当前位置:网站首页>[slam] lidar camera external parameter calibration (Hong Kong University marslab) does not need a QR code calibration board
[slam] lidar camera external parameter calibration (Hong Kong University marslab) does not need a QR code calibration board
2022-07-06 03:21:00 【iwander。】
review
Calibration is also a pose estimation problem , It essentially solves the same problem as various laser odometers and visual odometers . The calibration method can also be used for reference in the odometer problem . They all have a common process :
a. feature extraction
b. Feature matching
c. Pose solving
Reference paper : Pixel-level Extrinsic Self Calibration of High Resolution LiDAR and Camera in Targetless Environments
github: https://github.com/hku-mars/livox_camera_calib
This paper is the famous Hong Kong University Mars Lab Produce , What they solve is livox and camera Calibration of . also , There is no need to place a priori object like calibration board or QR code in the environment ! The paper is very long , A lot of space is devoted to introducing their reasons for doing so , Let's skip this part , Just look at what they do in the code .
1. camera image Feature extraction
Extract robust , The feature of high recognition is the most important point . When calibrating the camera , We can use checkerboard , Because it has obvious characteristics , The structure is known , It is easy to realize data association on different photos . about lidar and image for , Their data are different , How to find matching features is the first problem , So they chose Line features . Extracting line features from photos , Yes opencv The way to , Also have learning-based( Example ) The way to . This paper 2D The method of line feature extraction is relatively simple , They used opencv Self contained canny Algorithm ,canny Only the edge information in the photo can be extracted , in other words , It can only tell you which pixel is a straight line point , But I can't tell you which line this pixel belongs to . Generally, different straight lines should be recognized on the photos , To be in canny On the basis of , recycling hough Algorithm or LSD The algorithm further extracts straight lines , These algorithms have been opencv Built in .
void Calibration::edgeDetector(
const int &canny_threshold, const int &edge_threshold,
const cv::Mat &src_img, cv::Mat &edge_img,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr &edge_cloud)
{
// Gaussian blur
int gaussian_size = 5;
cv::GaussianBlur(src_img, src_img, cv::Size(gaussian_size, gaussian_size), 0, 0);
// Extract edge pixels
cv::Mat canny_result = cv::Mat::zeros(height_, width_, CV_8UC1);
cv::Canny(src_img, canny_result, canny_threshold, canny_threshold * 3, 3, true);
// Group these line points
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> contours;
std::vector<cv::Vec4i> hierarchy;
cv::findContours(canny_result, contours, hierarchy, cv::RETR_EXTERNAL, cv::CHAIN_APPROX_NONE, cv::Point(0, 0));
// If a group has too few points , Then don't , This is equivalent to filtering
edge_img = cv::Mat::zeros(height_, width_, CV_8UC1);
edge_cloud = pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
for (size_t i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)//contours.size()
{
if (contours[i].size() > edge_threshold)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < contours[i].size(); j++)
{
//what the use of p ???????
pcl::PointXYZ p;
p.x = contours[i][j].x;
p.y = -contours[i][j].y;
p.z = 0;
edge_img.at<uchar>(-p.y, p.x) = 255;
}
}
}
// Then save the pixel coordinates of the line points to pcl Point cloud
//edge_cloud is the real output
for (int x = 0; x < edge_img.cols; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < edge_img.rows; y++)
{
if (edge_img.at<uchar>(y, x) == 255)
{
pcl::PointXYZ p;
p.x = x;
p.y = -y; //TODO -y?
p.z = 0;
edge_cloud->points.push_back(p);
}
}
}
edge_cloud->width = edge_cloud->points.size();
edge_cloud->height = 1;
}In the code , They first did the photo gaussblur Noise removal , Then proceed canny Extract edge pixels . The reason why they finally saved pixels to pcl In the point cloud , Use these points to construct the next kdtree, It's because they need to borrow when matching features pcl Of kdtree Find the nearest neighbor .
2. lidar cloud Feature extraction
Next , The problem becomes how to find those points belonging to line features in the point cloud . Generally speaking , stay 3D Lift the thread in the cloud , You need to bring noodles first , The intersection line between faces is a straight line .github There is also some code for cloud lifting line , for example This article , But the position of the lifting line is not particularly accurate .
