of sidelobe cancellation
Saving and reading of network model
Serial port receives a packet of data
The combination of relay and led small night light realizes the control of small night light cycle on and off
2.非线性回归
Y59. Chapter III kubernetes from entry to proficiency - continuous integration and deployment (III, II)
8. Optimizer
Common effects of line chart
Share a latex online editor | with latex common templates
Su embedded training - C language programming practice (implementation of address book)
Ag7120 and ag7220 explain the driving scheme of HDMI signal extension amplifier | ag7120 and ag7220 design HDMI signal extension amplifier circuit reference