当前位置:网站首页>this+闭包+作用域 面试题
this+闭包+作用域 面试题
2022-07-05 02:41:00 【_语墨】
作用域链
let a = 'global';
console.log(a);
function course() {
let b = 'zhaowa';
console.log(b);
session();
function session() {
let c = 'this';
console.log(c);
teacher();
function teacher() {
let d = 'yy';
console.log(d);
console.log('test1', b);
}
}
}
console.log('test2', b);
course();
报错:b is not defined
if(true) {
let e = 111;
console.log(e);
}
console.log('test3', e)
报错: e is not defined
- 对于作用域链我们直接通过创建态来定位作用域链
- 手动取消全局,使用块级作用域
this - 上下文context
this是在执行时动态读取上下文决定的,而不是创建时
函数直接调用中 this指向的是window(函数表达式、匿名函数、嵌套函数)
function foo(){
console.log(this) //指向window
}
隐式绑定
1.this的指向是调用堆栈的上一级 => 对象、数组等引用关系逻辑
function fn() {
console.log('隐式绑定', this.a);
}
const obj = {
a: 1,
fn
}
obj.fn = fn;
obj.fn();
面试题:
const foo = {
bar: 10,
fn: function() {
console.log(this.bar);
console.log(this);
}
}
let fn1 = foo.fn;
fn1(); //this 指向windows
// 追问1, 如何改变指向
const o1 = {
text: 'o1',
fn: function() {
// 直接使用上下文 - 传统分活
return this.text;
}
}
const o2 = {
text: 'o2',
fn: function() {
// 呼叫领导执行 - 部门协作
return o1.fn();
}
}
const o3 = {
text: 'o3',
fn: function() {
// 直接内部构造 - 公共人
let fn = o1.fn;
return fn();
}
}
console.log('o1fn', o1.fn());
console.log('o2fn', o2.fn());
console.log('o3fn', o3.fn());
o1fn o1
o2fn o1
o3fn undefined //指向windows
- 在执行函数时,函数被上一级调用,上下文指向上一级
- or直接变成公共函数,指向window
追问: 现在我要 console.log(‘o2fn’, o2.fn()); 的结果是o2
// 1. 人为干涉,改变this - bind/call/apply
// 2. 不许改变this
const o1 = {
text: 'o1',
fn: function() {
return this.text;
}
}
const o2 = {
text: 'o2',
fn: o1.fn
}
console.log('o2fn', o2.fn());
// this指向最后调用他的对象,把在fn执行时,o1.fn抢过来挂载在自己o2fn上即可
2.new - this指向的是new之后得到的实例
class Course {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
console.log('构造函数中的this:', this);
}
test() {
console.log('类方法中的this:', this);
}
}
const course = new Course('this');
course.test();
//指向实例course
追问: 类中异步方法,this有区别吗
class Course {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
console.log('构造函数中的this:', this);
}
test() {
console.log('类方法中的this:', this);
}
asyncTest() {
console.log('异步方法外:', this);
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('异步方法内:', this);
}, 100)
}
}
const course = new Course('this');
course.test();
course.asyncTest();
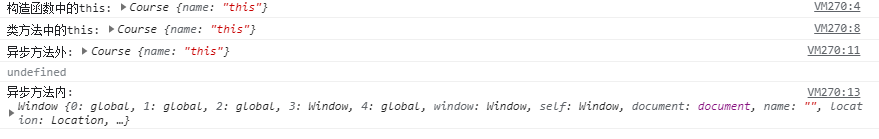
- 执行settimeout时,匿名方法执行时,效果和全局执行效果相同
- 追问 如何解决: 使用箭头函数
显式绑定(bind|apply|call)
function foo() {
console.log('函数内部this', this);
}
foo();
// 使用
foo.call({
a: 1});
foo.apply({
a: 1});
const bindFoo = foo.bind({
a: 1});
bindFoo();
追问:call、apply、bind的区别
- call 、apply 传参不同 依次传入/数组传入
- bind直接返回函数,需要再次执行 传参和call一样
bind 的原理 / 手写bind
原理或手写类题目,解题思路:
1.说明原理,写下注释
2.根据注释,补齐源码
function sum(a, b, c) {
console.log('sum', this);
return a + b + c;
}
// 1. 需求:手写bind => bind位置(挂在那里) => Function.prototype
Function.prototype.newBind = function() {
// 2. bind是什么?
const _this = this;
const args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
// args特点,第一项是新的this,第二项~最后一项函数传参
const newThis = args.shift();
// a. 返回一个函数
return function() {
// b. 返回原函数执行结果 c. 传参不变
return _this.apply(newThis, args);
}
}
//手写apply
Function.prototype.newApply = function(context) {
// 边缘检测
// 函数检测
if (typeof this !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('Error');
}
// 参数检测
context = context || window;
// 挂载执行函数
context.fn = this;
// 执行执行函数
let result = arguments[1]
? context.fn(...arguments[1])
: context.fn();
// 销毁临时挂载
delete context.fn;
return result;
}
如何突破作用域的束缚?
闭包
闭包:一个函数和他周围状态的引用捆绑在一起的组合
function mail() {
let content = '信';
return function() {
console.log(content);
}
}
const envelop = mail();
envelop();
- 函数外部获取到了函数作用域内的变量值
函数作为参数的时候
// 单一职责
let content;
// 通用存储
function envelop(fn) {
content = 1;
fn();
}
// 业务逻辑
function mail() {
console.log(content);
}
envelop(mail);

