当前位置:网站首页>Probability distribution
Probability distribution
2022-07-08 01:21:00 【YaoHa_】
A probability distribution (probability distribution): Describe the probability of random variables or a cluster of random variables in each possible state . How the probability distribution is described depends on whether the random variables are discrete or continuous .
Discrete variables and probabilistic mass functions
The probability distribution of discrete variables is Probability mass function (probability mass function,PMF), Usually in capital letters P Express . The probability mass function maps each state that a random variable can obtain to the probability that a random variable can obtain that state .
Joint probability distribution (joint probability distribution): Probability mass function can act on many random variables at the same time .P(x=x,y=y) Express x=x and y=y Probability of simultaneous occurrence , Or we could just write it as P(x,y).
function P It's a random variable x The probability mass function of , The following conditions must be met :
P The domain must be x A collection of all possible states .
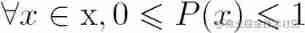 The probability of an unlikely event is 0, And there is no state with a lower probability . Similarly , It can ensure that the probability of certain events is 1, And there is no higher probability than this .
The probability of an unlikely event is 0, And there is no state with a lower probability . Similarly , It can ensure that the probability of certain events is 1, And there is no higher probability than this . normalization (normalized) nature , Prevent getting greater than 1 Probability .
normalization (normalized) nature , Prevent getting greater than 1 Probability .
Continuous variables and probability density functions
When the object of study is continuous random variable , use Probability density function (probability density function,PDF) Describe its probability distribution .
function P It's a probability density function , The following conditions must be met :
- p The domain must be x A collection of all possible states .
 Be careful , There is no demand for p(x)≤1.
Be careful , There is no demand for p(x)≤1.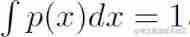
边栏推荐
- Su embedded training - C language programming practice (implementation of address book)
- Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)
- 2021 tea master (primary) examination materials and tea master (primary) simulation test questions
- Know how to get the traffic password
- Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)
- Ag9310meq ag9310mfq angle two USB type C to HDMI audio and video data conversion function chips parameter difference and design circuit reference
- Recommend a document management tool Zotero | with tutorials and learning paths
- A little experience from reading "civilization, modernization, value investment and China"
- 5、離散控制與連續控制
- 5. Over fitting, dropout, regularization
猜你喜欢
4. Strategic Learning
High quality USB sound card / audio chip sss1700 | sss1700 design 96 kHz 24 bit sampling rate USB headset microphone scheme | sss1700 Chinese design scheme explanation
How to transfer Netease cloud music /qq music to Apple Music
Vs code configuration latex environment nanny level configuration tutorial (dual system)
Prediction of the victory or defeat of the League of heroes -- simple KFC Colonel
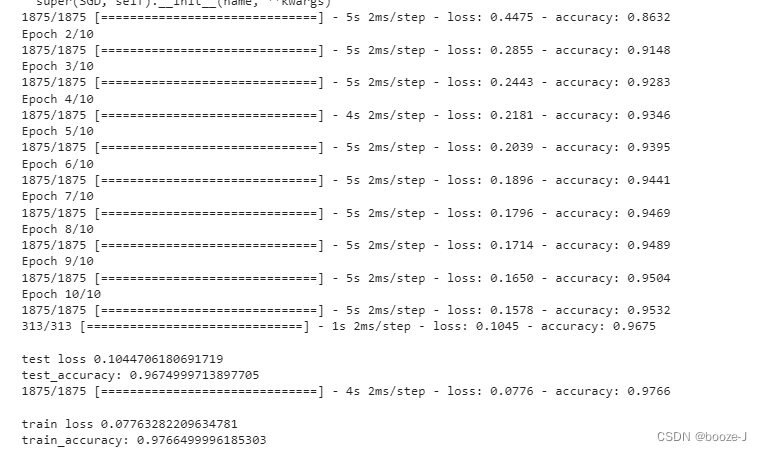
6.Dropout应用
完整的模型验证(测试,demo)套路
Chapter 5 neural network
12. RNN is applied to handwritten digit recognition
Su embedded training - Day6
随机推荐
7. Regularization application
Redis 主从复制
Chapter improvement of clock -- multi-purpose signal modulation generation system based on ambient optical signal detection and custom signal rules
13. Enregistrement et chargement des modèles
Ag9310 for type-C docking station scheme circuit design method | ag9310 for type-C audio and video converter scheme circuit design reference
Leetcode notes No.7
5. Contrôle discret et contrôle continu
[deep learning] AI one click to change the sky
How to get the first and last days of a given month
How to transfer Netease cloud music /qq music to Apple Music
Recommend a document management tool Zotero | with tutorials and learning paths
13.模型的保存和載入
4. Apprentissage stratégique
Su embedded training - Day5
2022 chemical automation control instrument examination summary and chemical automation control instrument simulation examination questions
Swift get URL parameters
High quality USB sound card / audio chip sss1700 | sss1700 design 96 kHz 24 bit sampling rate USB headset microphone scheme | sss1700 Chinese design scheme explanation
Apt get error
General configuration title
Design method and application of ag9311maq and ag9311mcq in USB type-C docking station or converter