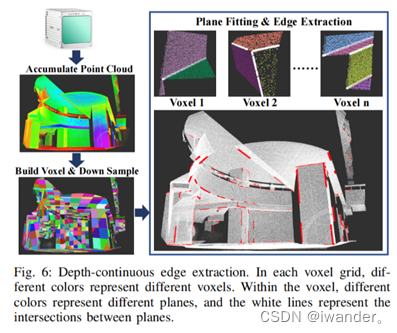
pcl There are ready-made face segmentation algorithms , Also use ransac The way to fit a plane . But if the point cloud contains more faces , that ransac It will fail. . So in this code , They divide the point cloud into side lengths 1m Voxels of , For every voxel , There are not many planes inside , Reduce the probability of error . And then use pcl The divider of adopts RANSAC The way to lift the plane , Keep those intersecting and included angles 30-150 Degree plane , Extract intersection . There is another one in the paper depth-continuous edge The concept of . This concept has spent a lot of time in the paper . The general meaning is that the extracted straight line is not the whole segment , Only keep the small segment close to the model point cloud , If a certain position of the intersection line is very close to both plane point clouds , Then it will be selected . These small lines are in the paper depth-continuous edge, The code is actually very short .
So , When calibrating , You can't be in the wilderness, deep mountains and forests , It is better to have some angular buildings in the surrounding environment , For example, the campus of Hong Kong University .
void Calibration::LiDAREdgeExtraction(
const std::unordered_map<VOXEL_LOC, Voxel *> &voxel_map,
const float ransac_dis_thre, const int plane_size_threshold, //0.02, 60
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr &lidar_line_cloud_3d)
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Extracting Lidar Edge");
ros::Rate loop(5000);
lidar_line_cloud_3d = pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
for (auto iter = voxel_map.begin(); iter != voxel_map.end(); iter++)
{
if (iter->second->cloud->size() > 50)
{
std::vector<Plane> plane_list;
//1. Create a voxel filter
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud_filter(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*iter->second->cloud, *cloud_filter);
// Create a model parameter object , Used to record results
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
// inliers Indicates the point where the error can be tolerated , Record point cloud serial number
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
// Create a splitter
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZI> seg;
// Optional, Set whether the points displayed on the result plane are the separated points or the remaining points
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
// Mandatory- Set the target geometry
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
// Segmentation method : Random sampling
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
// Set the error tolerance range , That's the threshold
if (iter->second->voxel_origin[0] < 10)
{
seg.setDistanceThreshold(ransac_dis_thre);
}
else
{
seg.setDistanceThreshold(ransac_dis_thre);
}
//2. Point cloud segmentation , Extract plane
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> color_planner_cloud;
int plane_index = 0;
while (cloud_filter->points.size() > 10)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI> planner_cloud;
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZI> extract;
// Enter the point cloud
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filter);
seg.setMaxIterations(500);
// Split point cloud
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size() == 0)
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Could not estimate a planner model for the given dataset");
break;
}
extract.setIndices(inliers);
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filter);
extract.filter(planner_cloud);
if (planner_cloud.size() > plane_size_threshold)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> color_cloud;
std::vector<unsigned int> colors;
colors.push_back(static_cast<unsigned int>(rand() % 256));
colors.push_back(static_cast<unsigned int>(rand() % 256));
colors.push_back(static_cast<unsigned int>(rand() % 256));
pcl::PointXYZ p_center(0, 0, 0);
for (size_t i = 0; i < planner_cloud.points.size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZRGB p;
p.x = planner_cloud.points[i].x;
p.y = planner_cloud.points[i].y;
p.z = planner_cloud.points[i].z;