函数嵌套
let counter = 0;
function outerFn() {
function innerFn() {
counter++;
console.log(counter);
// ...
}
return innerFn;
}
outerFn()();

事件处理(异步执行)的闭包
let lis = document.getElementsByTagName('li');
for(var i = 0; i < lis.length; i++) {
(function(i) {
lis[i].onclick = function() {
console.log(i);
}
})(i);
}
解决:
1.改为立即执行函数,传参形式。
2.将var 改为let
追问:
立即执行嵌套
(function immediateA(a) {
return (function immediateB(b) {
console.log(a); // 0
})(1);
})(0);
立即执行函数遇上块级作用域
let count = 0;
(function immediate() {
if(count === 0) {
let count = 1;
console.log(count);
}
console.log(count);
})();

拆分执行 - 关注
function createIncrement() {
let count = 0;
function increment() {
count++;
}
let message = `count is ${
count}`;
function log() {
console.log(message);
}
return [increment, log];
}
const [increment, log] = createIncrement();
increment();
increment();
increment();
log();
实现私有变量
function createStack() {
return {
items: [],
push(item) {
this.item.push(item);
}
}
}
const stack = {
items: [],
push: function() {
}
}
function createStack() {
const items = [];
return {
push(item) {
items.push(item);
}
}
}
// Vuex store
边栏推荐
- [Yu Yue education] National Open University spring 2019 0505-22t basic nursing reference questions
- PHP cli getting input from user and then dumping into variable possible?
- [技术发展-26]:新型信息与通信网络的数据安全
- Kotlin - coroutine
- 使用druid连接MySQL数据库报类型错误
- Pytorch register_ Hook (operate on gradient grad)
- Asynchronous and promise
- 【LeetCode】98. Verify the binary search tree (2 brushes of wrong questions)
- 返回二叉树中两个节点的最低公共祖先
- STL container
猜你喜欢
Open source SPL optimized report application coping endlessly

Zabbix
Design and implementation of high availability website architecture

Zabbix

Action News
Matrixone 0.2.0 is released, and the fastest SQL computing engine is coming
Write a thread pool by hand, and take you to learn the implementation principle of ThreadPoolExecutor thread pool
Character painting, I use characters to draw a Bing Dwen Dwen
Traditional chips and AI chips
Marubeni Baidu applet detailed configuration tutorial, approved.
随机推荐
丸子百度小程序详细配置教程,审核通过。
平台入驻与独立部署优缺点对比
Process scheduling and termination
Security level
Advanced conditional statements of common SQL operations
[機緣參悟-38]:鬼穀子-第五飛箝篇 - 警示之一:有一種殺稱為“捧殺”
Character painting, I use characters to draw a Bing Dwen Dwen
Visual studio 2019 set transparent background (fool teaching)
2022/02/13
Pytest (4) - test case execution sequence
Asp+access campus network goods trading platform
Timescaledb 2.5.2 release, time series database based on PostgreSQL
Moco V2 literature research [self supervised learning]
Variables in postman
Can you really learn 3DMAX modeling by self-study?
Kotlin - coroutine
【微服务|SCG】Filters的33种用法
2021 Li Hongyi machine learning (1): basic concepts
Naacl 2021 | contrastive learning sweeping text clustering task
Openresty ngx Lua Execution stage