当前位置:网站首页>State mode - Unity (finite state machine)
State mode - Unity (finite state machine)
2022-07-07 19:13:00 【Just be interesting】
List of articles
The state pattern ( Finite state machine )
State mode is an object mode , He extracts complex logical judgments into objects in different states , Allow state objects to change their internal state , Change their behavior . The change of state and the behavior of each state are the core of state mode .
Here we need to talk about the form of a state mode that is often used in games . It is finite state machine , Finite state machine is used as the management of different states of objects ( game AI Finite state machines are also often used ). Its main idea is that the program can only be in a limited number of states at any time . In any state , Program behavior will change with the state , Change . And the switching between States is pre designed .
The predefined state switching rule is called Transfer .
structure
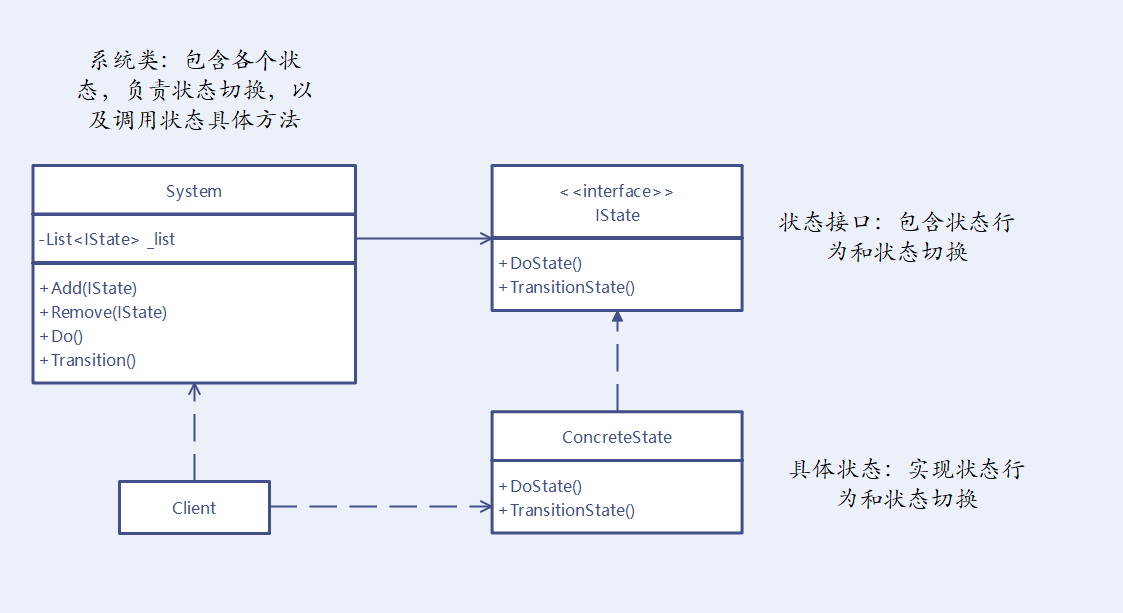
explain
- State interface - Define state behavior and state switching
- Specific state - Realize state behavior and state switching
- System - Responsible for state switching, actual state calling and state management .
Realization ( Finite state machine )
Here we will implement a finite state machine , The state machine is divided into four parts
- State enumeration
- State interface and state class
- Condition interface and condition class
- State system
We used Generic To enhance the reusability of finite state machines , Use factory To create a state machine ( Avoid complex creation process , Stay on the caller side to pollute the code )
For convenience , I just enumerated Idle( idle ) and Chase( chase ) Two kinds of state
- The first part
State enumeration
public enum StateId
{
Idle,
Chase,
}
- The second part
State interface
public interface IState<T>
where T : Enum
{
// Get the corresponding state class Id
T Id {
get; }
// Before entering the state , Call this function
void OnEnterState();
// In the state of , Call this function
void OnUpdateState();
// Before the status exits , Call this function
void OnExitState();
// State transition functions , Use this function to determine whether to transfer the state
bool TransitionState(out T id);
}
Enemy abstract state
public abstract class EnemyState : IState<StateId>
{
private readonly StateId _id;
private readonly ITransitionState<StateId> _transitionState;
protected EnemyState(StateId id, ITransitionState<StateId> transitionState)
{
_id = id;
_transitionState = transitionState;
}
public StateId Id => _id;
public virtual void OnEnterState() {
}
public abstract void OnUpdateState();
public virtual void OnExitState() {
}
public bool TransitionState(out StateId id) => _transitionState.Transition(out id);
}
The reason why there are so many abstract classes , It is to separate the state condition logic from the state behavior logic , So that subclasses do not need to pay attention to state transition , Just focus on implementation . The implementation of state transition is transferred to the condition class ( Realize the separation of state judgment and state behavior ).
Specific status class (Idle,Chase)
public class EnemyIdleState : EnemyState
{
public EnemyIdleState(ITransitionState<StateId> transitionState) :
base(StateId.Idle, transitionState)
{
}
public override void OnUpdateState()
{
}
}
public class EnemyChaseState : EnemyState
{
private float _chaseSpeed;
private float _chaseRange;
private GameObject _go;
private GameObject _chaseTarget;
// Physical cache
private Collider[] _colliders = new Collider[1];
public EnemyChaseState(float chaseSpeed, float chaseRange, GameObject go, ITransitionState<StateId> transitionState) :
base(StateId.Chase, transitionState)
{
_go = go;
_chaseSpeed = chaseSpeed;
_chaseRange = chaseRange;
}
public override void OnEnterState()
{
_chaseTarget = null;
int num = Physics.OverlapSphereNonAlloc(_go.transform.position, _chaseRange,
_colliders, 1 << LayerMask.NameToLayer("Player"));
if (num != 0) _chaseTarget = _colliders[0].gameObject;
}
public override void OnUpdateState()
{
// Move
var position = _go.transform.position;
position += _chaseSpeed * Time.deltaTime * (_chaseTarget.transform.position - position).normalized;
_go.transform.position = position;
// rotate
_go.transform.LookAt(_chaseTarget.transform);
}
public override void OnExitState()
{
_chaseTarget = null;
}
}
- The third part
Conditional interface
public interface ITransitionState<T>
where T : Enum
{
bool Transition(out T id);
}
Specific condition interface (IdleTransition,Chase Transition)
public class EnemyIdleStateTransition : ITransitionState<StateId>
{
// Own game object
private GameObject _go;
// Reconnaissance range
private float _scoutingRange;
// Reconnaissance range interval ( Each frame call , Not conducive to program performance )
private readonly float _scoutingTime = 0.2f;
private float _currentTime;
public EnemyIdleStateTransition(GameObject go, float scoutingRange)
{
_scoutingRange = scoutingRange;
_go = go;
}
public bool Transition(out StateId id)
{
_currentTime += Time.deltaTime;
if (_currentTime >= _scoutingTime)
{
_currentTime = 0f;
if (Physics.CheckSphere(_go.transform.position, _scoutingRange, 1 << LayerMask.NameToLayer("Player")))
{
id = StateId.Chase;
return true;
}
}
id = StateId.Idle;
return false;
}
}
public class EnemyChaseStateTransition : ITransitionState<StateId>
{
// Out of the pursuit distance
private float _outChaseDistance;
// Own game object
private GameObject _go;