p_center.x += p.x;
p_center.y += p.y;
p_center.z += p.z;
p.r = colors[0];
p.g = colors[1];
p.b = colors[2];
color_cloud.push_back(p);
color_planner_cloud.push_back(p);
}
p_center.x = p_center.x / planner_cloud.size();
p_center.y = p_center.y / planner_cloud.size();
p_center.z = p_center.z / planner_cloud.size();
Plane single_plane;
single_plane.cloud = planner_cloud;
single_plane.p_center = p_center;
single_plane.normal << coefficients->values[0], coefficients->values[1], coefficients->values[2];
single_plane.index = plane_index;
plane_list.push_back(single_plane);
plane_index++;
}
//3. The remaining point cloud after extracting the plane , unused
extract.setNegative(true);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI> cloud_f;
extract.filter(cloud_f);
*cloud_filter = cloud_f;
}
if (plane_list.size() >= 2)
{
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 planner_cloud2;
pcl::toROSMsg(color_planner_cloud, planner_cloud2);
planner_cloud2.header.frame_id = "livox";
planner_cloud_pub_.publish(planner_cloud2);
//loop.sleep();
}
//4. Get the plane intersection point cloud
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>> line_cloud_list;
calcLine(plane_list, voxel_size_, iter->second->voxel_origin, line_cloud_list);
// ouster 5,normal 3
//if contains too many lines, it is more likely to have fake lines
if (line_cloud_list.size() > 0 && line_cloud_list.size() <= 8)
{
for (size_t cloud_index = 0; cloud_index < line_cloud_list.size(); cloud_index++)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < line_cloud_list[cloud_index].size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZI p = line_cloud_list[cloud_index].points[i];
plane_line_cloud_->points.push_back(p);
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pub_cloud;
pcl::toROSMsg(line_cloud_list[cloud_index], pub_cloud);
pub_cloud.header.frame_id = "livox";
line_cloud_pub_.publish(pub_cloud);
//loop.sleep();
plane_line_number_.push_back(line_number_);
}
line_number_++;
}
}
}
}
}After dividing the planes within a voxel range , Seeking a straight line is more violent . Because there are not many planes in a voxel , Then it's good to be violent between the two , This part of the code is in this function :
void Calibration::calcLine(
const std::vector<Plane> &plane_list, const double voxel_size,
const Eigen::Vector3d origin,
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>> &line_cloud_list)
{
...
//5. if current location is close to both 2 plane clouds, so the point is on the depth contiuous edge
if ((dis1 < min_line_dis_threshold_*min_line_dis_threshold_ && dis2 < max_line_dis_threshold_*max_line_dis_threshold_) || (dis1 < max_line_dis_threshold_*max_line_dis_threshold_ && dis2 < min_line_dis_threshold_*min_line_dis_threshold_))
{
line_cloud.push_back(p);
}
...
}that if Your judgment is about depth-continuous edge.
3. lidar-camera Feature association
Whether extracted from point clouds 3D Line , still image Extracted from 2D Line , The author did not use something similar to Ax+By+Cz+D=0 To describe , It is still saved in the form of points . When 3D When the line point is re projected to the plane , Just use image Constructed by pixels kdtree Query the nearest neighbor as a set of associated data , Don't use all kinds of trick, A simple and efficient . In the code ,void Calibration::buildVPnp() Is the function of constructing feature matching .
//find the correspondance of 3D points and 2D points with their directions
void Calibration::buildVPnp(
const Vector6d &extrinsic_params, const int dis_threshold,
const bool show_residual,
const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr &cam_edge_cloud_2d,
const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr &lidar_line_cloud_3d,
std::vector<VPnPData> &pnp_list)
{
//1.initialize containers for 3D lines: for each pixel there is a corresponding cloud
//because some closed 3D points may preject onto same pixel, so the container helpes to calculate averagy value
pnp_list.clear();
std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<pcl::PointXYZI>>> img_pts_container;
for (int y = 0; y < height_; y++)
{
std::vector<std::vector<pcl::PointXYZI>> row_pts_container;
