当前位置:网站首页>Interpretation of iterator related "itertools" module usage
Interpretation of iterator related "itertools" module usage
2022-07-06 13:58:00 【Algorithm channel】
0 Preface
When it comes to processing cycles , We are used to using for, while etc. , For example, print the characters in each list in turn :
lis = ['I', 'love', 'python']
for i in lis:
print(i)
I
love
pythonWhen the number of bytes of printed content is small , When all is loaded in memory , Re print , No problem . But , If there are millions of vehicle tracks now , Ask you to analyze the travel rules of each of them , Traffic jams, etc , If it's on a single computer .
You may have to face... First , It can also be ignored by you , After the final code is written , A problem that could be exposed :outofmemory, This is often encountered in practical projects .
This question reminds us of , While processing data , How to write programs that make efficient use of memory , It's very important . today , Let's explore how to use memory efficiently , Save memory and get things done .
Actually ,Python There is a module ready to deal with this , It is itertools modular , The functions of these functions are actually well understood .
I'm not going to give you a general idea of what they can do , I want to analyze the implementation code behind these functions , How to save memory efficiently ,Python How did the kernel contributors write beautiful code , This is very interesting. , isn't it? ?
OK,let's go. Hope you enjoy the journey!
1 Patchwork elements
itertools Medium chain Function implementation element splicing , The prototype is as follows , Parameters * Represents a variable number of parameters
chain(iterables)
The application is as follows :
In [33]: list(chain(['I','love'],['python'],['very', 'much']))
Out[33]: ['I', 'love', 'python', 'very', 'much']wow , It's no longer easy to use , It's a little join The smell of , But compared to join strong , It focuses on the fact that the parameters are all iteratable instances .
that ,chain How to achieve efficient memory saving ?chain The general implementation code is as follows :
def chain(*iterables):
for it in iterables:
for element in it:
yield element The above code is not difficult to understand ,chain Essence returns a generator , So it actually reads one element at a time into memory , So save the most memory .
2 One by one
Returns the cumulative total value of the list , Prototype :
accumulate(iterable[, func, *, initial=None])
The application is as follows :
In [36]: list(accumulate([1,2,3,4,5,6],lambda x,y: x*y))
Out[36]: [1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720]accumulate The general implementation code is as follows :
def accumulate(iterable, func=operator.add, *, initial=None):
it = iter(iterable)
total = initial
if initial is None:
try:
total = next(it)
except StopIteration:
return
yield total
for element in it:
total = func(total, element)
yield total Above code , Are you all right? ? And chain ordinary yield Different , It's a little more complicated here ,yield It's kind of like return, therefore yield total That line directly returns an element , That is to say iterable The first element of , Because the first element returned by this function at any time is its first . Again because yield Back to a generator object , Such as name gen, therefore next(gen) when , The code will execute to for element in it: This line , And the iterator at this time it Has pointed to iterable The second element of ,OK, I believe you understand !
3 Funnel screening
It is compress function , Function is similar to funnel function , So I call it funnel screening , Prototype :
compress(data, selectors)
In [38]: list(compress('abcdefg',[1,1,0,1]))
Out[38]: ['a', 'b', 'd']Easy to see ,compress The number of elements returned is equal to the shorter list length of the two parameters .
Its general implementation code :
def compress(data, selectors):
return (d for d, s in zip(data, selectors) if s)This function is very useful
4 Segment screening
Scan list , Start to hold back if you don't meet the conditions , The prototype is as follows :
dropwhile(predicate, iterable)
Application examples :
In [39]: list(dropwhile(lambda x: x<3,[1,0,2,4,1,1,3,5,-5]))
Out[39]: [4, 1, 1, 3, 5, -5]The general code to implement it is as follows :
def dropwhile(predicate, iterable):
iterable = iter(iterable)
for x in iterable:
if not predicate(x):
yield x
break
for x in iterable:
yield x5 Segment screening 2
Scan list , Return elements from iteratable objects as long as conditions are met , Until the conditions are not met , The prototype is as follows :
takewhile(predicate, iterable)
Application examples :
In [43]: list(takewhile(lambda x: x<5, [1,4,6,4,1]))
Out[43]: [1, 4]The general code to implement it is as follows :
def takewhile(predicate, iterable):
for x in iterable:
if predicate(x):
yield x
else:
break # Return immediately 6 Selection of defective products
Scan list , Keep... As long as you don't meet the conditions , The prototype is as follows :
dropwhile(predicate, iterable)
Application examples :
In [40]: list(filterfalse(lambda x: x%2==0, [1,2,3,4,5,6]))
Out[40]: [1, 3, 5]The general code to implement it is as follows :
def dropwhile(predicate, iterable):
iterable = iter(iterable)
for x in iterable:
if not predicate(x):
yield x
break
for x in iterable:
yield x7 Slice screening
Python General slicing operation in , such as :
lis = [1,3,2,1]
lis[:1]Their defect is still lis You have to load all the memory , So more memory saving operations islice, The prototype is as follows :
islice(iterable, start, stop[, step])
Application examples :
In [41]: list(islice('abcdefg',1,4,2))
Out[41]: ['b', 'd']The general code to implement it is as follows :
def islice(iterable, *args):
s = slice(*args)
start, stop, step = s.start or 0, s.stop or sys.maxsize, s.step or 1
it = iter(range(start, stop, step))
try:
nexti = next(it)
except StopIteration:
for i, element in zip(range(start), iterable):
pass
return
try:
for i, element in enumerate(iterable):
if i == nexti:
yield element
nexti = next(it)
except StopIteration:
for i, element in zip(range(i + 1, stop), iterable):
pass Clever use of the generator will throw an exception at the end of the iteration StopIteration, Do something about boundary handling .
