当前位置:网站首页>The solution of frame dropping problem in gnuradio OFDM operation
The solution of frame dropping problem in gnuradio OFDM operation
2022-07-08 01:22:00 【You roll, I don't roll】
Recently running GNURadio Medium OFDM The problem of losing frames was found during routine .
The use of gnuradio yes 3.8 Version of ,Ubuntu by 20.04, And at least for now gnuradio 3.9 There's a problem , Here are the causes and solutions .
When using the original routine ( One time transmission 10 frame 960 Bytes of data ) There is no frame loss during the test , But when we replace the data to be sent with picture data to send, we cannot receive it correctly , Even if the channel condition is changed to an ideal noise-free and distortion free channel in the simulation, the same number of data frames will still be lost at the same location .
Found in debugging , When the interval between two trigger signals of timing information is generally 4 In this case , Respectively 958、959、960、961. But only when the job is 958( A complete OFDM The data frame is 960 individual QPSK data ) Frame loss will occur , No problem with anything else , and 958 And normal 960 Two short QPSK data . in addition , The generation of trigger signal for timing is normal , The problem should be in the module that uses the trigger signal after the trigger signal is generated .
After re analyzing the process of data sending and parsing in the routine , I think it could be Header/Payload Demux Problems in the module source code , So let's look at the source code of this module .
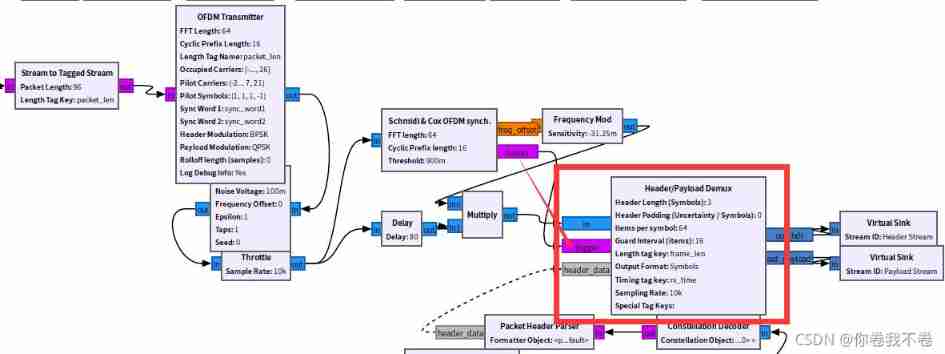
Source code process and problems :
in general , The reason for frame loss is that the interval between two adjacent timing signals is too short , When extracting data from the current frame, the timing signal of the data of the next frame is read as the data of the current frame , In this way, the timing signal of the next frame of data is lost , Therefore, it causes the phenomenon of frame loss . This phenomenon is inherent in the source code . The specific analysis is as follows :
chart 2 The parallel transmission relationship between the data and the trigger signal is strictly implemented at the corresponding position ,Header/Payload Demux Module read first trigger The signal , When reading the value 1 Time is considered to be the beginning of a frame of data , At this time, it starts from the corresponding position of the data signal and then extracts 1919 Data is output as the data of the current frame .
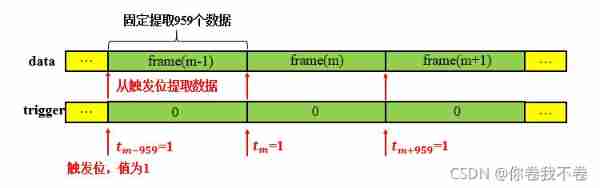
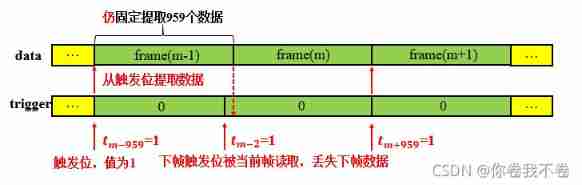
According to the data processing process of the source code , In the source code, every time a timing signal is received , Will be extracted immediately after the timing signal 959 Data is output as the current frame , Therefore, it puts forward high requirements for the accuracy of timing signals , If the interval between two adjacent timing signals is smaller than the length of the normal data frame , For example, the normal interval is 960, If there is an interval of 958 The interval of , Pictured 3, Then in the subsequent extraction 959 The timing signal of the next frame will be read together with the data of the current frame when the data is received , In this way, the timing signal of the next frame of data is lost , Therefore, it causes the phenomenon of frame loss .
The way to solve this problem is to modify the source code , On the basis of ensuring that adjacent timing signals do not want to interfere with each other, compile and install the source code again . The source code that needs to be modified is gr-digital/lib/header_payload_demux_impl.cc as well as gr-digital/lib/header_payload_demux_impl.h . First, in the header_payload_demux_impl.h Add variables to :
int d_next_trigger_offset;And then in header_payload_demux_impl.cc Change in find_trigger_signal Function as follows :
......
int trigger_nums = 0;
if (max_rel_offset < skip_items) {
return rel_offset;
}
if (in_trigger) {
for (int i = skip_items; i < max_rel_offset; i++) {
if (in_trigger[i]) {
trigger_nums++;
// record location of the first trigger
if(trigger_nums == 1) {
rel_offset = i;
}
// If there is a second trigger signal,record offset of between the first and second trigger
else if (trigger_nums == 2) {
d_next_trigger_offset = i - rel_offset;
break;
}
}
}
}
......And then modify general_work() Medium case STATE_PAYLOAD In state consume The process is as follows :
......