for (int x = 0; x < width_; x++)
{
std::vector<pcl::PointXYZI> col_pts_container;
row_pts_container.push_back(col_pts_container);
}
img_pts_container.push_back(row_pts_container);
}
//2.get 3D lines, initial pose, intrinsics
std::vector<cv::Point3d> pts_3d;
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector3;
rotation_vector3 = Eigen::AngleAxisd(extrinsic_params[0], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(extrinsic_params[1], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(extrinsic_params[2], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
for (size_t i = 0; i < lidar_line_cloud_3d->size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZI point_3d = lidar_line_cloud_3d->points[i];
pts_3d.emplace_back(cv::Point3d(point_3d.x, point_3d.y, point_3d.z));
}
cv::Mat camera_matrix = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << fx_, 0.0, cx_, 0.0, fy_, cy_, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
cv::Mat distortion_coeff = (cv::Mat_<double>(1, 5) << k1_, k2_, p1_, p2_, k3_);
cv::Mat r_vec = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 1)
<< rotation_vector3.angle() * rotation_vector3.axis().transpose()[0],
rotation_vector3.angle() * rotation_vector3.axis().transpose()[1],
rotation_vector3.angle() * rotation_vector3.axis().transpose()[2]);
cv::Mat t_vec = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 1) << extrinsic_params[3], extrinsic_params[4], extrinsic_params[5]);
// debug
// std::cout << "camera_matrix:" << camera_matrix << std::endl;
// std::cout << "distortion_coeff:" << distortion_coeff << std::endl;
// std::cout << "r_vec:" << r_vec << std::endl;
// std::cout << "t_vec:" << t_vec << std::endl;
// std::cout << "pts 3d size:" << pts_3d.size() << std::endl;
//3.project 3d-points into image view and fall into the container, look out these info are from 3D lines
std::vector<cv::Point2d> pts_2d;
cv::projectPoints(pts_3d, r_vec, t_vec, camera_matrix, distortion_coeff, pts_2d);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr line_edge_cloud_2d(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
std::vector<int> line_edge_cloud_2d_number;
for (size_t i = 0; i < pts_2d.size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZ p;
p.x = pts_2d[i].x;
p.y = -pts_2d[i].y;
p.z = 0;
pcl::PointXYZI pi_3d;
pi_3d.x = pts_3d[i].x;
pi_3d.y = pts_3d[i].y;
pi_3d.z = pts_3d[i].z;
pi_3d.intensity = 1;
if (p.x > 0 && p.x < width_ && pts_2d[i].y > 0 && pts_2d[i].y < height_)
{
if (img_pts_container[pts_2d[i].y][pts_2d[i].x].size() == 0)
{
line_edge_cloud_2d->points.push_back(p);
line_edge_cloud_2d_number.push_back(plane_line_number_[i]);
img_pts_container[pts_2d[i].y][pts_2d[i].x].push_back(pi_3d);
}
else
{
img_pts_container[pts_2d[i].y][pts_2d[i].x].push_back(pi_3d);
}
}
}
if (show_residual)
{
cv::Mat residual_img = getConnectImg(dis_threshold, cam_edge_cloud_2d, line_edge_cloud_2d);
cv::imshow("residual", residual_img);
cv::waitKey(50);
}
//4.build kdtree to find the closest 2D point of each 3D point
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr kdtree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr kdtree_lidar(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr search_cloud = pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree_cloud = pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree_cloud_lidar = pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
kdtree->setInputCloud(cam_edge_cloud_2d);
kdtree_lidar->setInputCloud(line_edge_cloud_2d);
tree_cloud = cam_edge_cloud_2d;
tree_cloud_lidar = line_edge_cloud_2d;
search_cloud = line_edge_cloud_2d;
// Specify the number of nearest neighbors
int K = 5;
// Create two vectors , Store the index values of the nearest neighbors respectively 、 The center distance of the nearest neighbor
std::vector<int> pointIdxNKNSearch(K);
std::vector<float> pointNKNSquaredDistance(K);
std::vector<int> pointIdxNKNSearchLidar(K);
std::vector<float> pointNKNSquaredDistanceLidar(K);
int match_count = 0;
double mean_distance;
int line_count = 0;
std::vector<cv::Point2d> lidar_2d_list;
std::vector<cv::Point2d> img_2d_list;
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> camera_direction_list;
