当前位置:网站首页>Flash implements forced login
Flash implements forced login
2022-07-06 14:37:00 【Xiaobai aYuan】
Why use forced login
This is already a APP The regular route to take , If you don't log in , Developer Platform , It's not easy to analyze your big data , They can't push you the content you like according to your hobbies ( Not absolute ), Or some functions cannot be used without login , for instance :
If you often use one APP, You saw it on your iPhone today , I watched it on my tablet again at noon , I went outside and took my friend's mobile phone for a while .
In this scene , If you don't log in , The platform doesn't know that these behaviors are viewed by the same person , If APP You are required to login , Then use the same account number these times , He knew it was you who changed several devices to watch .
Okay , With this premise , Then you can do a lot around your account , No matter how you change the equipment , General account number , You like to watch delicious food , You like watching beautiful women and so on , All marked for you backstage .
And then one day , You'll find that , The friend who just had dinner with you yesterday showed off a newly bought dress with you , Your so and so APP The same link advertisement pops up .
here , Your question is bigger than the coincidence of seeing the same model , What the hell is going on ????
The reason is , It's because of each APP You need to log in , All need positioning , All require various permissions , Then the people around you highly overlap with many factors , There are these wonderful coincidences .
Whether a user logs in is determined by whether the user carries token, Therefore, before landing, Mr. Cheng token, And when logging in token Carry the past flask In the middle of token You can use the following methods :
Encapsulate a build token The method of is called to generate when logging in token, The meaning of some parameters can be understood by referring to the corresponding comments in the code , Here we generate token The method of jwt Medium encode Method , And set the expiration time , The specific expiration time can be set according to your own needs , The encryption algorithm here uses HS256 To encrypt
Note that since the date format cannot be serialized, it is necessary to convert the date format data to string format data
We need to send him one first SECRET_KEY, This SECRET_KEY It can be an arbitrary string
def generate_token(payload, expiry, secret=None, algorithm='HS256'): """ :param payload: dict load , User information :param expiry: date The period of validity :param secret: Private key of each item , Store in the configuration file :param algorithm: encryption algorithm :return: token """ # Private variables , No external supply # Generation validity _payload = { 'expiry': str(expiry) # Date format cannot be serialized } try: _payload.update(payload) if not secret: # Read from the object of the configuration file secret = current_app.config.get('SECRET_KEY') # Generative token Splicing , Then write the request header token = jwt.encode(payload=_payload, key=secret,algorithm=algorithm) return token except Exception as e: error = traceback.format_exc() print(' Generate token error :{}'.format(error))
Generate token After that, it must be verified, otherwise it may be because token The login fails or other operations cannot be carried out due to its own reasons , the token The decoding world of must be and generated token The encryption method of corresponds to , Because of the generation token By jwt Medium encode, Therefore, when decoding, we use jwt Medium docode To decode , After decoding, check whether it is consistent , And pay attention to token Is it overdue , Every token Both have expiration dates , If it expires, it will also appear token A situation of inconsistency , And note that the encryption algorithm must be consistent with the generated one when decrypting , Take this as an example to use HS256
def verify_token(token,secret=None,algorithm='HS256'):
"""
check token
:param token: It's delivered token
:param secret: Private key of each item , Store in the configuration file
:param algorithm: encryption algorithm
:return: payload User information section
"""
if not secret:
# Read from configuration file SECRET_KEY
secret = current_app.config.get('SECRET_KEY')
try:
payload = jwt.decode(token, secret, algorithms=algorithm)
except Exception as e:
print(" Decrypt the error message >>>", e)
payload = None
return payload
because token Set the expiration time and require users to log in regularly , Otherwise, you need to log in again , For the convenience of users , We can realize automatic refresh token, The so-called automatic refresh token That is, set a longer expiration time token, Because no matter token The length of expiration time carries user information , Therefore, we can use the short expiration time token expires , Use a longer expiration time token Regenerate a token, To achieve token Auto refresh of , Greatly optimize the user experience , The code is as follows ( For reference only )