// Out of range interval ( Calling every frame is bad for program performance )
private readonly float _outChaseTime = 0.2f;
private float _currentTime;
public EnemyChaseStateTransition(GameObject go, float outChaseDistance)
{
_outChaseDistance = outChaseDistance;
_go = go;
}
public bool Transition(out StateId id)
{
_currentTime += Time.deltaTime;
if (_currentTime >= _outChaseTime)
{
_currentTime = 0f;
if (!Physics.CheckSphere(_go.transform.position, _outChaseDistance, 1 << LayerMask.NameToLayer("Player")))
{
id = StateId.Idle;
return true;
}
}
id = StateId.Chase;
return false;
}
}
- The fourth part
Finite state machine system class
public class FsmSystem<T>
where T : Enum
{
private Dictionary<T, IState<T>> _stateDic;
private T _currentStateId;
private IState<T> _currentState;
public T Id => _currentStateId;
public FsmSystem()
{
_stateDic = new Dictionary<T, IState<T>>();
}
public void Add(IState<T> state)
{
if (state == null) return;
if (_stateDic.ContainsKey(state.Id)) return;
_stateDic.Add(state.Id, state);
}
public void Remove(T id)
{
if (!_stateDic.ContainsKey(id)) return;
_stateDic.Remove(id);
}
public bool Enable(T id)
{
if (!_stateDic.ContainsKey(id)) return false;
_currentStateId = id;
_currentState = _stateDic[id];
_currentState.OnEnterState();
return true;
}
public void Update()
{
if (_currentState.TransitionState(out T id))
TransferState(id);
_currentState.OnUpdateState();
}
// Transition state function
private void TransferState(T id)
{
if (!_stateDic.ContainsKey(id)) return;
_currentState.OnExitState();
_currentState = _stateDic[id];
_currentStateId = id;
_currentState.OnEnterState();
}
}
Factory
public class FsmFactory
{
public static FsmSystem<StateId> CreateEnemyFsm(GameObject go, float chaseRange, float chaseSpeed, float outChaseRange)
{
var fsm = new FsmSystem<StateId>();
// Create conditions , And add the corresponding parameters required by the condition
var idleStateTransition = new EnemyIdleStateTransition(go, chaseRange);
var chaseStateTransition = new EnemyChaseStateTransition(go, outChaseRange);
// Create a state of , And add the parameters required for the status , And bind conditions to States
var idleState = new EnemyIdleState(idleStateTransition);
var chaseState = new EnemyChaseState(chaseSpeed, chaseRange, go, chaseStateTransition);
fsm.Add(idleState);
fsm.Add(chaseState);
fsm.Enable(StateId.Idle);
return fsm;
}
}
Calling end
public class StateExample : MonoBehaviour
{
// Pursuit speed
[SerializeField] private float _chaseSpeed = 3.0f;
// Pursuit range
[SerializeField] private float _chaseRange = 4.0f;
// Out of pursuit distance
[SerializeField] private float _outChaseRange = 5.0f;
// At this time, the State
[SerializeField] private StateId _stateId;
private FsmSystem<StateId> _system;
private void Awake()
{
_system = FsmFactory.CreateEnemyFsm(gameObject, _chaseRange, _chaseSpeed, _outChaseRange);
}
private void Update()
{
_system.Update();
_stateId = _system.Id;
}
}
Set player object to Player layer
design sketch 
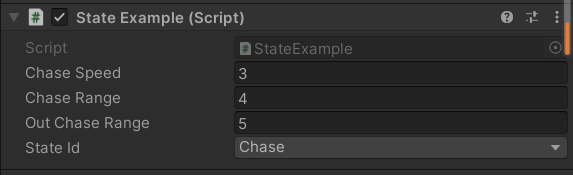
Because I can't make an action diagram, I can only make do with it , There's no problem with the code , The effect is not bad .
Application scenarios
- Game enemy AI
- It needs to be changed according to different states , Have different behaviors .
- If a class needs to change its behavior according to the current value of the member variable , When a lot of judgment conditions are needed , You can use state mode .
Advantages and disadvantages
advantage
- Separate the state , Principle of single responsibility
- Simplify the judgment of conditions
shortcoming
- Implementation is too cumbersome
- Too many classes , It is easy to cause system complexity
Relationships with other models
- The state pattern Be regarded as The strategy pattern An extension of , The state mode itself is different from the policy mode , Policy classes are independent , They don't interfere with each other . And the states need to be switched , There is a dependency between States . But the essence is based on the mechanism of combination .
- Bridging mode 、 The state pattern The interface of is very similar . Bridging patterns focus on realization and abstraction , Different implementations are not related , Realize their own business logic , Abstract objects and combine them . In essence, both are implemented based on the combination mechanism . Delegate work to objects .
- The creation of state machine can be done by factory pattern .
- State machines can use bridging patterns to separate state transitions from state implementations .
边栏推荐
- 3. About cookies
- ES6 note 1
- Tapdata 的 2.0 版 ,开源的 Live Data Platform 现已发布
- Short selling, overprinting and stock keeping, Oriental selection actually sold 2.66 million books in Tiktok in one month
- POJ 2392 Space Elevator
- The top of slashdata developer tool is up to you!!!
- 企业MES制造执行系统的分类与应用
- 反爬虫的重点:识别爬虫
- Redis cluster and expansion
- Cloud security daily 220707: Cisco Expressway series and telepresence video communication server have found remote attack vulnerabilities and need to be upgraded as soon as possible
猜你喜欢
二叉树的基本概念和性质
![[Blue Bridge Cup training 100 questions] sort scratch from small to large. Blue Bridge Cup scratch competition special prediction programming question centralized training simulation exercise question](/img/08/5f4b4e2700606554516807c01454fd.png)
[Blue Bridge Cup training 100 questions] sort scratch from small to large. Blue Bridge Cup scratch competition special prediction programming question centralized training simulation exercise question
Redis