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> lidar_direction_list;
std::vector<int> lidar_2d_number;
//scan each 3D point
for (size_t i = 0; i < search_cloud->points.size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZ searchPoint = search_cloud->points[i];
if ((kdtree ->nearestKSearch(searchPoint, K, pointIdxNKNSearch, pointNKNSquaredDistance) > 0) &&
(kdtree_lidar->nearestKSearch(searchPoint, K, pointIdxNKNSearchLidar, pointNKNSquaredDistanceLidar) > 0))
{
bool dis_check = true;
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++)
{
float distance = sqrt(pow(searchPoint.x - tree_cloud->points[pointIdxNKNSearch[j]].x, 2) +
pow(searchPoint.y - tree_cloud->points[pointIdxNKNSearch[j]].y, 2));
if (distance > dis_threshold)
{
dis_check = false;
}
}
//5.calculate the direction of 3D lines and 2D lines on pixel frame
//if the distances with all 5 closest 2D points is <20
if (dis_check)
{
Eigen::Vector2d direction_cam(0, 0);
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> points_cam;
for (size_t i = 0; i < pointIdxNKNSearch.size(); i++)
{
Eigen::Vector2d p(tree_cloud->points[pointIdxNKNSearch[i]].x, tree_cloud->points[pointIdxNKNSearch[i]].y);
points_cam.push_back(p);
}
calcDirection(points_cam, direction_cam);
Eigen::Vector2d direction_lidar(0, 0);
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> points_lidar;
for (size_t i = 0; i < pointIdxNKNSearch.size(); i++)
{
Eigen::Vector2d p(tree_cloud_lidar->points[pointIdxNKNSearchLidar[i]].x, tree_cloud_lidar->points[pointIdxNKNSearchLidar[i]].y);
points_lidar.push_back(p);
}
calcDirection(points_lidar, direction_lidar);
// direction.normalize();
cv::Point p_l_2d(search_cloud->points[i].x, -search_cloud->points[i].y);
cv::Point p_c_2d(tree_cloud->points[pointIdxNKNSearch[0]].x, -tree_cloud->points[pointIdxNKNSearch[0]].y);
if (checkFov(p_l_2d))
{
lidar_2d_list.push_back(p_l_2d); //projected point of the 3D point
img_2d_list.push_back(p_c_2d); //corresponding 2D point
camera_direction_list.push_back(direction_cam); //direction of corresponding 2D point
lidar_direction_list.push_back(direction_lidar); //direction of the projected point of the 3D point
lidar_2d_number.push_back(line_edge_cloud_2d_number[i]); //the idx of each 3D lines
}
}
}
}
//6.build correspondance
for (size_t i = 0; i < lidar_2d_list.size(); i++)
{
int y = lidar_2d_list[i].y;
int x = lidar_2d_list[i].x;
int pixel_points_size = img_pts_container[y][x].size();
if (pixel_points_size > 0)
{
VPnPData pnp;
pnp.x = 0;
pnp.y = 0;
pnp.z = 0;
//corresponding 2D point
pnp.u = img_2d_list[i].x;
pnp.v = img_2d_list[i].y;
//3D point (averaged), TODO what if they are far to each other?
for (size_t j = 0; j < pixel_points_size; j++)
{
pnp.x += img_pts_container[y][x][j].x;
pnp.y += img_pts_container[y][x][j].y;
pnp.z += img_pts_container[y][x][j].z;
}
pnp.x = pnp.x / pixel_points_size;
pnp.y = pnp.y / pixel_points_size;
pnp.z = pnp.z / pixel_points_size;
//direction of corresponding 2D point
pnp.direction = camera_direction_list[i];
//direction of the projected point of the 3D point
pnp.direction_lidar = lidar_direction_list[i];
//the idx of the 3D line which the 3D point belongs to
pnp.number = lidar_2d_number[i];
float theta = pnp.direction.dot(pnp.direction_lidar);
if (theta > direction_theta_min_ || theta < direction_theta_max_) //-30-+30, 150-270 deg.
{
pnp_list.push_back(pnp);
}
}
}
}about 3D Every line of point cloud , According to the current external parameters Tcl Initial value of , Internal reference K Projection to image On , Get a pixel coordinate , Then the query kdree Find the recent ones that just passed canny Algorithm extracted 2D Pixels , With these pixels, we can calculate an average , Line vector , You can get a set of feature matching :
3D spot +2D spot /2D Point vector .
In the final analysis , What you get is (lidar) Point and (image) Matching relationship between points , Of course, it can also be regarded as (lidar) Point and (image) The matching relationship of lines , Because the latter preserves the line vector . Also have Other options The saved 3D Line and 2D Lines are described by two endpoints , In the true sense (lidar) Line and (image) Match between lines .