8 cell division
tee The function is similar to the well-known cell division , It can replicate the original iterator n individual , The prototype is as follows :
tee(iterable, n=2)
The application is as follows , It can be seen that the two iterators are independent
a = tee([1,4,6,4,1],2)
In [51]: next(a[0])
Out[51]: 1
In [52]: next(a[1])
Out[52]: 1The code to implement it is as follows :
def tee(iterable, n=2):
it = iter(iterable)
deques = [collections.deque() for i in range(n)]
def gen(mydeque):
while True:
if not mydeque:
try:
newval = next(it)
except StopIteration:
return
for d in deques:
d.append(newval)
yield mydeque.popleft()
return tuple(gen(d) for d in deques)tee The implementation uses a queue type internally deques, At first, an empty queue is generated , Add elements... To each of the copied queues newval, meanwhile yield Currently called mydeque The leftmost element in .
9 map variant
starmap You can view it as map A variation of the , It can save more memory , meanwhile iterable The element of must also be an iteratable object , The prototype is as follows :
starmap(function, iterable)
Apply it :
In [63]: list(starmap(lambda x,y: str(x)+'-'+str(y), [('a',1),('b',2),('c',3)]))
Out[63]: ['a-1', 'b-2', 'c-3']starmap The implementation details are as follows :
def starmap(function, iterable):
for args in iterable:
yield function(*args)10 Copy elements
repeat Implement copy elements n Time , The prototype is as follows :
repeat(object[, times])
The application is as follows :
In [66]: list(repeat(6,3))
Out[66]: [6, 6, 6]
In [67]: list(repeat([1,2,3],2))
Out[67]: [[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]Its implementation details are as follows :
def repeat(object, times=None):
if times is None:# If times Not set up , Will always repeat down
while True:
yield object
else:
for i in range(times):
yield object11 The cartesian product
The effect of Cartesian product is the same as that of :
((x,y) for x in A for y in B)therefore , The effect of Cartesian product is as follows :
In [68]: list(product('ABCD', 'xy'))
Out[68]:
[('A', 'x'),
('A', 'y'),
('B', 'x'),
('B', 'y'),
('C', 'x'),
('C', 'y'),
('D', 'x'),
('D', 'y')]Its implementation details :
def product(*args, repeat=1):
pools = [tuple(pool) for pool in args] * repeat
result = [[]]
for pool in pools:
result = [x+[y] for x in result for y in pool]
for prod in result:
yield tuple(prod)12 Enhanced Edition zip
Combination value . If the length of the iteratable object is not aligned , Based on the fillvalue Fill in missing values , Be careful : Iterations continue to the longest consuming iteratable object , The effect is as follows :
In [69]: list(zip_longest('ABCD', 'xy', fillvalue='-'))
Out[69]: [('A', 'x'), ('B', 'y'), ('C', '-'), ('D', '-')]Its implementation details :
def zip_longest(*args, fillvalue=None):
iterators = [iter(it) for it in args]
num_active = len(iterators)
if not num_active:
return
while True:
values = []
for i, it in enumerate(iterators):
try:
value = next(it)
except StopIteration:
num_active -= 1
if not num_active:
return
iterators[i] = repeat(fillvalue)
value = fillvalue
values.append(value)
yield tuple(values)It uses repeat, That is, when the length of the iteratable object is not aligned , according to fillvalue Fill in missing values . The key to understanding the code above is the iterator object (iter),next The particularity of the method :
In [74]: for i, it in enumerate([iter([1,2,3]),iter(['x','y'])]):
...: print(next(it))
# Output :
1
xCombined with this prompt to understand the above code , It's not going to work .
summary
Python Of itertools Memory efficient iterator provided by the module , Basically, the implementation inside is based on the generator , So on the one hand, understand this 12 The basic functions implemented by functions , At the same time, it can also deepen the generator (generator) The understanding of the , Write for us more efficiently 、 concise 、 Beautiful code laid a solid foundation .
Read more :
The most straightforward explanation of machine learning , Just look at this article !
Python List generator 12 A little function , Which ones do you often use ?
Python The most underrated Library , Use it well and improve efficiency 10 times !