Zhong Xuegao wants to remain innocent in the world

高温火烧浑不怕,钟薛高想留清白在人间

Borui data was selected in the 2022 love analysis - Panoramic report of it operation and maintenance manufacturers

99% of people don't know that privatized deployment is also a permanently free instant messaging software!

In the first half of 2022, I found 10 books that have been passed around by my circle of friends

CVPR 2022 - learning non target knowledge for semantic segmentation of small samples
![[tpm2.0 principle and Application guide] Chapter 16, 17 and 18](/img/7a/b16549590e6445d9199c8000d47d36.png)
[tpm2.0 principle and Application guide] Chapter 16, 17 and 18
随机推荐
多个kubernetes集群如何实现共享同一个存储
IP netns command (memo)
Where does brain hole come from? New research from the University of California: creative people's neural connections will "take shortcuts"
Draw squares with Obama (Lua)
Cadre de validation des données Apache bval réutilisé
Three forms of multimedia technology commonly used in enterprise exhibition hall design
6. About JWT
初识缓存以及ehcache初体验「建议收藏」
Reinforcement learning - learning notes 8 | Q-learning
反爬虫的重点:识别爬虫
二叉树的基本概念和性质
[Base64 notes] [suggestions collection]
Seize Jay Chou
我感觉被骗了,微信内测 “大小号” 功能,同一手机号可注册两个微信
AI写首诗
[tpm2.0 principle and Application guide] Chapter 16, 17 and 18
RISCV64
[software test] from the direct employment of the boss of the enterprise version, looking at the resume, there is a reason why you are not covered
Do you know all four common cache modes?
【软件测试】从企业版BOSS直聘,看求职简历,你没被面上是有原因的