当前位置:网站首页>7-8 7104 Joseph problem (PTA program design)
7-8 7104 Joseph problem (PTA program design)
2022-07-06 13:56:00 【Programming Lindaiyu】
Joseph's question : Yes n Only monkey , Circle clockwise to choose the king ( Number from 1 To n), From 1 We'll start counting on the , Count to m, Count to m The monkey out of the circle , The rest of the monkeys went on from 1 Start counting . That's it , Until there's only one monkey left in the circle , This monkey is the monkey king , Programming for input n,m after , Output the number of the last Monkey King .
Input format :
Each line is two integers separated by spaces , The first is n, The second is m ( 0 < m, n < 300) . The last line is :0 0 .
Output format :
For each row of input data ( Except for the last line ), The output data is also a line , The number of the last Monkey King .
sample input :
6 2
12 4
8 3
0 0
sample output :
5
1
7
Code (Python):
Method 1 :
n,m=map(int,input().split()) # Input n,m
list1=[] # For storage “ monkey ”
list2=[] # Used to store the final results
f=0 # There are several groups
for i in range(300): # First, add elements to the list , Otherwise, the list is empty , Cannot modify elements in the list
list1.append(0)
while 1:
if n==0 and m==0: # Input “0 0” when , end
break
else: # Or start choosing the monkey king
for i in range(1,n+1): # Because the monkey sequence is from 1 At the beginning , So our list also starts from 1 Start
list1[i]=1 # First initialize the numbers in the list so that they are all 1, use 1 To show the monkeys that have not been eliminated
f+=1 # Count , A total of several groups of numbers were calculated , Last act list2 The length of , use for Output results
i=1 # Start with the first number
sum=n # At the beginning n individual 1
count=0 #count Namely 1~m
while sum>1: #sum by n In number 1 The number of , Remnant 1 individual 1 It means that the monkey king has been selected
if list1[i]!=0: # Not for everyone 0 Number of numbers ( Monkeys that have not been eliminated ),count+1
count+=1
if count==m: # until count Add to equal m When , Count to m The monkey out of the circle
count=0 #count Start counting again
list1[i]=0 # Make the corresponding element equal to 0, It means that it has been eliminated
sum-=1 #sum Number of minus 1, It means that there are few monkeys 1
i+=1 # Every time a monkey is eliminated ,i Add 1, Start looking for the next monkey
if i==n+1: # After subscript exceeds the range , Just go back to the beginning and find , It is equivalent to forming a circle
i=1
for i in range(1,n+1): # Traverse the list
if list1[i]!=0: # Look for not 0 The position of the number of , That is, the serial number of the monkey king
list2.append(i) # And add its serial number to the result list
n,m=map(int,input().split()) # Input again , Ready for the next cycle
for i in range(f): # Output the results in the result list
print(list2[i])Method 2 :
n,m=map(int,input().split()) ## Input n,m
wang=[] # For storage “ monkey ”
while 1:
if n==0 and m==0 : # Input “0 0” when , end
break
else: # Or start choosing the monkey king
k=0 #k Indicates the order of reported amount , Set it to 0
wang.clear() # First empty the last monkey sequence
for i in range(1,n+1): # take n Monkey from 1 Numbered starting
wang.append(i)
while len(wang) > 1: #wang The length of the list is greater than 1 when , It means that the monkey king has not been elected , Into the loop
i=0
while i<len(wang): # Traverse all monkeys in the king list
k+=1 # From 1 We'll start counting on the , Count to m, Every time I report k Add 1
if k == m: # When k Add to m when , It means that the monkey just counts to m
del wang[i] # Eliminate the monkey , Delete it from the list
k=0 # The rest of the monkeys went on from 1 Start counting , So first of all k Set as 0
# Be careful , On the count of m when , Delete the monkey , So the number of monkeys behind it will be reduced by one , therefore i No need to add 1 You can directly judge the next monkey
else: # If k It's not equal to m, Then the monkey will not be eliminated , send i Add 1, Start judging the next monkey
i+=1
a=wang[0] # Last , Out of the while loop , There must be only one monkey left , The monkey king
print(a) # Because it existed at the beginning wang In the list is the serial number of each monkey , So the value in the direct output is the serial number of the monkey
n,m=map(int,input().split()) # Input again , Ready for the next cycle Ideas : The above provides two ways to solve this problem , It's basically the same , Are stored through a list “ monkey ”, Then gradually eliminate the selected monkeys , Finally find the monkey king . The difference lies in , In method 1 , First save the data in the list “1” To show the monkeys that have not been eliminated , Then count to m The monkey is set 0 Indicates elimination , There is only one left in the final list “1” when , It means to choose the monkey king . In method two , The serial number of the monkey is directly stored in the list , Then count to m The monkey of is directly deleted from the list , The only remaining element in the final list is the monkey king .
The above program gives more detailed comments , For novice Xiaobai's reference . The idea of program design or code implementation is not optimal , You are welcome to correct your mistakes or give better ideas .
I am a rookie who wants to be Kunpeng , Everyone's encouragement is my driving force , Welcome to like collection comments !
边栏推荐
- 实验五 类和对象
- PriorityQueue (large root heap / small root heap /topk problem)
- 7-11 机工士姆斯塔迪奥(PTA程序设计)
- SRC挖掘思路及方法
- 7-3 构造散列表(PTA程序设计)
- About the parental delegation mechanism and the process of class loading
- 为什么要使用Redis
- 甲、乙机之间采用方式 1 双向串行通信,具体要求如下: (1)甲机的 k1 按键可通过串行口控制乙机的 LEDI 点亮、LED2 灭,甲机的 k2 按键控制 乙机的 LED1
- Canvas foundation 1 - draw a straight line (easy to understand)
- Experiment 9 input and output stream (excerpt)
猜你喜欢