Long press QR code , Follow my public number
边栏推荐
- Custom RPC project - frequently asked questions and explanations (Registration Center)
- 1. Preliminary exercises of C language (1)
- Matlab opens M file garbled solution
- Wechat applet
- Why use redis
- JS several ways to judge whether an object is an array
- About the parental delegation mechanism and the process of class loading
- A comprehensive summary of MySQL transactions and implementation principles, and no longer have to worry about interviews
- Programme de jeu de cartes - confrontation homme - machine
- TypeScript快速入门
猜你喜欢
Write a program to simulate the traffic lights in real life.
HackMyvm靶机系列(3)-visions
Meituan dynamic thread pool practice ideas, open source
![[面试时]——我如何讲清楚TCP实现可靠传输的机制](/img/d6/109042b77de2f3cfbf866b24e89a45.png)
[面试时]——我如何讲清楚TCP实现可靠传输的机制
仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(三)

QT meta object qmetaobject indexofslot and other functions to obtain class methods attention

1. First knowledge of C language (1)
A piece of music composed by buzzer (Chengdu)
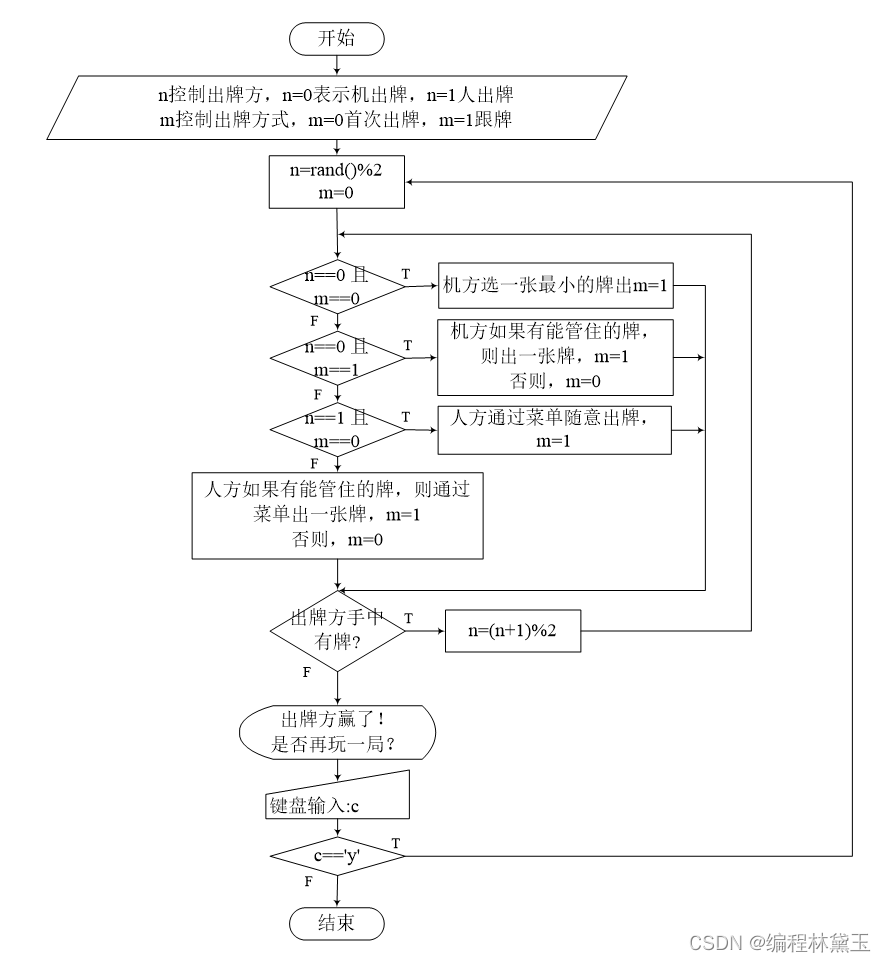
撲克牌遊戲程序——人機對抗
HackMyvm靶机系列(6)-videoclub
随机推荐
强化学习基础记录
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2021 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
自定义RPC项目——常见问题及详解(注册中心)
This time, thoroughly understand the MySQL index
2022 Teddy cup data mining challenge question C idea and post game summary
A piece of music composed by buzzer (Chengdu)
实验九 输入输出流(节选)
Force deduction 152 question multiplier maximum subarray
Poker game program - man machine confrontation
[modern Chinese history] Chapter 6 test
记一次猫舍由外到内的渗透撞库操作提取-flag
Nuxtjs快速上手(Nuxt2)
Strengthen basic learning records
2022泰迪杯数据挖掘挑战赛C题思路及赛后总结
7-15 h0161. Find the greatest common divisor and the least common multiple (PTA program design)
Using qcommonstyle to draw custom form parts
透彻理解LRU算法——详解力扣146题及Redis中LRU缓存淘汰
HackMyvm靶机系列(2)-warrior
[insert, modify and delete data in the headsong educator data table]
7-5 staircase upgrade (PTA program design)