def _generate_token(account,user_id, refresh=True):
"""
Generate token and Refresh token
:return: token, refresh_token
"""
secret = current_app.config.get('SECRET_KEY')
# Define expiration time : 2 Hours validity
expiry = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(hours=2)
# Generate Token
token = 'Bearer ' + generate_token({'account': account, 'user_id': user_id}, expiry, secret).decode()
if refresh:
# Generate new token, No sense refresh
expiry = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(days=15)
# is_refresh As update token The signal of
refresh_token = 'Bearer ' + generate_token({'account': account, 'user_id': user_id, 'is_refresh': True}, expiry, secret).decode()
else:
refresh_token = None
return token, refresh_tokenThe encryption method and decryption method are the same as those mentioned above
token The generation and verification of are the above contents
Bring it when logging in token
You can pass in the required fields and token And automatically refreshed token, You can print it in the middle to see if you have obtained token, In this way, you can also quickly locate the wrong place when it goes wrong
user_id = user.id
token, refresh_token = _generate_token(account=account, user_id=user.id)
print(' Landed token', token)
data = {
'message': 'login success',
'data': {'code': 200, 'token': token, 'refresh': refresh_token,
'account': account, 'id': user.id, 'uid': user_id}
}
return dataImplementation of forced login
def login_required(func):
""" Force login decorator """
# wraps Is the return decorator , The parameter is the function passed ,
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("func The name of is >>", func.__name__)
if g.user_id is not None:
print(g.user_id)
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return {'code': 401, 'message': ' Invalid token The account number is empty '}
return wrapperflask Medium g The object is specialized ⽤ To preserve ⽤ User data . We can understand this g The object is ⼀ A global object , This object stores one of us ⼀ All the information requested for this time ,g As flask Program global ⼀ Temporary variables , Act as an intermediary ⽤, We can pass it ⼀ Some data ,g Save the global variables of the current request
So we can start from g Object to retrieve the user passed in our request id, Through users id Judge whether it is empty token Is it empty , To ensure that the reason appears when the user logs in token Errors occurred
Forced login is to prevent some functions in the project from being used without login , We can write the forced login in a decorator , This not only reduces the amount of code , Avoid code that looks redundant , It is also convenient to use , Where the decorator is needed, it can be called directly
The call of decorator is also very simple ,@+ The name of the decorator we define , You can call
The name of the decorator can be written at will , But to make our code simple , When naming, try to know the meaning by seeing the name
@login_requiredTake this as an example Can be realized flask Realize forced login , I hope it can help you
边栏推荐
- Statistics, 8th Edition, Jia Junping, Chapter 11 summary of knowledge points of univariate linear regression and answers to exercises after class
- 函数:字符串反序存放
- 循环队列(C语言)
- 内网渗透之内网信息收集(三)
- Statistics, 8th Edition, Jia Junping, Chapter VIII, summary of knowledge points of hypothesis test and answers to exercises after class
- JDBC事务、批处理以及连接池(超详细)
- Hcip -- MPLS experiment
- 【指针】求二维数组中最大元素的值
- 链队实现(C语言)
- Intranet information collection of Intranet penetration (4)
猜你喜欢

Network technology related topics
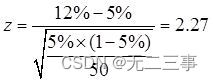
《统计学》第八版贾俊平第八章假设检验知识点总结及课后习题答案
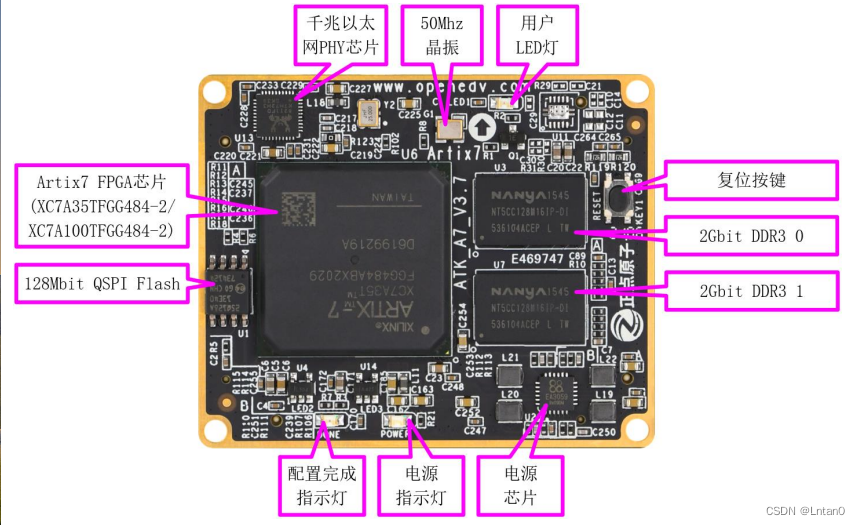
移植蜂鸟E203内核至达芬奇pro35T【集创芯来RISC-V杯】(一)
Hcip -- MPLS experiment
Intranet information collection of Intranet penetration (I)
Record an API interface SQL injection practice
Intranet information collection of Intranet penetration (5)

Mysql的事务是什么?什么是脏读,什么是幻读?不可重复读?
Keil5-MDK的格式化代码工具及添加快捷方式
![New version of postman flows [introductory teaching chapter 01 send request]](/img/0f/a41a39093a1170cc3f62075fd76182.jpg)
New version of postman flows [introductory teaching chapter 01 send request]
随机推荐
flask实现强制登陆
Sentinel overall workflow
[pointer] delete all spaces in the string s
函数:求两个正数的最大公约数和最小公倍
Intel oneapi - opening a new era of heterogeneity
数字电路基础(三)编码器和译码器
{1,2,3,2,5}查重问题
Mathematical modeling idea of 2022 central China Cup
《统计学》第八版贾俊平第一章课后习题及答案总结
Lintcode logo queries the two nearest saplings
【指针】删除字符串s中的所有空格
Fundamentals of digital circuit (IV) data distributor, data selector and numerical comparator
servlet中 servlet context与 session与 request三个对象的常用方法和存放数据的作用域。
XSS (cross site scripting attack) for security interview
Attack and defense world misc practice area (simplerar, base64stego, no matter how high your Kung Fu is, you are afraid of kitchen knives)
SystemVerilog discusses loop loop structure and built-in loop variable I
浙大版《C语言程序设计实验与习题指导(第3版)》题目集
刷视频的功夫,不如看看这些面试题你掌握了没有,慢慢积累月入过万不是梦。
Pointers: maximum, minimum, and average
C language learning summary (I) (under update)