4. Optimization model
The loss function is a common point - Line distance or point - A little distance . about 3D spot , According to the to be optimized Tcl go to cam system , Convert to pixel coordinates , To distort , In matching 2D Point out the pixel distance as residual.
vpnp_calib(VPnPData p) {pd = p;}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T *_q, const T *_t, T *residuals) const
{
//camera param
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 3> innerT = inner.cast<T>();
Eigen::Matrix<T, 4, 1> distorT = distor.cast<T>();
const T &fx = innerT.coeffRef(0, 0);
const T &cx = innerT.coeffRef(0, 2);
const T &fy = innerT.coeffRef(1, 1);
const T &cy = innerT.coeffRef(1, 2);
//initial value of Tcl
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_incre{_q[3], _q[0], _q[1], _q[2]};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> t_incre{_t[0], _t[1], _t[2]};
//project 3D point onto pixel frame
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> p_l(T(pd.x), T(pd.y), T(pd.z));
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> p_c = q_incre.toRotationMatrix() * p_l + t_incre;
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> p_2 = innerT * p_c;
T uo = p_2[0] / p_2[2];
T vo = p_2[1] / p_2[2];
//undistort
T xo = (uo - cx) / fx;
T yo = (vo - cy) / fy;
T r2 = xo * xo + yo * yo;
T r4 = r2 * r2;
T distortion = 1.0 + distorT[0] * r2 + distorT[1] * r4;
T xd = xo * distortion + (distorT[2] * xo * yo + distorT[2] * xo * yo) + distorT[3] * (r2 + xo * xo + xo * xo);
T yd = yo * distortion + distorT[3] * xo * yo + distorT[3] * xo * yo + distorT[2] * (r2 + yo * yo + yo * yo);
T ud = fx * xd + cx;
T vd = fy * yd + cy;
if (T(pd.direction(0)) == T(0.0) && T(pd.direction(1)) == T(0.0))
{
residuals[0] = ud - T(pd.u);
residuals[1] = vd - T(pd.v);
}
else
{
residuals[0] = ud - T(pd.u);
residuals[1] = vd - T(pd.v);
Eigen::Matrix<T, 2, 2> I = Eigen::Matrix<float, 2, 2>::Identity().cast<T>();
Eigen::Matrix<T, 2, 1> n = pd.direction.cast<T>();
Eigen::Matrix<T, 1, 2> nt = pd.direction.transpose().cast<T>();
Eigen::Matrix<T, 2, 2> V = n * nt;
V = I - V;
Eigen::Matrix<T, 2, 2> R = Eigen::Matrix<float, 2, 2>::Zero().cast<T>();
R.coeffRef(0, 0) = residuals[0];
R.coeffRef(1, 1) = residuals[1];
R = V * R * V.transpose();
residuals[0] = R.coeffRef(0, 0);
residuals[1] = R.coeffRef(1, 1);
}
return true;
}
边栏推荐
- 八道超经典指针面试题(三千字详解)
- Mysql database operation
- Deep parsing pointer and array written test questions
- Huawei, H3C, Cisco command comparison, mind map form from the basic, switching, routing three directions [transferred from wechat official account network technology alliance station]
- The next industry outlet: NFT digital collection, is it an opportunity or a foam?
- SWC介绍
- SD卡報錯“error -110 whilst initialising SD card
- JS音乐在线播放插件vsPlayAudio.js
- Exness foreign exchange: the governor of the Bank of Canada said that the interest rate hike would be more moderate, and the United States and Canada fell slightly to maintain range volatility
- SAP ALV颜色代码对应颜色(整理)
猜你喜欢
pytorch加载数据
银行核心业务系统性能测试方法

Pytorch load data

ERA5再分析资料下载攻略
Crazy, thousands of netizens are exploding the company's salary

three.js网页背景动画液态js特效
Analyze menu analysis
Modeling specifications: naming conventions
js凡客banner轮播图js特效
The next industry outlet: NFT digital collection, is it an opportunity or a foam?
随机推荐
ERA5再分析资料下载攻略
js 正则过滤和增加富文本中图片前缀
three.js网页背景动画液态js特效
深入刨析的指针(题解)
[Li Kou] the second set of the 280 Li Kou weekly match
2022工作中遇到的问题四
[risc-v] external interrupt
Quartz misfire missed and compensated execution
NR modulation 1
Problems encountered in 2022 work IV
MPLS experiment
指针笔试题~走近大厂
Idea push rejected solution
Selenium share
Safety science to | travel, you must read a guide
Pytorch基础——(1)张量(tensor)的初始化
Pytorch基础——(2)张量(tensor)的数学运算
[concept] Web basic concept cognition
Handwriting database client
Prototype design