2. First knowledge of C language (2)

优先队列PriorityQueue (大根堆/小根堆/TopK问题)

Mixlab unbounded community white paper officially released
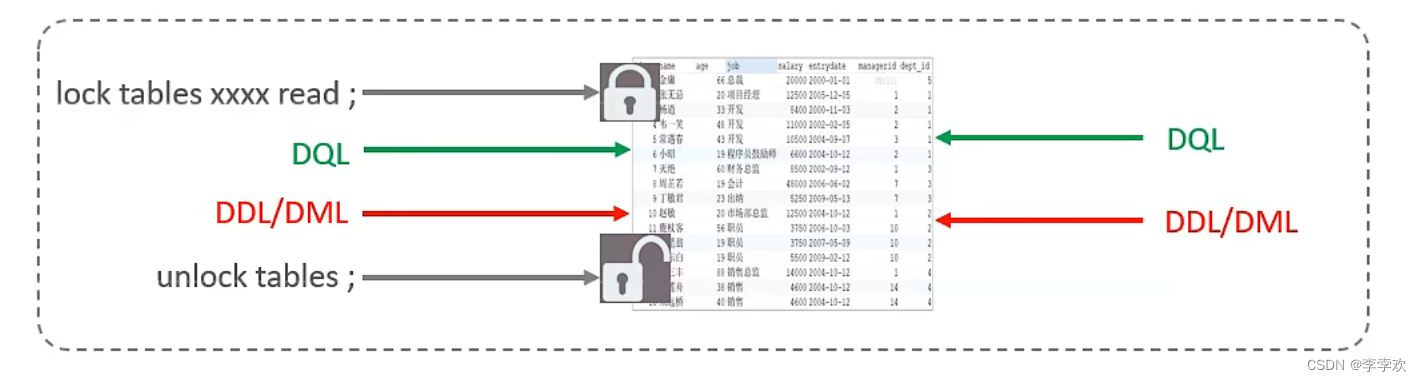
MySQL锁总结(全面简洁 + 图文详解)
Leetcode. 3. Longest substring without repeated characters - more than 100% solution