// Calculate whether the current frame consumes the trigger signal of the next frame data
// If yes, then make corrections
int consume_compensation = 0;
int consume_nums = 0;
// Calculate total consumption
consume_nums = (d_curr_payload_len + d_header_len) * (d_items_per_symbol + d_gi) +
d_header_padding_total_items +
d_curr_payload_offset -
items_padding ;
// make a decision
if(d_next_trigger_offset <= consume_nums) {
consume_compensation = consume_nums - d_next_trigger_offset + 1;
}
else {
consume_compensation = 0;
}
// add the corrections
const int items_to_consume =
d_curr_payload_len * (d_items_per_symbol + d_gi) - items_padding - consume_compensation;
......After modification, compile and install the source code again , Problem solving ~
边栏推荐
- 2022 R1 fast opening pressure vessel operation test question bank and R1 fast opening pressure vessel operation free test questions
- 2022 refrigeration and air conditioning equipment operation examination questions and refrigeration and air conditioning equipment operation examination skills
- Mathematical modeling -- knowledge map
- 2021 tea master (primary) examination materials and tea master (primary) simulation test questions
- Get started quickly using the local testing tool postman
- Basic realization of line graph
- C#中string用法
- Chapter 7 Bayesian classifier
- Capstone/cs5210 chip | cs5210 design scheme | cs5210 design data
- 2022 operation certificate examination for main principals of hazardous chemical business units and main principals of hazardous chemical business units
猜你喜欢
130. 被围绕的区域
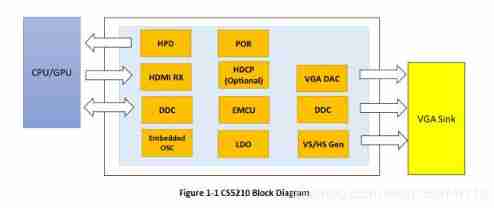
HDMI to VGA acquisition HD adapter scheme | HDMI to VGA 1080p audio and video converter scheme | cs5210 scheme design explanation
2022 operation certificate examination for main principals of hazardous chemical business units and main principals of hazardous chemical business units
General configuration title
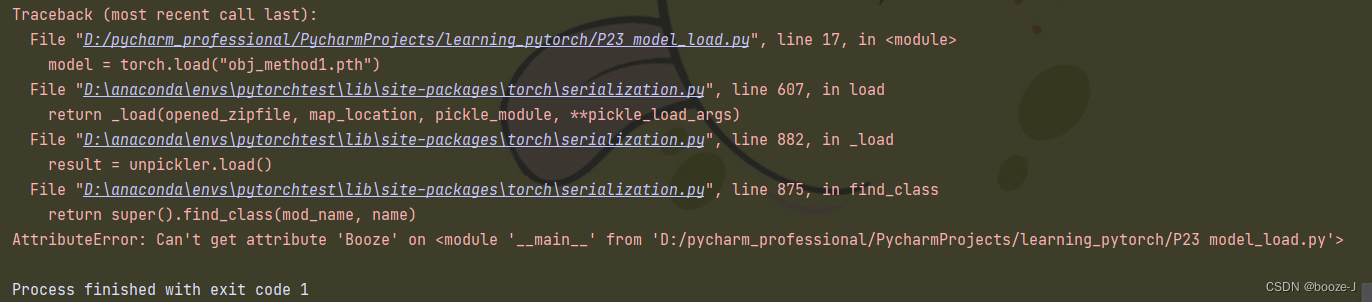
Saving and reading of network model
Cs5261type-c to HDMI alternative ag9310 | ag9310 alternative
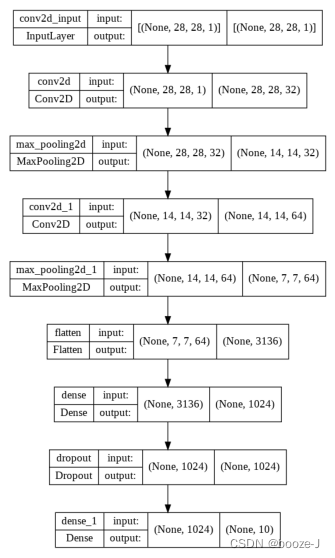
14.绘制网络模型结构

130. Surrounding area

2022 high altitude installation, maintenance and demolition examination materials and high altitude installation, maintenance and demolition operation certificate examination
Su embedded training - Day9
随机推荐
11. Recurrent neural network RNN
Parade ps8625 | replace ps8625 | EDP to LVDS screen adapter or screen drive board
How to get the first and last days of a given month
Chapter IV decision tree
The whole life cycle of commodity design can be included in the scope of industrial Internet
7.正则化应用
Frrouting BGP protocol learning
130. 被围绕的区域
130. 被圍繞的區域
General configuration toolbox
Taiwan Xinchuang sss1700 latest Chinese specification | sss1700 latest Chinese specification | sss1700datasheet Chinese explanation
Chapter 16 intensive learning
2022 safety officer-c certificate examination paper and safety officer-c certificate simulated examination question bank
Redis 主从复制
2022 tea master (intermediate) examination questions and tea master (intermediate) examination skills
11.递归神经网络RNN
Cs5261type-c to HDMI alternative ag9310 | ag9310 alternative
redis的持久化方式-RDB和AOF 两种持久化机制
2022 refrigeration and air conditioning equipment operation examination questions and refrigeration and air conditioning equipment operation examination skills
y59.第三章 Kubernetes从入门到精通 -- 持续集成与部署(三二)