【手撕代码】单例模式及生产者/消费者模式
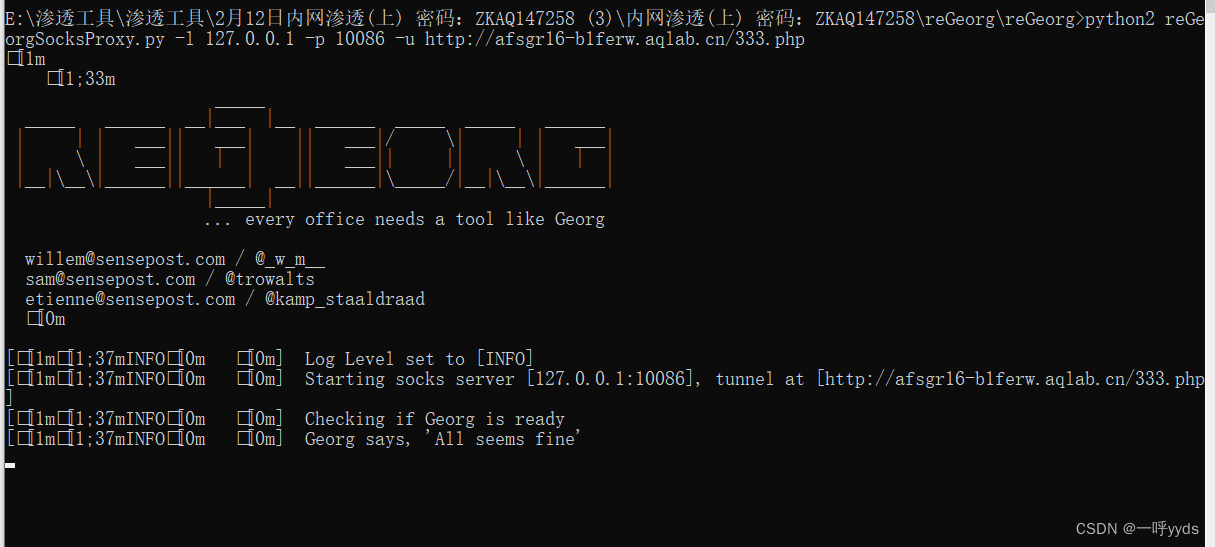
记一次猫舍由外到内的渗透撞库操作提取-flag
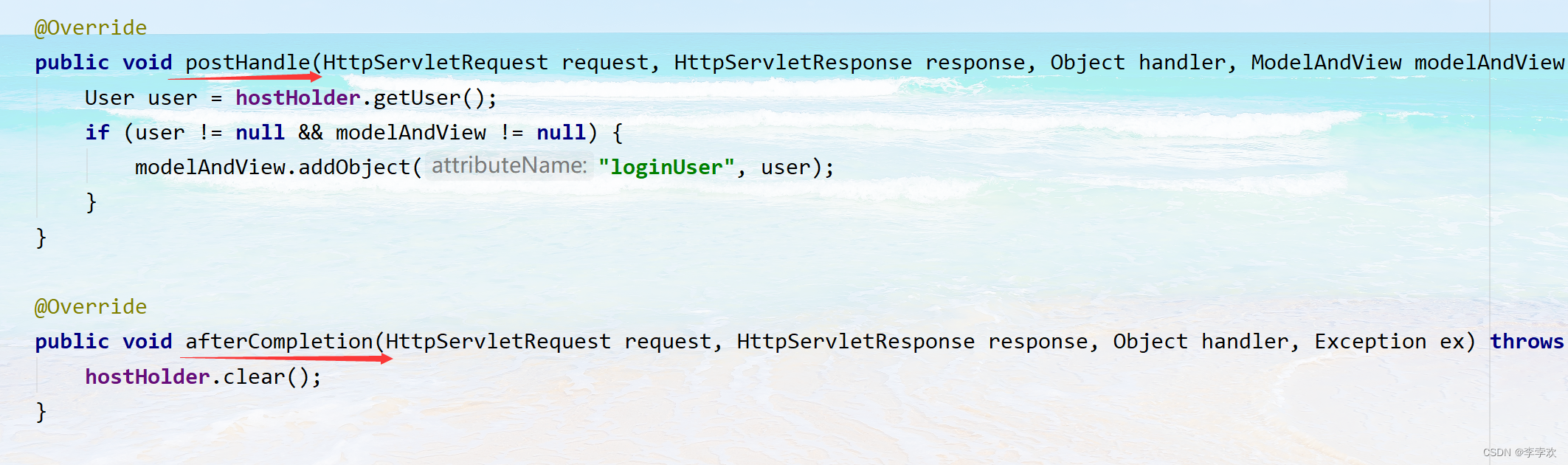
仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(一)

【黑马早报】上海市监局回应钟薛高烧不化;麦趣尔承认两批次纯牛奶不合格;微信内测一个手机可注册俩号;度小满回应存款变理财产品...
Differences among fianl, finally, and finalize
随机推荐
Implementation principle of automatic capacity expansion mechanism of ArrayList
7-3 构造散列表(PTA程序设计)
7-14 错误票据(PTA程序设计)
Relationship between hashcode() and equals()
自定义RPC项目——常见问题及详解(注册中心)
canvas基础2 - arc - 画弧线
Force deduction 152 question multiplier maximum subarray
仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(一)
[面試時]——我如何講清楚TCP實現可靠傳輸的機制
渗透测试学习与实战阶段分析
[dark horse morning post] Shanghai Municipal Bureau of supervision responded that Zhong Xue had a high fever and did not melt; Michael admitted that two batches of pure milk were unqualified; Wechat i
【黑马早报】上海市监局回应钟薛高烧不化;麦趣尔承认两批次纯牛奶不合格;微信内测一个手机可注册俩号;度小满回应存款变理财产品...
2022泰迪杯数据挖掘挑战赛C题思路及赛后总结
. How to upload XMIND files to Jinshan document sharing online editing?
Callback function ----------- callback
7-7 7003 组合锁(PTA程序设计)
撲克牌遊戲程序——人機對抗
7-8 7104 约瑟夫问题(PTA程序设计)
Redis实现分布式锁原理详解
实验七 常用类的使用(修正帖)